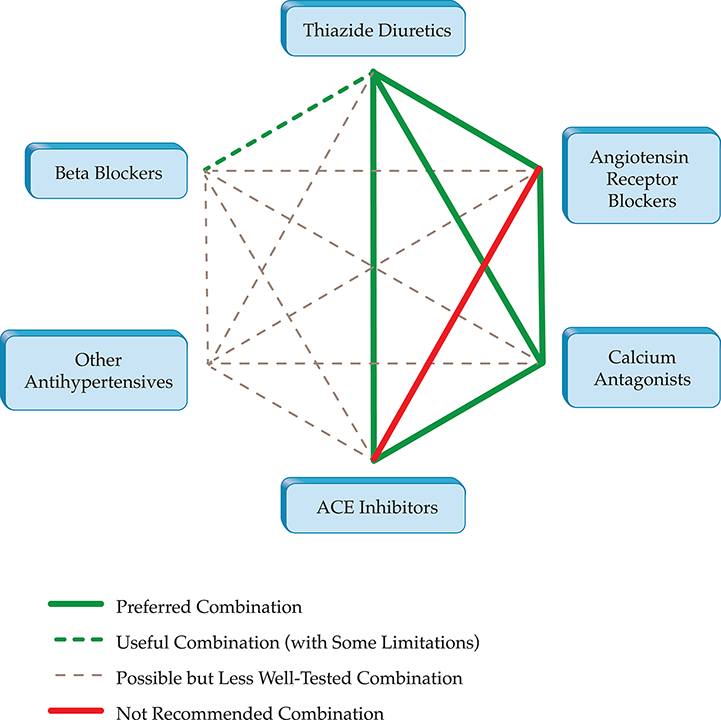
- Increasing recognition of the importance of home-based and ambulatory blood pressure monitoring reflected in expanded indications for use
- Specific guidance from professional societies with regard to patients with chronic kidney disease
- Recent clinical outcomes trials adding important data about optimal treatment targets
- 2020 ISH and 2017 ACC/AHA practice guidelines indicating role of telehealth strategies in management of hypertension in adults.
Latest Updates

- Increasing recognition of the importance of home-based and ambulatory blood pressure monitoring reflected in expanded indications for use
- Specific guidance from professional societies with regard to patients with chronic kidney disease
- Recent clinical outcomes trials adding important data about optimal treatment targets
- 2020 ISH and 2017 ACC/AHA practice guidelines indicating role of telehealth strategies in management of hypertension in adults.


- Dyslipidemias are clinically important, principally because of their contribution to atherogenesis.
- Pancreatitis and fatty liver disease are less common but clinically significant manifestations of lipid disorders.
- Most recent practice guidelines for dyslipidemia diagnosis and management include the 2019 AAFP summary of the 2018 AHA/ACC practice guidelines, as well as the 2020 Veterans Health Administration guidelines.

- ATS guidelines for exercise-induced bronchoconstriction, asthma in the elderly, and asthma in the workplace
- ERS/ATS guideline for severe asthma discusses pharmacologic modalities of asthma management and bronchial thermoplasty.
- 2020 GINA practice guidelines no longer recommend treatment with SABA alone, without inhaled ICS. Recommend that all adults and adolescents with asthma should receive ICS-containing controller treatment.
- 2020 NAEPP practice guidelines delineating optimal treatment steps in adolescents and adults with asthma. This includes bronchial thermoplasty and immunotherapy.

Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
- 2020 ATS and 2019 CTS practice guidelines delineating pharmacologic management of COPD.
- Introduced the new Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease (GOLD) Combined COPD Assessment using symptoms of breathlessness, spirometric classification, and risk of exacerbation to evaluate patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and guide treatment
- Epidemiology section updated to reflect new data suggesting a decline in the age-adjusted prevalence of COPD, likely as a result of decreased smoking rates
- Multiple new common genetic risk factors associated with COPD described, including a recently discovered functional genetic variant
- Discussion about the long-term care of patients with COPD extensively revised to include the most recent trials assessing indications for long-acting inhaled bronchodilators and inhaled corticosteroids, among other therapies
- Recent evidence supporting lung cancer screening in patients with COPD reviewed
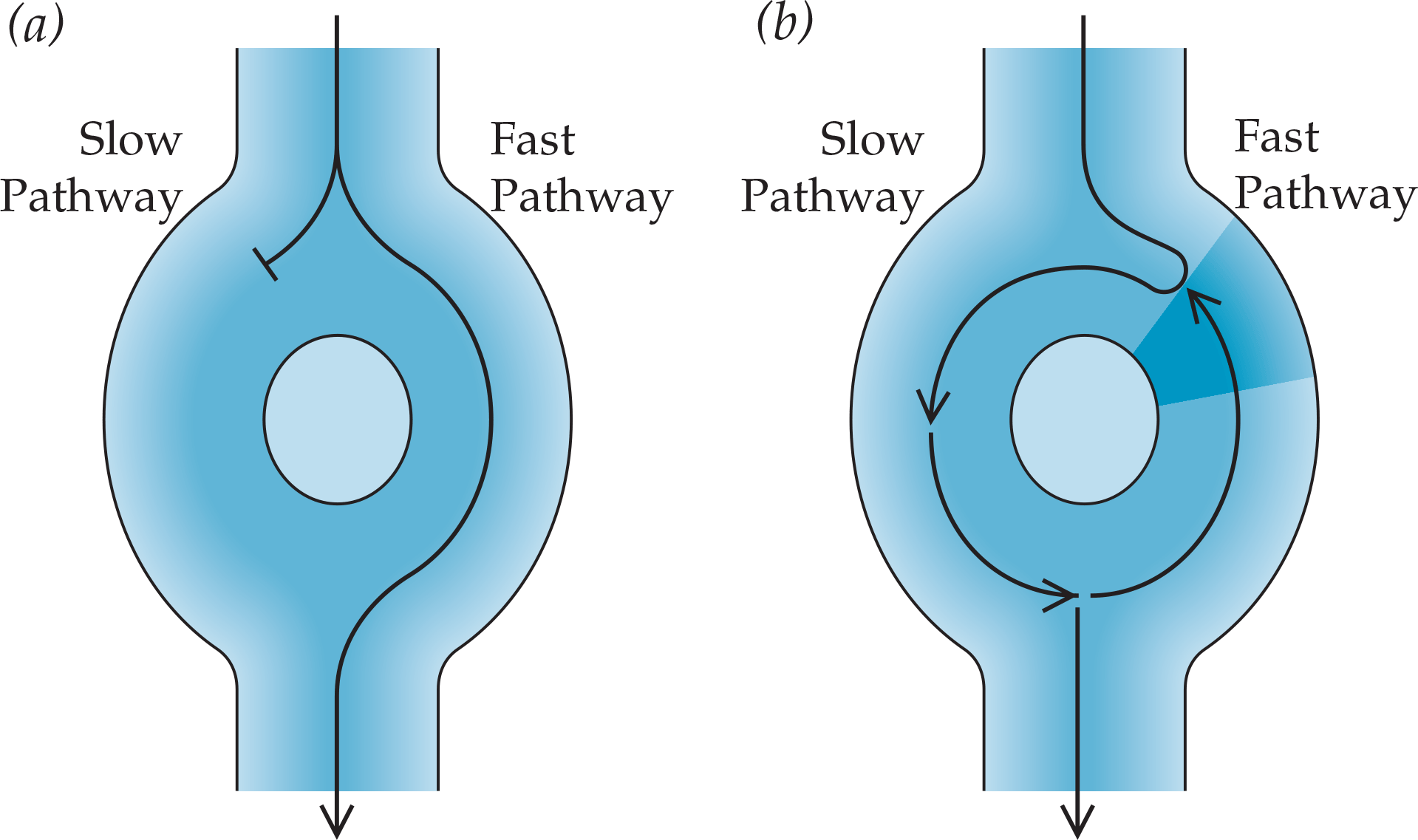
- Radiofrequency ablation as a treatment modality has revolutionized therapy for many SVTs; acts as a first-line alternative to drug therapy in some circumstances, with a high acute success rate and relatively low complication rate.
- Cryoablation therapy emerging as an alternative in ablative therapies. Investigation of this modality for SVTs is ongoing.
- Detailed drug regimens optimized for acute and chronic management of specific SVTs; detailed in the 2015 ACC/AHA/HRS practice guidelines.
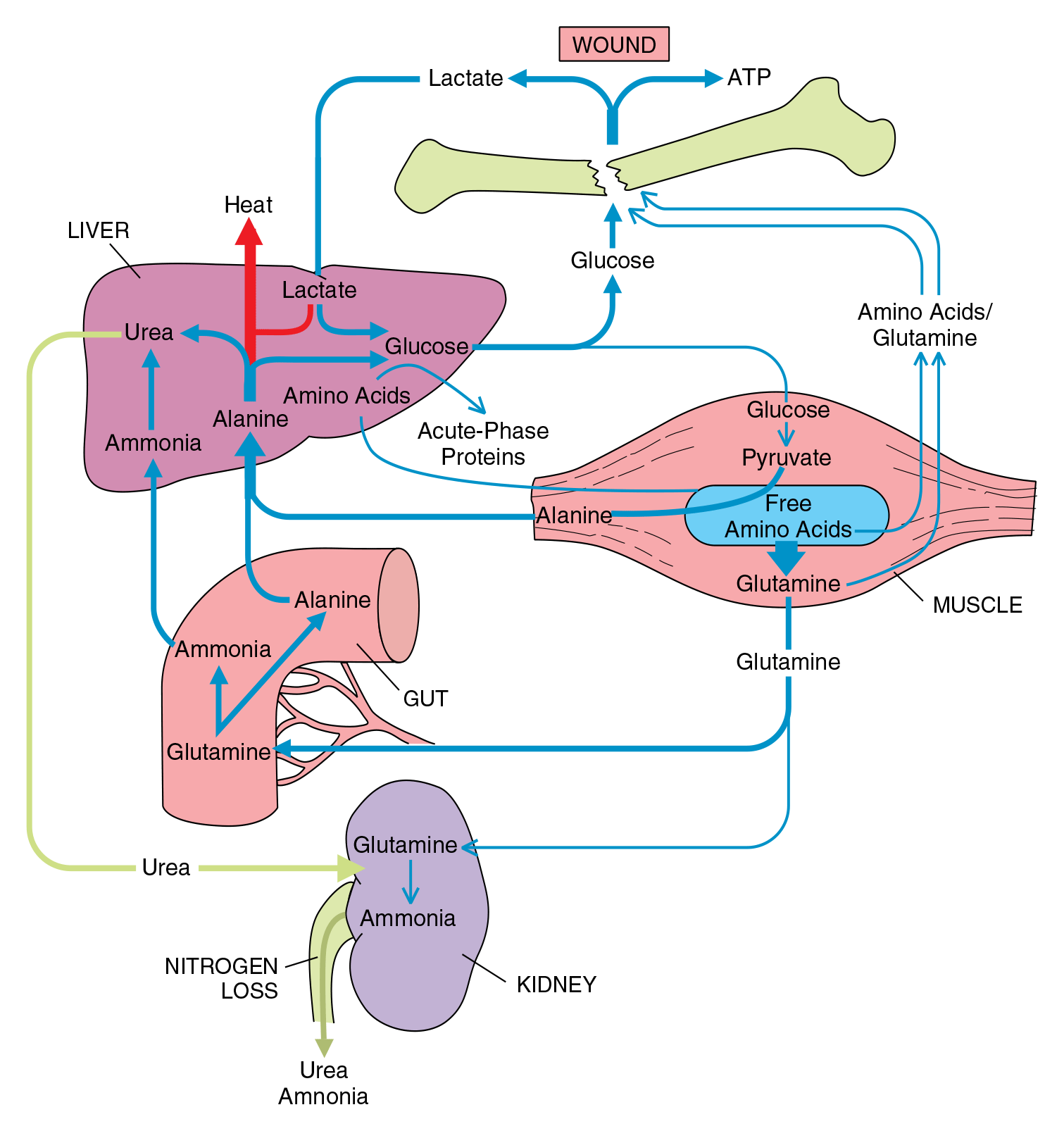
Metabolic Response to Critical Illness - Part 1
- Understanding the important role the gut has during injury and critical illness, for amino acid intake and altered circulation.
- Antibiotic-integrated catheters which delay complications of infection in suboptimal conditions.
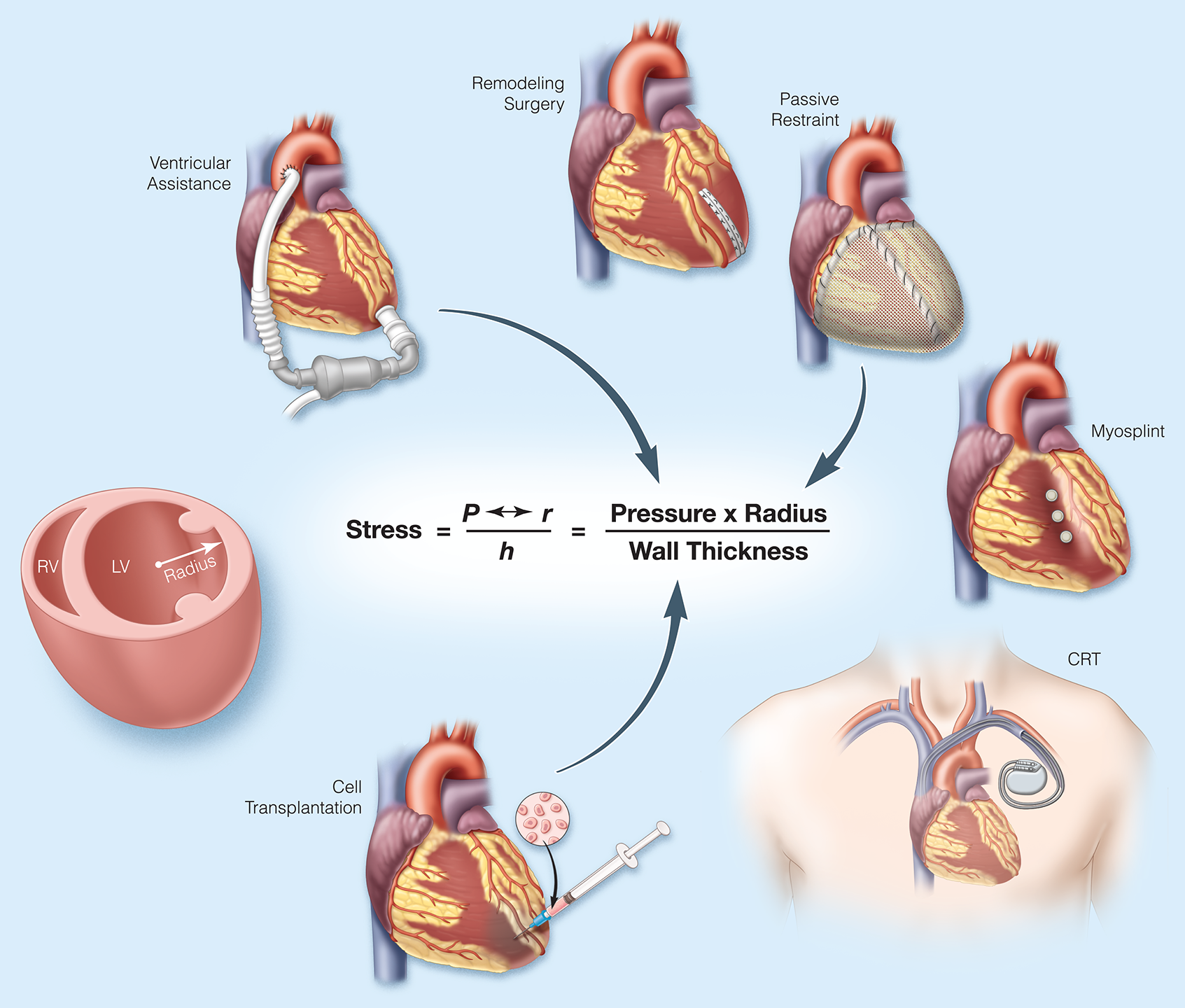
- Emerging evidence is refining an understanding of the role of the splanchnic circulation and the abdominal compartment in heart failure. The abdominal organs and splanchnic circulation appear to play an active role in volume distribution and renal filtration, thereby affecting balance between a compensated and a decompensated state. The understanding of the homeostatic role of the abdominal compartment in the compensated state and the maladaptive role in the decompensated state is evolving and may provide targets for new therapies and better application of available treatment strategies in the future.
- 2017 focused update to ACC/AHA/HFSA practice guidelines for management of heart failure delineate further considerations for pharmacologic therapy and interventions.

