- Classic familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP) syndromes have been expanded to include attenuated FAP (aFAP) and new syndromes, such as MUTYH-associated polyposis (MAP).
- Additional studies support chemoprevention of extracolonic manifestations of FAP, including sulindac with high-dose selective estrogen receptor modulators for FAP-associated desmoid tumors and sulindac with erlotinib for suppression of duodenal polyps.
- The diagnostic criteria for attenuated polyposis syndromes including aFAP and MAP are a cumulative 10 to 100 lifetime polyps, with an APC gene mutation or biallelic MUTYH mutations.
Latest Updates

Seronegative Spondyloarthritis: Diagnosis And Management
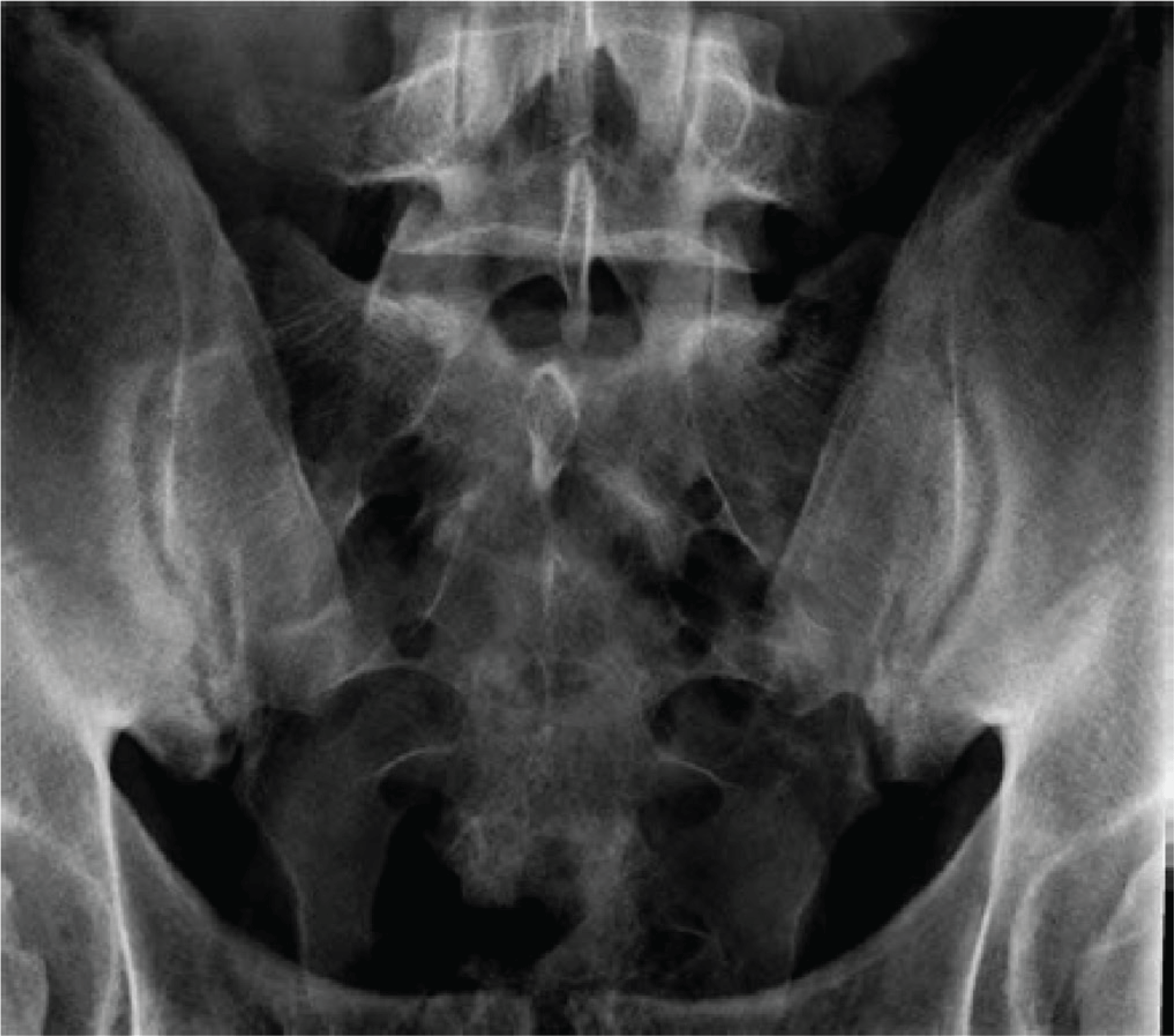
- The combined use of T1-weighted MRI with a water-sensitive MRI sequence significantly enhances early detection of spondyloarthritis, identifies patients responsive to therapeutic intervention with tumor necrosis factor inhibitors (TNFIs), and constitutes a key prognostic factor for structural progression.
- Treatment of patients with TNFI early in the disease course when radiographic sacroiliitis is not yet evident is highly effective, especially in patients with an elevated C-reactive protein and/or features of inflammation on MRI.
- Treatment targeting interleukin-17 is an effective new treatment option for patients with spondyloarthritis, especially in the setting of concomitant psoriasis.
- Imaging recommendations that allow for precision in diagnosis.

- Classic familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP) syndromes have been expanded to include attenuated FAP (aFAP) and new syndromes, such as MUTYH-associated polyposis (MAP).
- Additional studies support chemoprevention of extracolonic manifestations of FAP, including sulindac with high-dose selective estrogen receptor modulators for FAP-associated desmoid tumors and sulindac with erlotinib for suppression of duodenal polyps.
- The diagnostic criteria for attenuated polyposis syndromes including aFAP and MAP are a cumulative 10 to 100 lifetime polyps, with an APC gene mutation or biallelic MUTYH mutations.

Pulmonary Diseases: Preoperative Assessment
- After emergence from general anesthesia, vital capacity may remain decreased from baseline in 50% of healthy patients for up to 1 week postoperatively.
- A change from the upright to supine position alone reduces FRC by approximately 0.8 to 1.0 L. This underscores the importance of perioperative optimization to prevent postoperative atelectasis.
- There is no prohibitive level of obstruction on spirometry that precludes surgery. Routine perioperative spirometry testing has not been associated with decreased rates of PPCs or mortality, and PFTs should not be the primary or sole determinant for denying surgery.
- Patients with well-controlled asthma that require general anesthesia with endotracheal intubation are not considered at higher risk for PPCs than the general surgical population.
- Obesity by itself has not been consistently demonstrated to be an independent risk factor for PPCs across several meta-analyses. Conversely, underweight patients were found to have a fivefold increased risk of 30-day mortality, underscoring the importance of optimizing nutrition status.

Treatment of Sternal Wound Infections
- Sternal wound complications have dramatically decreased due to improvements in perioperative care of cardiac surgical patients
- Innovation in flap design has made treatment of sternal wound infections more reliable
- New sternal plating systems hold potential to further reduce sternotomy complications in high risk patients

- Newer lung isolation devices may increase the success of placement with decreased difficulty.
- Bronchial blockers can be used for lung isolation in a suspected difficult airway.
- Stepwise ways to predict and manage hypoxia during one-lung ventilation.

Seronegative Spondyloarthritis: Diagnosis And Management
- The combined use of T1-weighted MRI with a water-sensitive MRI sequence significantly enhances early detection of spondyloarthritis, identifies patients responsive to therapeutic intervention with tumor necrosis factor inhibitors (TNFIs), and constitutes a key prognostic factor for structural progression.
- Treatment of patients with TNFI early in the disease course when radiographic sacroiliitis is not yet evident is highly effective, especially in patients with an elevated C-reactive protein and/or features of inflammation on MRI.
- Treatment targeting interleukin-17 is an effective new treatment option for patients with spondyloarthritis, especially in the setting of concomitant psoriasis.
- Imaging recommendations that allow for precision in diagnosis.

Neurogenic Bladder Dysfunction: Surgical Treatment
- Surgery for neurogenic bladder aims to protect the upper urinary tract and optimize continence.
- Major factors to consider are the injury level, gender, habitus, dexterity, and cognitive functions.
- Surgical options for storage and emptying failure are discussed, including indication, technique, and complications.
- New surgical technology and regenerative medicine are mentioned together.


