Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
- Imaging modalities in the assessment of NAFLD
- Controlled attenuation parameter as a point of care measure for hepatic steatosis
- Proton density fat fraction as MRI based measure for hepatic steatosis
- Liver stiffness measurement on elastography as a correlate of hepatic fibrosis or cirrhosis
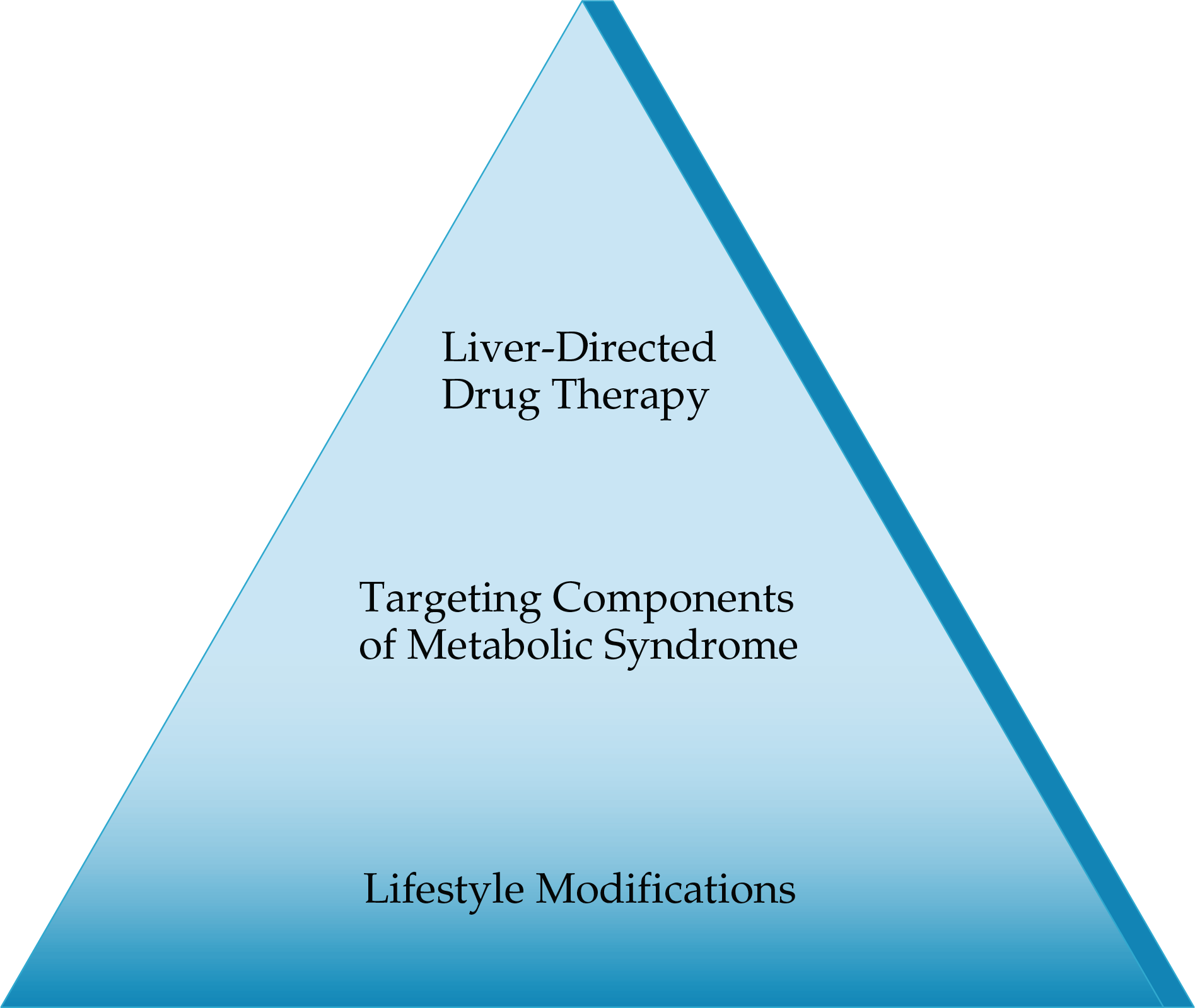
- Active clinical trials in phase 2b and 3, yet no FDA approved therapy
- Intense lifestyle changes with 5-10% weight loss can improve fibrosis and steatosis