Pulmonary Edema I: Cardiogenic Pulmonary Edema
- Meta-analyses reveal that noninvasive positive pressure ventilation decreases mortality in patients with acute cardiogenic pulmonary edema.
- Noninvasive positive pressure ventilation (NPPV) is useful in treating hypoxemia and decreases the work of breathing and may improve mortality in acute cardiogenic pulmonary edema.
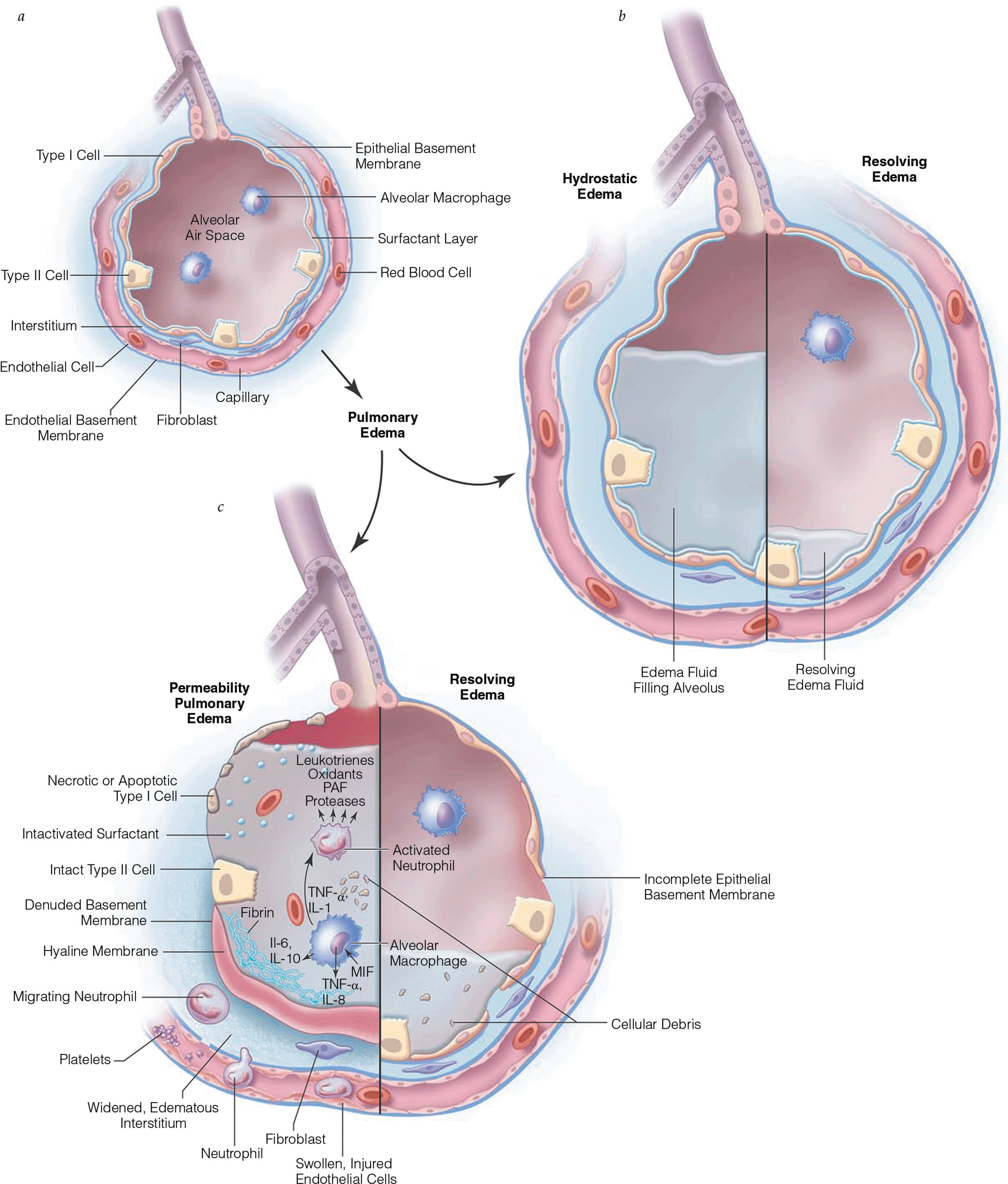
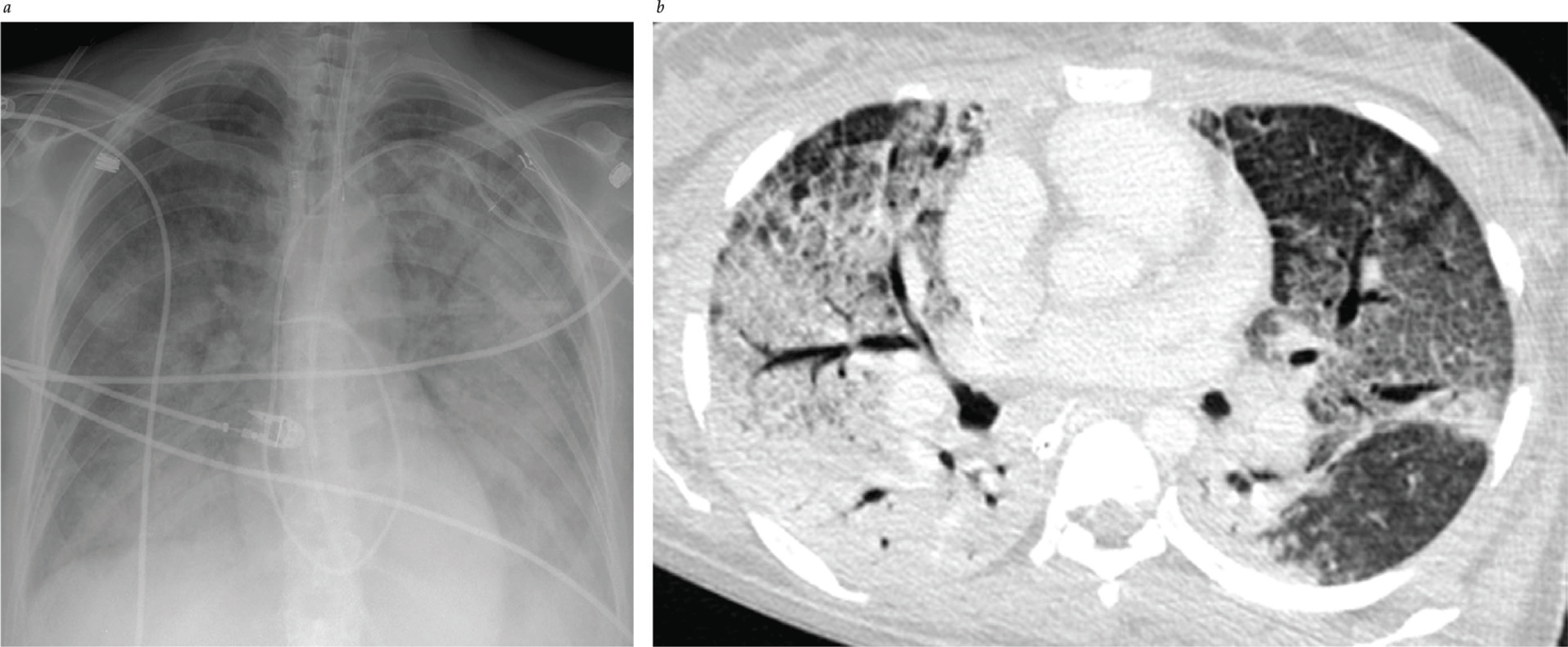
- Ancillary features that can be routinely visualized on an anteroposterior chest radiograph made with a portable x-ray machine may help differentiate cardiogenic from noncardiogenic pulmonary edema. A widened vascular pedicle and an increase in the cardiothoracic ratio suggest increased pulmonary capillary pressure; distinct air bronchograms are more common with noncardiogenic pulmonary edema.