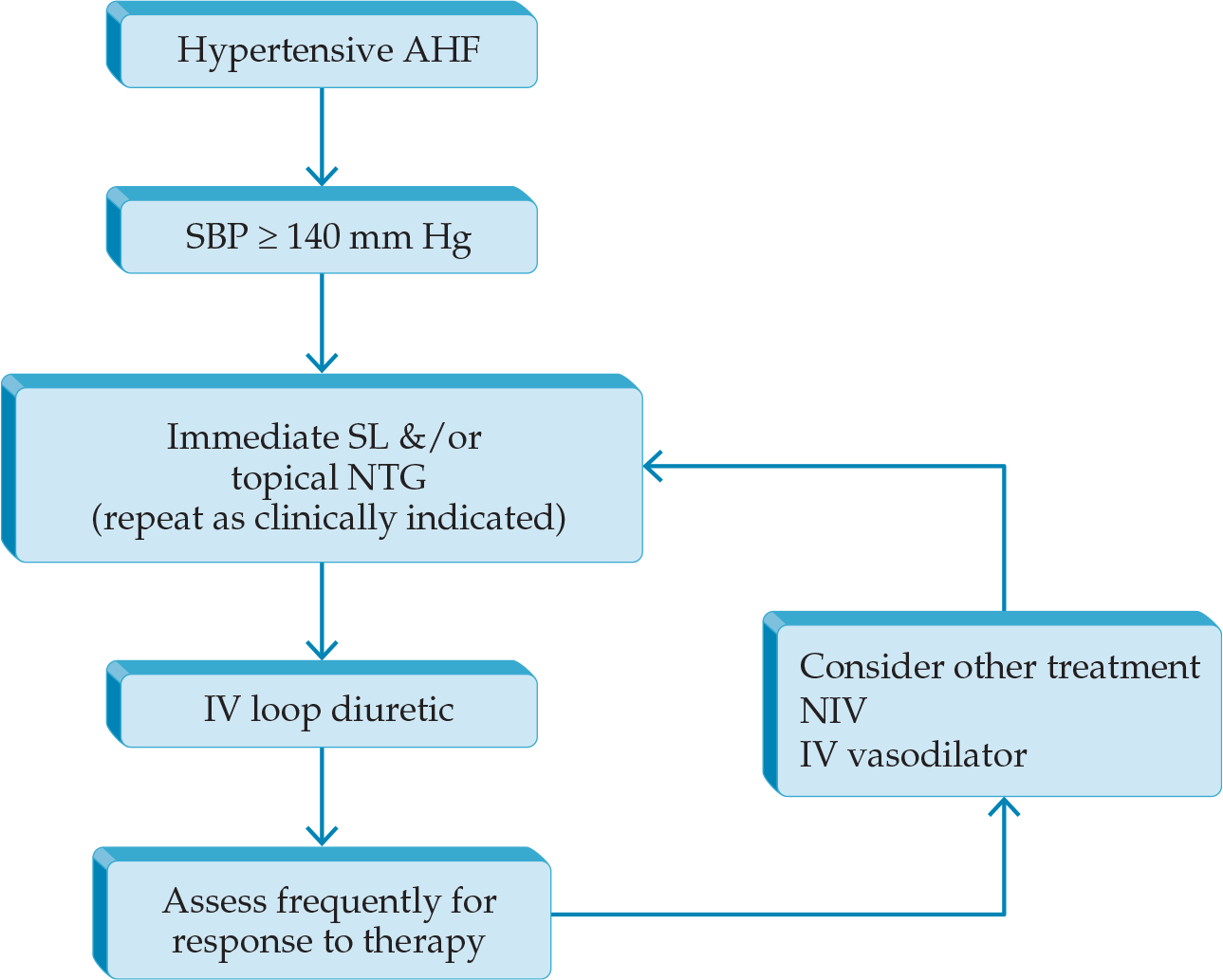
Management of Acute Heart Failure
- The initial assessment of the patient with suspected AHF should focus on immediate life-threatening conditions. Careful attention should be paid to vital signs. Hypoxia should be treated with supplemental oxygenation and may be a marker for impending respiratory failure. The history should help ascertain possible causes of exacerbation of HF, as well as risk factors or symptoms suggestive of HF mimics.
- Nesiritide is a recombinant BNP that, similar to NTG, is a venous, arterial, and coronary dilator. Several early trials demonstrated improved hemodynamics with nesiritide, with a suggestion of some clinical benefit. However, data from these trials failed to demonstrate a mortality benefit and questions arose about the possibility of increased renal insufficiency and worse mortality with its use.
- Sodium nitroprusside can be similarly used to decrease both preload and afterload. Observational data have suggested a mortality benefit in AHF patients treated with nitroprusside, but randomized trial data appear to be limited to patients with acute myocardial infarction and have not been able to demonstrate a mortality decrease.