Coma, Cognitive Impairment, and Seizures
- When treating an unresponsive patient, targeted therapy is advised instead of routine use of the “coma cocktail” (empirical treatment with dextrose, naloxone, thiamine, and sometimes flumazenil).
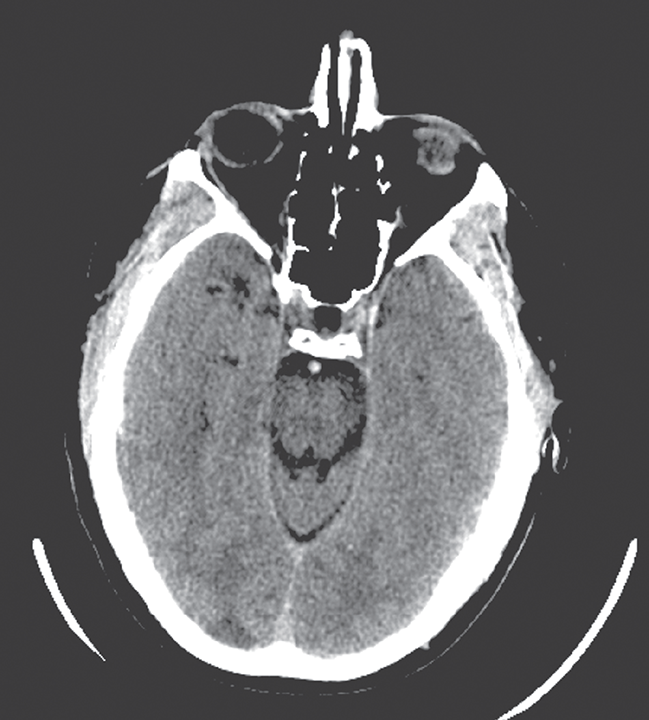
- Avoidance of hypotension and maintenance of normoglycemia and normothermia are critical to the management of intracranial hypertension.
- Differing levels of awareness were noted among patients found to be in a minimally conscious state (MCS); subsequently, this condition was further subdivided into two categories, MCS plus (MCS+) and MCS minus (MCS-), based on the ability to follow commands versus just visual pursuit. Permanent vegetative state is no longer used.