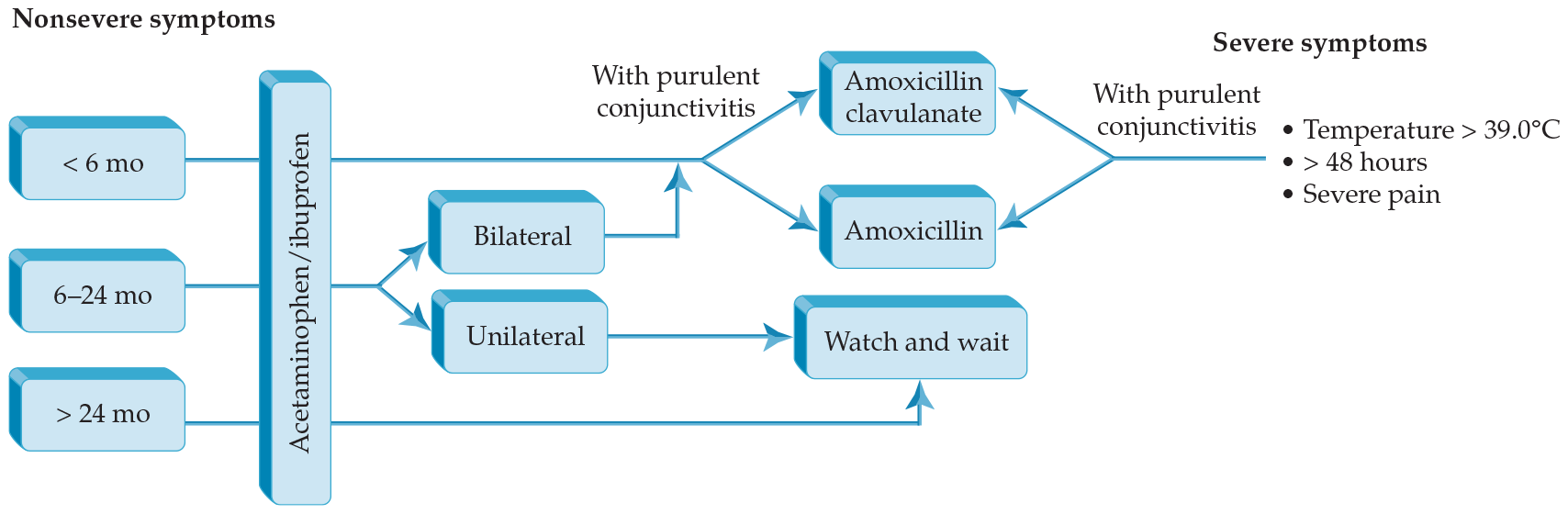
- Explores the more common diseases that may cause fevers in pediatric patients.
- Provides algorithms to guide practitioners in managing a pediatric fever in various age groups.
- Reinforces that antibiotics be reserved for clinically diagnosed bacterial infections.
Latest Updates

- Explores the more common diseases that may cause fevers in pediatric patients.
- Provides algorithms to guide practitioners in managing a pediatric fever in various age groups.
- Reinforces that antibiotics be reserved for clinically diagnosed bacterial infections.
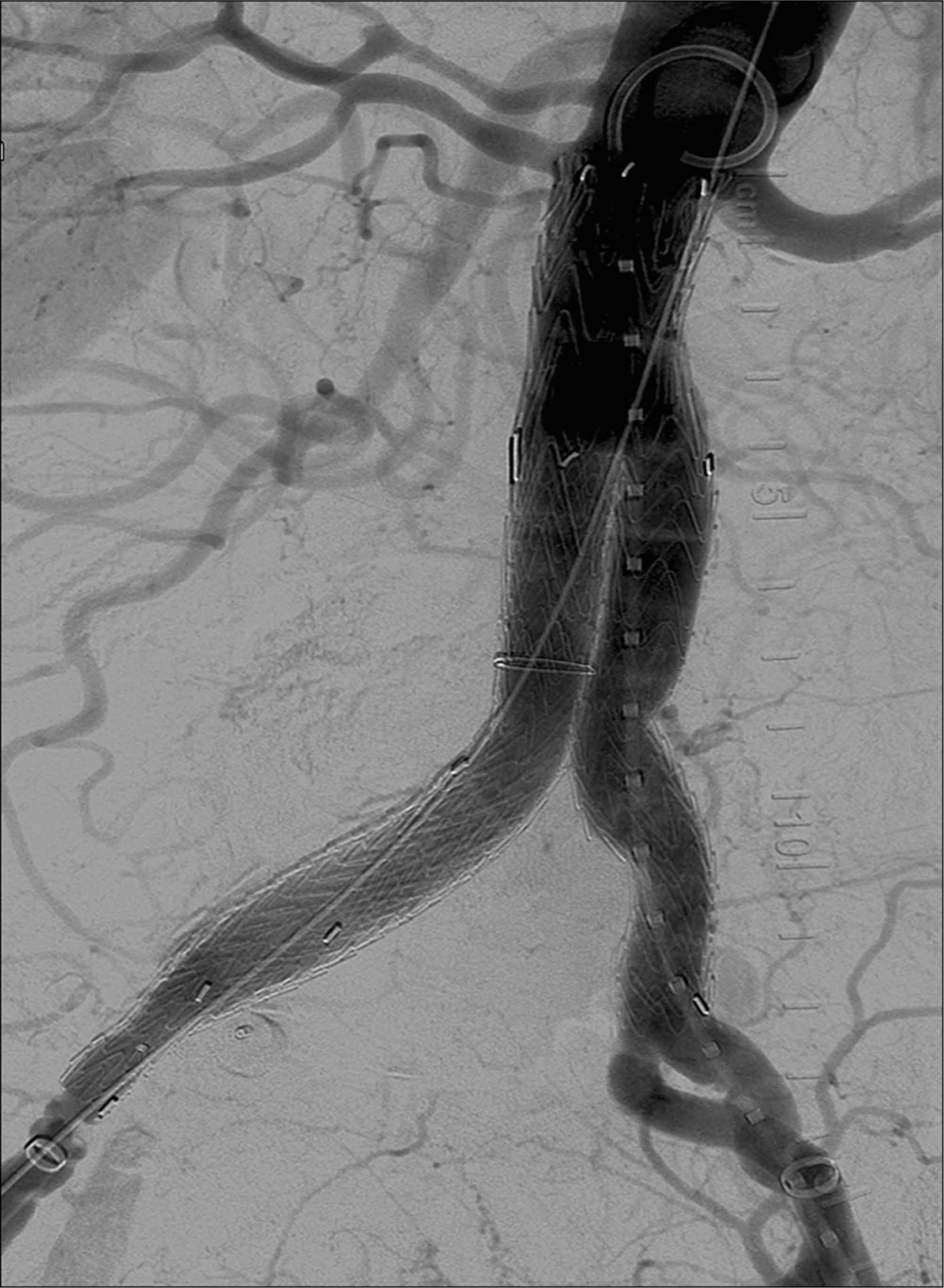
Repair of Infrarenal Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms
- Chronic kidney disease, diabetes, and anemia/thrombocytopenia have been linked to poor outcomes after AAA repair and, therefore, also require investigation and optimization. Current guidelines recommend deferral of aneurysm treatment for active cardiac conditions (unstable angina, recent myocardial infarction, active congestive heart failure, significant arrhythmia, or severe valvular disease).
- Iliac disease, whether aneurysmal or occlusive, can present special challenges to endovascular repair of aortic aneurysms. Several options exist to meet these challenges. For common and/or internal iliac artery aneurysms, treatment may require embolization of the internal iliac artery and extension of the endograft into the external iliac artery.
- After open repair, patients are typically evaluated in the clinic after several weeks to ensure proper wound healing and progress of recovery. Beyond this, patients may be monitored for the development of incisional hernia and should be considered for imaging with ultrasonography or CT at 5 years to evaluate for aneurysmal degeneration of other areas of the arterial tree, such as the visceral aortic segment or iliac arteries.

Repair of Infrarenal Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms
- Chronic kidney disease, diabetes, and anemia/thrombocytopenia have been linked to poor outcomes after AAA repair and, therefore, also require investigation and optimization. Current guidelines recommend deferral of aneurysm treatment for active cardiac conditions (unstable angina, recent myocardial infarction, active congestive heart failure, significant arrhythmia, or severe valvular disease).
- Iliac disease, whether aneurysmal or occlusive, can present special challenges to endovascular repair of aortic aneurysms. Several options exist to meet these challenges. For common and/or internal iliac artery aneurysms, treatment may require embolization of the internal iliac artery and extension of the endograft into the external iliac artery.
- After open repair, patients are typically evaluated in the clinic after several weeks to ensure proper wound healing and progress of recovery. Beyond this, patients may be monitored for the development of incisional hernia and should be considered for imaging with ultrasonography or CT at 5 years to evaluate for aneurysmal degeneration of other areas of the arterial tree, such as the visceral aortic segment or iliac arteries.

Repair of Infrarenal Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms
- Chronic kidney disease, diabetes, and anemia/thrombocytopenia have been linked to poor outcomes after AAA repair and, therefore, also require investigation and optimization. Current guidelines recommend deferral of aneurysm treatment for active cardiac conditions (unstable angina, recent myocardial infarction, active congestive heart failure, significant arrhythmia, or severe valvular disease).
- Iliac disease, whether aneurysmal or occlusive, can present special challenges to endovascular repair of aortic aneurysms. Several options exist to meet these challenges. For common and/or internal iliac artery aneurysms, treatment may require embolization of the internal iliac artery and extension of the endograft into the external iliac artery.
- After open repair, patients are typically evaluated in the clinic after several weeks to ensure proper wound healing and progress of recovery. Beyond this, patients may be monitored for the development of incisional hernia and should be considered for imaging with ultrasonography or CT at 5 years to evaluate for aneurysmal degeneration of other areas of the arterial tree, such as the visceral aortic segment or iliac arteries.
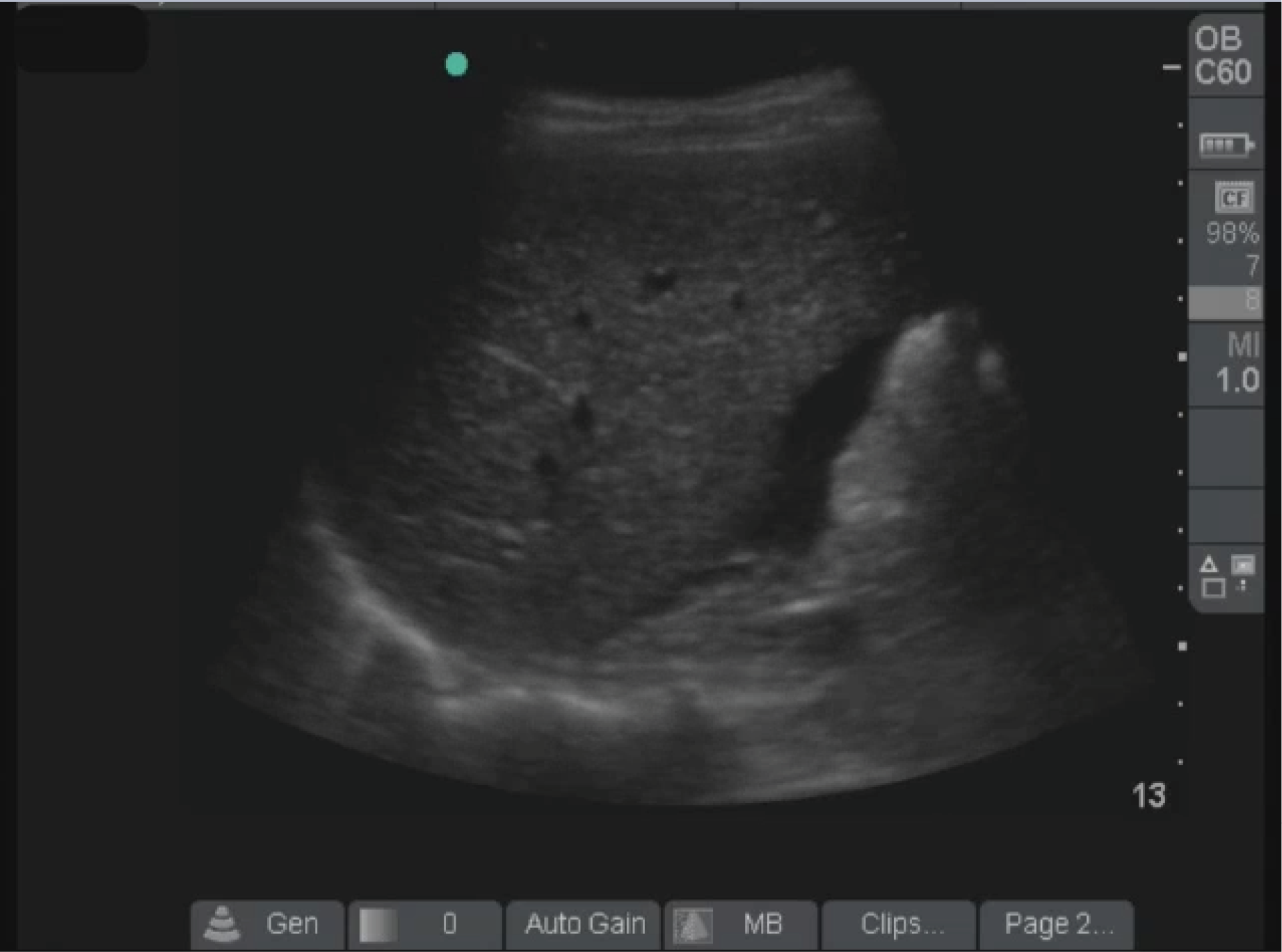
Focused Assessment with Sonography for Trauma
- Recent studies indicate that the focused assessment with sonography for trauma (FAST) examination has a more limited sensitivity for intra-abdominal injury than was initially reported
- Validated assessments of FAST examiner skill are being developed to assess user competence and control for the factor of operator dependence
- The extended FAST (E-FAST) examination is a reliable method for rapidly diagnosing pneumothorax and hemothorax at the bedside
- Contrast-enhanced ultrasonography is an area of active research that uses a nonnephrotoxic contrast agent to improve ultrasonographic evaluation of solid-organ injuries

Focused Assessment with Sonography for Trauma
- Recent studies indicate that the focused assessment with sonography for trauma (FAST) examination has a more limited sensitivity for intra-abdominal injury than was initially reported
- Validated assessments of FAST examiner skill are being developed to assess user competence and control for the factor of operator dependence
- The extended FAST (E-FAST) examination is a reliable method for rapidly diagnosing pneumothorax and hemothorax at the bedside
- Contrast-enhanced ultrasonography is an area of active research that uses a nonnephrotoxic contrast agent to improve ultrasonographic evaluation of solid-organ injuries

Focused Assessment with Sonography for Trauma
- Recent studies indicate that the focused assessment with sonography for trauma (FAST) examination has a more limited sensitivity for intra-abdominal injury than was initially reported
- Validated assessments of FAST examiner skill are being developed to assess user competence and control for the factor of operator dependence
- The extended FAST (E-FAST) examination is a reliable method for rapidly diagnosing pneumothorax and hemothorax at the bedside
- Contrast-enhanced ultrasonography is an area of active research that uses a nonnephrotoxic contrast agent to improve ultrasonographic evaluation of solid-organ injuries


