- Currently, there is a belief that the incidence of SS is congruent with the increasing number of serotoninergic agents prescribed and nutraceutical agents, such as St. John’s wort. In 2002, the Toxic Exposure Surveillance System reported 26,633 incidences of exposure to selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) that caused significant adverse events in 7,349 patients, with a total of 93 deaths within the year.
- The Hunter Serotonin Toxicity Criteria are simpler, more sensitive, and more specific compared with Sternbach’s criteria. The Hunter criteria require a patient to have taken a serotoninergic agent and to meet one of the following conditions: spontaneous clonus; inducible clonus with agitation or diaphoresis; ocular clonus with agitation or diaphoresis; tremor with hyperreflexia; hypertonia with temperature above 38ºC (100.4°F) with ocular clonus or inducible clonus.
- In the setting of severe hyperthermia (temperature greater than 41°C [105.8°F]), immediate sedation with neuromuscular paralysis and intubation should occur to eliminate excessive muscle activity and thus prevent further complications. Nondepolarizing agents (e.g., vecuronium or atracurium) should be used for paralysis prior to intubation.
Latest Updates

- The only available test to diagnose adrenal insufficiency is cosyntropin stimulation, where synthetic adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) (cosyntropin) is administered in a 250 μg intravenous bolus, and plasma cortisol levels are measured 45 and 60 minutes later. Responses to the test with values less than 20 μg/dL usually mean that adrenal compromise is a contributing factor. In severe cases of acute adrenal insufficiency that may require intensive care, cosyntropin stimulation testing can be replaced by the measurement of plasma cortisol levels. Patients with low plasma albumin concentration, however, have lower cortisol concentrations and are thus excepted from the test.
- The most common form of congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH) is the 21-hydroxylase deficiency syndrome (95%). There are three clinical presentations: the so-called salt wasting, associated with essentially no 21-hydroxylase activity; simple virilizing, associated with a modest reduction in 21-hydroxylase activity; and the nonclassical form in which the enzyme activity is nearly normal.
- All patients with 21-hydroxylase deficiency should be considered to have some degree of salt loss. Fludrocortisone, 0.2 mg every morning, should be the first therapy. Hydrocortisone, 12 to 15 mg/m2 as a single morning dose, should be initiated several days later. After 2 weeks of combined therapy, a morning 17-OH progesterone level should be measured.
Asymptomatic Carotid Bruit/Carotid Artery Stenosis
- There has been increased interest in using statins to slow the progression of carotid artery disease. In the Asymptomatic Carotid Artery Plaque Study, lovastatin was compared in a double-blinded study to evaluate the effect on intima-media thickness and cardiovascular events. In both men and women with moderately elevated low-density lipoprotein levels, the progression of intima-media thickness in the carotid arteries was reduced compared with placebo, and lovastatin was also associated with reduced cardiovascular events and mortality.
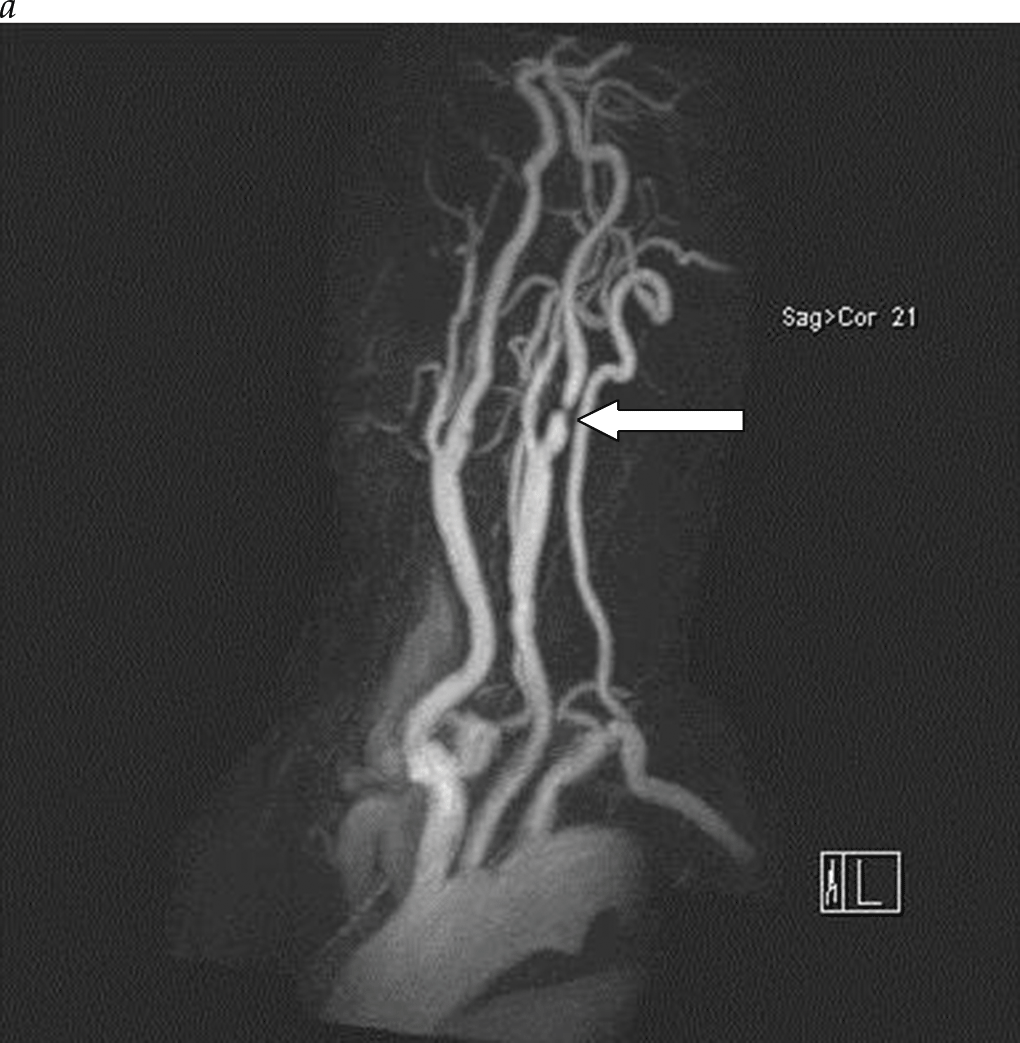
- The initial imaging study for patients with carotid bruit or cerebrovascular symptoms is duplex imaging of the extracranial carotid arteries. Duplex ultrasonography is an accurate and reliable noninvasive tool to determine the degree of carotid stenosis and plaque morphology in most patients.
- Conventional angiography, once considered the gold standard for carotid imaging, is now reserved for patients with conflicting studies or patients being considered for carotid stenting. Conventional contrast selective carotid angiography poses a stroke risk of approximately 1% and therefore has a limited role in place of modern MRA and CTA, except in cases of planned carotid stenting.

- The only available test to diagnose adrenal insufficiency is cosyntropin stimulation, where synthetic adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) (cosyntropin) is administered in a 250 μg intravenous bolus, and plasma cortisol levels are measured 45 and 60 minutes later. Responses to the test with values less than 20 μg/dL usually mean that adrenal compromise is a contributing factor. In severe cases of acute adrenal insufficiency that may require intensive care, cosyntropin stimulation testing can be replaced by the measurement of plasma cortisol levels. Patients with low plasma albumin concentration, however, have lower cortisol concentrations and are thus excepted from the test.
- The most common form of congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH) is the 21-hydroxylase deficiency syndrome (95%). There are three clinical presentations: the so-called salt wasting, associated with essentially no 21-hydroxylase activity; simple virilizing, associated with a modest reduction in 21-hydroxylase activity; and the nonclassical form in which the enzyme activity is nearly normal.
- All patients with 21-hydroxylase deficiency should be considered to have some degree of salt loss. Fludrocortisone, 0.2 mg every morning, should be the first therapy. Hydrocortisone, 12 to 15 mg/m2 as a single morning dose, should be initiated several days later. After 2 weeks of combined therapy, a morning 17-OH progesterone level should be measured.

Asymptomatic Carotid Bruit/Carotid Artery Stenosis
- There has been increased interest in using statins to slow the progression of carotid artery disease. In the Asymptomatic Carotid Artery Plaque Study, lovastatin was compared in a double-blinded study to evaluate the effect on intima-media thickness and cardiovascular events. In both men and women with moderately elevated low-density lipoprotein levels, the progression of intima-media thickness in the carotid arteries was reduced compared with placebo, and lovastatin was also associated with reduced cardiovascular events and mortality.
- The initial imaging study for patients with carotid bruit or cerebrovascular symptoms is duplex imaging of the extracranial carotid arteries. Duplex ultrasonography is an accurate and reliable noninvasive tool to determine the degree of carotid stenosis and plaque morphology in most patients.
- Conventional angiography, once considered the gold standard for carotid imaging, is now reserved for patients with conflicting studies or patients being considered for carotid stenting. Conventional contrast selective carotid angiography poses a stroke risk of approximately 1% and therefore has a limited role in place of modern MRA and CTA, except in cases of planned carotid stenting.

Asymptomatic Carotid Bruit/Carotid Artery Stenosis
- There has been increased interest in using statins to slow the progression of carotid artery disease. In the Asymptomatic Carotid Artery Plaque Study, lovastatin was compared in a double-blinded study to evaluate the effect on intima-media thickness and cardiovascular events. In both men and women with moderately elevated low-density lipoprotein levels, the progression of intima-media thickness in the carotid arteries was reduced compared with placebo, and lovastatin was also associated with reduced cardiovascular events and mortality.
- The initial imaging study for patients with carotid bruit or cerebrovascular symptoms is duplex imaging of the extracranial carotid arteries. Duplex ultrasonography is an accurate and reliable noninvasive tool to determine the degree of carotid stenosis and plaque morphology in most patients.
- Conventional angiography, once considered the gold standard for carotid imaging, is now reserved for patients with conflicting studies or patients being considered for carotid stenting. Conventional contrast selective carotid angiography poses a stroke risk of approximately 1% and therefore has a limited role in place of modern MRA and CTA, except in cases of planned carotid stenting.
Postherpetic Neuralgia: A Patient’s and a Physician’s Perspective
- Today, most experts in interventional pain management recommend an evidence-based stepladder approach for the management of all patients with PHN that includes an advancing combination of therapeutic strategies as needed on a graduated basis to control pain and anxiety and prevent complications, including suicide.
- The most important immunologic risk factor for herpes zoster and PHN is the decline in cell-mediated immunity to VZV that occurs over time as people age, with an onset around 50 years of age. Although possible, second episodes of zoster are uncommon due to the boosting or anamnestic effect of the first episode of zoster.
- The nonpharmacologic treatment options for PHN include combinations of acupuncture, cryotherapy, heat therapy, and transcutaneous and/or percutaneous electrical nerve stimulation. The multimodal nonpharmacologic treatment options for PHN are stratified and compared by their evidence levels.
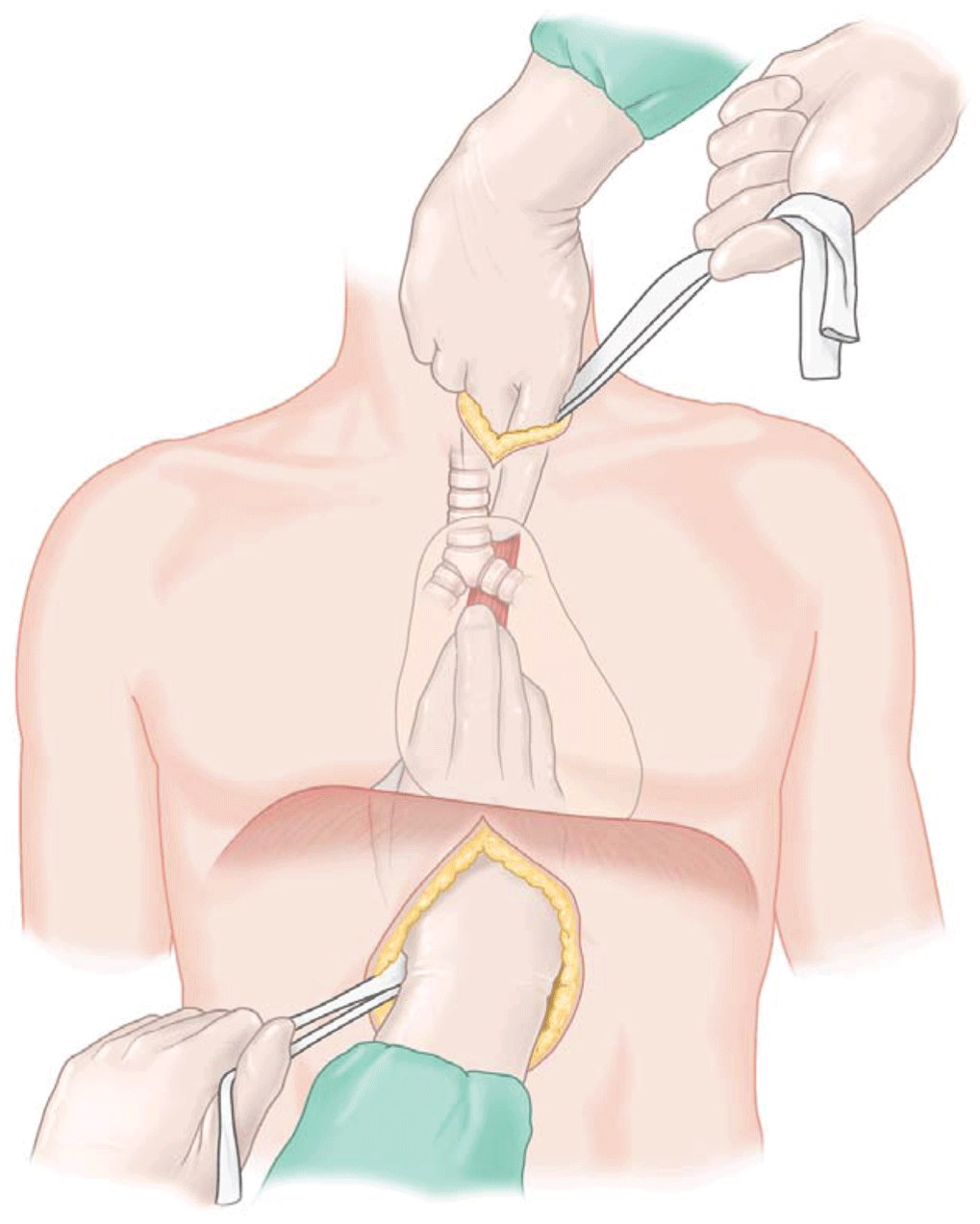
- Operative techniques employed to treat esophageal disease have advanced considerably as a result of the successful introduction of minimally invasive approaches to the esophagus. For a number of diseases (e.g., achalasia and routine antireflux surgery), minimally invasive procedures have proved to be as effective as their open counterparts while causing less postoperative morbidity.
- If esophageal obstruction prevents oral intake, endoscopic dilation of the stricture, accompanied by either nasogastric intubation or percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy (PEG), is often indicated; the patient should then be able to resume at least a liquid diet.
- Transhiatal esophagectomy is commonly performed to treat end-stage benign esophageal disease and carcinomas of the cardia and the lower esophagus. Esophageal resection through a combined laparotomy–right thoracotomy approach (Ivor Lewis esophagectomy) is ideal for cancers of the middle esophagus but is also used by many for lower third cancers. A three-hole esophagectomy (also known as a McKeown esophagectomy) is sometimes preferred for its excellent exposure of all lymph node stations.


