- The mortality for severe acute pancreatitis is 15 to 30%; however, the overall mortality for all patients with acute pancreatitis is less than 5%. Over the last several decades, mortality related to acute pancreatitis has decreased substantially, which likely reflects improved critical care and better strategies for operative management.
- Recent guidelines identify the SIRS criteria as the best and most pragmatic predictor of severe acute pancreatitis at admission and at 48 hours. A 1991 consensus committee first coined the term SIRS as the clinical manifestation of the hypermetabolic response to infection or a noninfectious insult. SIRS criteria include (1) temperature greater than 38°C (100.4°F) or less than 36°C (96.8°F); (2) heart rate greater than 90 beats/min; (3) tachypnea with a respiratory rate greater than 20 breaths/min or hyperventilation with arterial carbon dioxide tension (PaCO2) less than 32 mm Hg; and (4) a white blood cell count greater than 12,000/µL or less than 4,000/µL or greater than 10% immature neutrophils (“bands”).
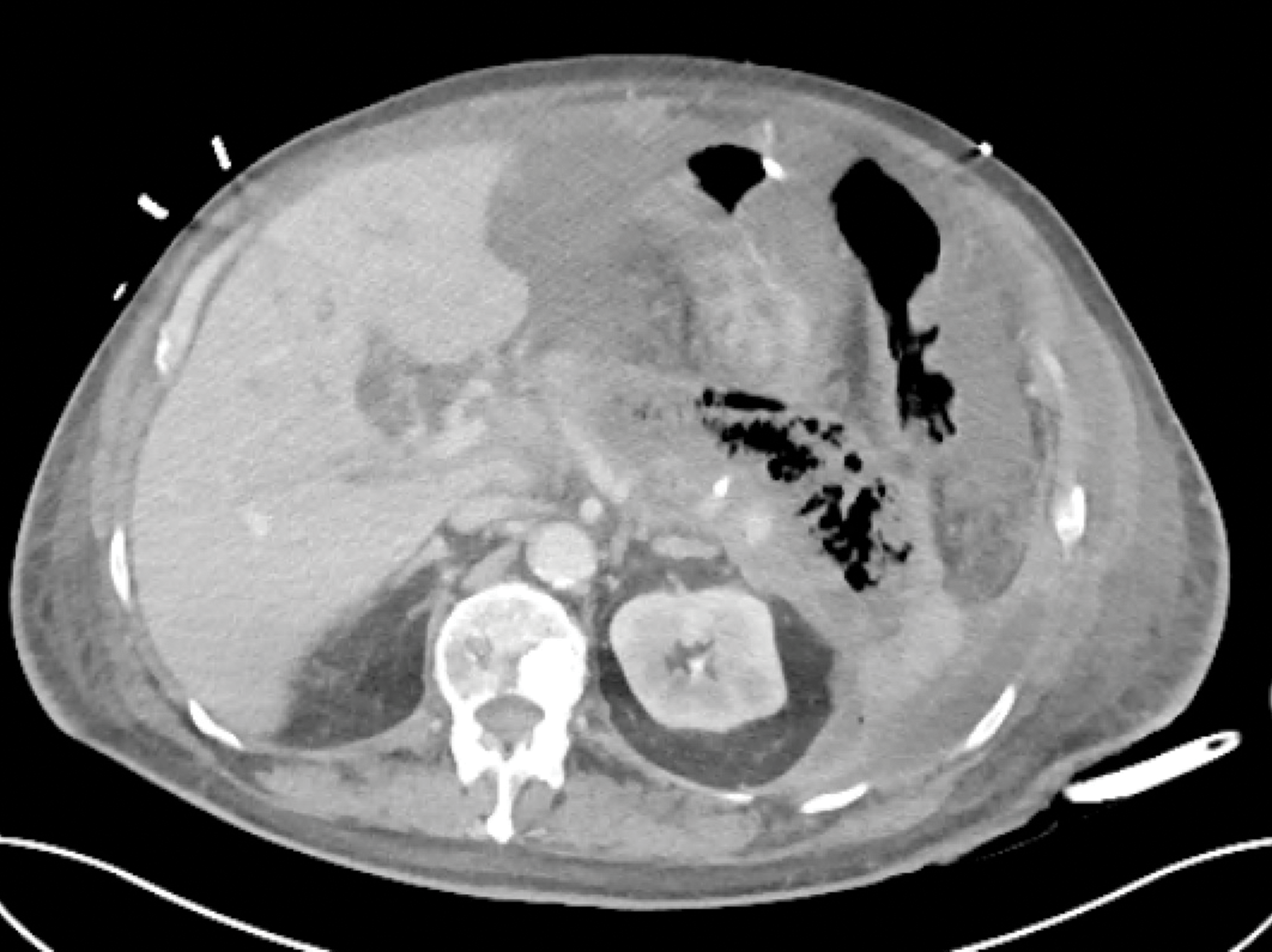
- The optimal strategy for intervention in patients with confirmed infected necrotizing pancreatitis is initial image-guided percutaneous retroperitoneal catheter drainage or endoscopic transluminal drainage, followed, when necessary, by minimally invasive endoscopic or surgical necrosectomy.
Latest Updates
- Until recently, it was thought that chromosomal translocations are very uncommon in carcinomas occurring in adults. However, a series of studies have now demonstrated that the majority of prostate carcinomas harbor translocations between genes encoding one of two ETS-related transcription factors, ERG or ETV1, and the androgen-regulated gene TMPRSS2.
- Exposure to ionizing radiation is another cause of cancer linked directly to genetic damage. The incidence of leukemias and various solid tumors in atomic bomb survivors provided data for classic studies of radiation dosage and its consequences. More recent data derive from cancer cases arising as a late complication of radiation therapy or radiomimetic chemotherapy used for treatment of an initial malignancy.
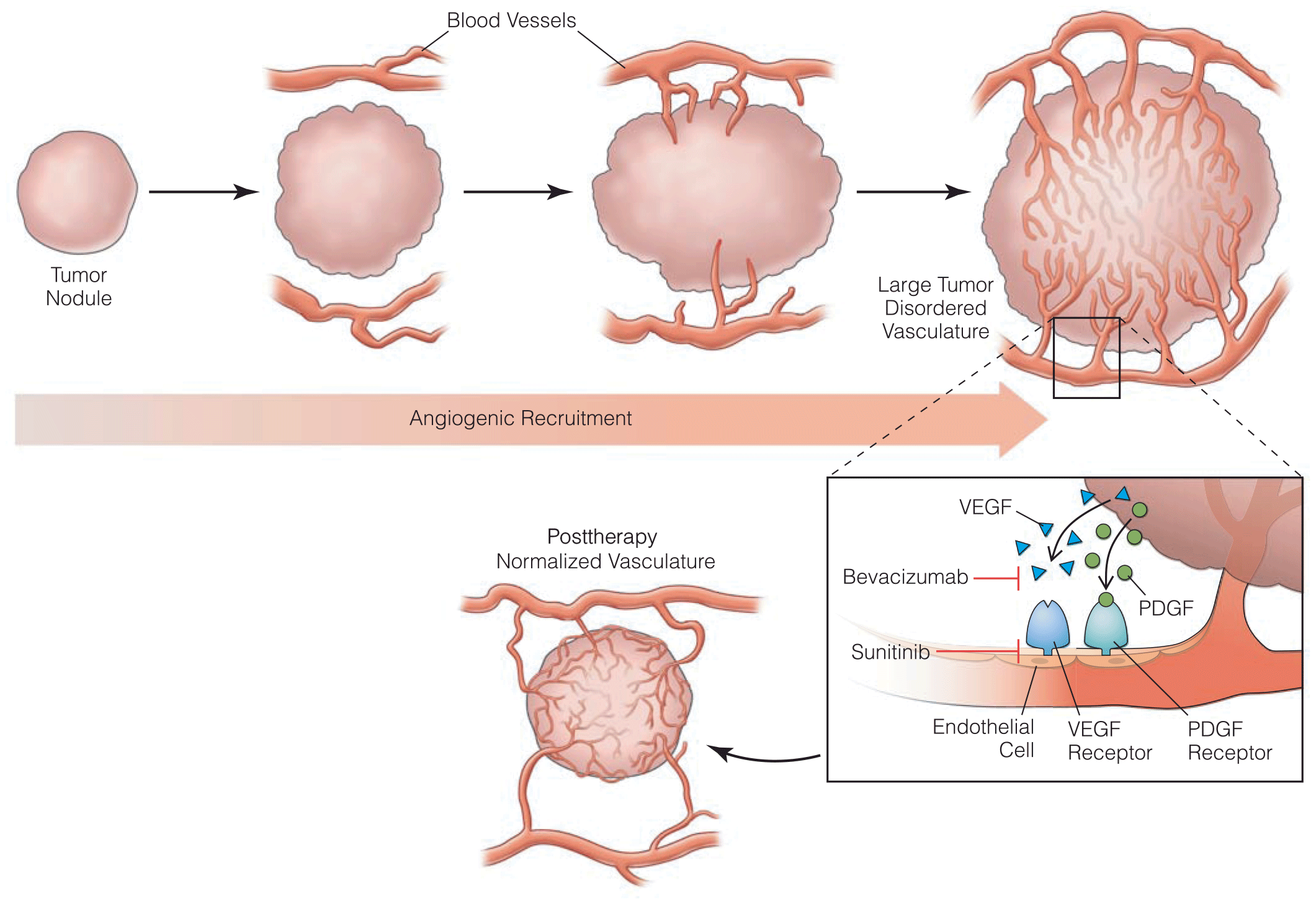
- In addition to general metastasis promoters, recent studies have begun to uncover factors that mediate metastasis to specific organs such as lung and bone. A critical property required for the growth of cancers beyond a minimal size is the recruitment of blood vessel.
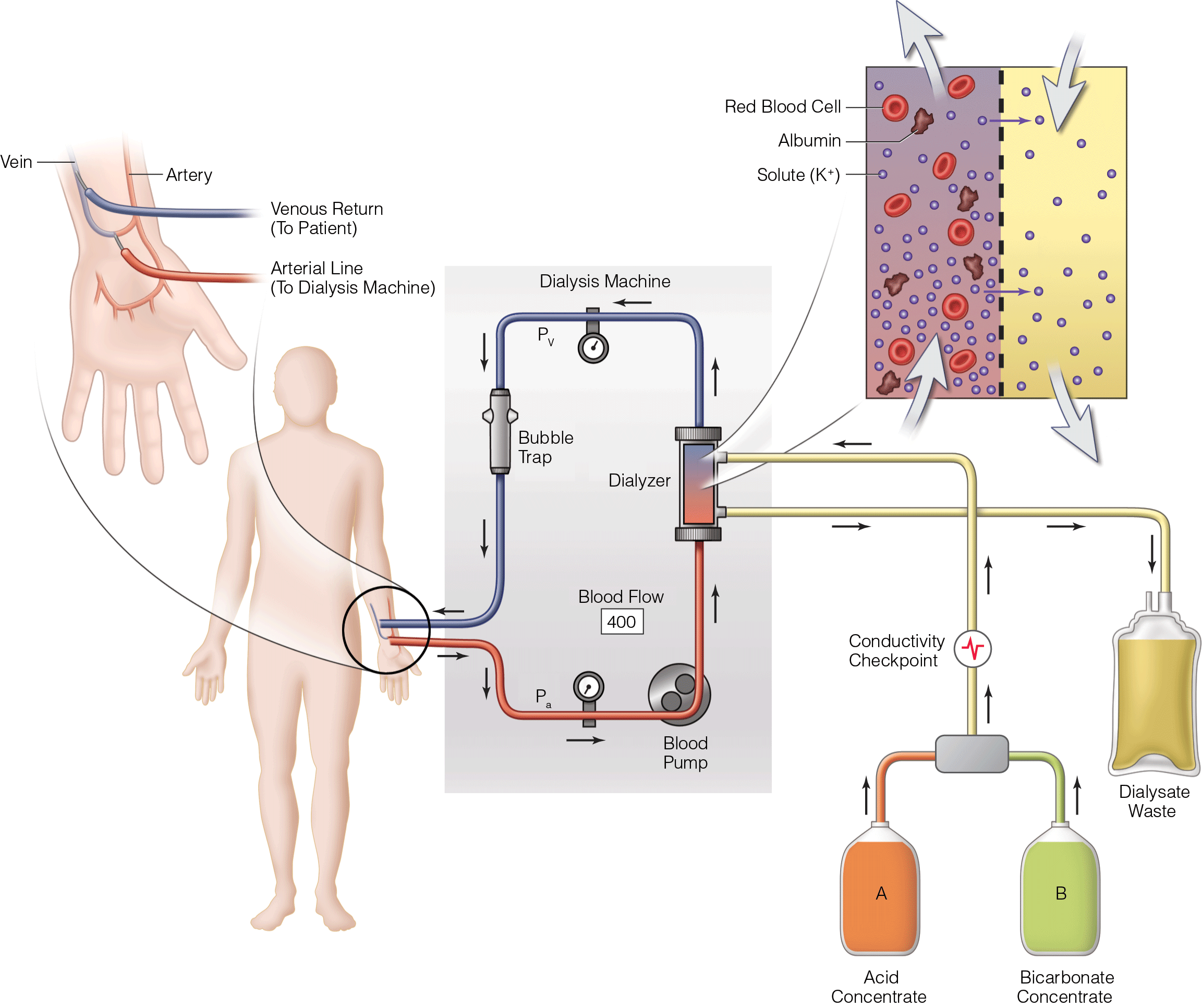
Acute Kidney Injury in Critically Ill Patients
- Sepsis as a prevalent syndrome and precipitant for AKI in the surgical ICU population
- Biomarkers as tool to facilitate early diagnosis of AKI
- AKI severity and duration as determinants of poor long-term outcome
- AKI severity as stratification tool for those that may benefit from closer monitoring

Acute Kidney Injury in Critically Ill Patients
- Sepsis as a prevalent syndrome and precipitant for AKI in the surgical ICU population
- Biomarkers as tool to facilitate early diagnosis of AKI
- AKI severity and duration as determinants of poor long-term outcome
- AKI severity as stratification tool for those that may benefit from closer monitoring
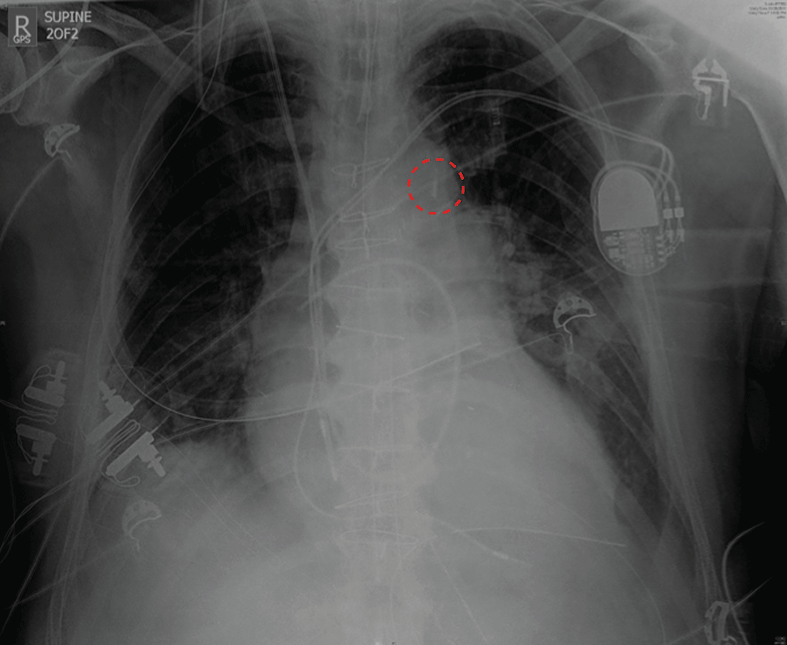
- Intra-aortic balloon counterpulsation in cardiac surgery
- Short-term percutaneous and surgically placed devices for circulatory support
- Long-term continuous-flow left ventricular assist devices in the treatment of chronic heart failure
- Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) for the treatment of acute heart failure and cardiogenic shock
- ECMO applications in the setting of advanced cardiac life support, or extracorporeal life support

- Intra-aortic balloon counterpulsation in cardiac surgery
- Short-term percutaneous and surgically placed devices for circulatory support
- Long-term continuous-flow left ventricular assist devices in the treatment of chronic heart failure
- Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) for the treatment of acute heart failure and cardiogenic shock
- ECMO applications in the setting of advanced cardiac life support, or extracorporeal life support

- Intra-aortic balloon counterpulsation in cardiac surgery
- Short-term percutaneous and surgically placed devices for circulatory support
- Long-term continuous-flow left ventricular assist devices in the treatment of chronic heart failure
- Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) for the treatment of acute heart failure and cardiogenic shock
- ECMO applications in the setting of advanced cardiac life support, or extracorporeal life support
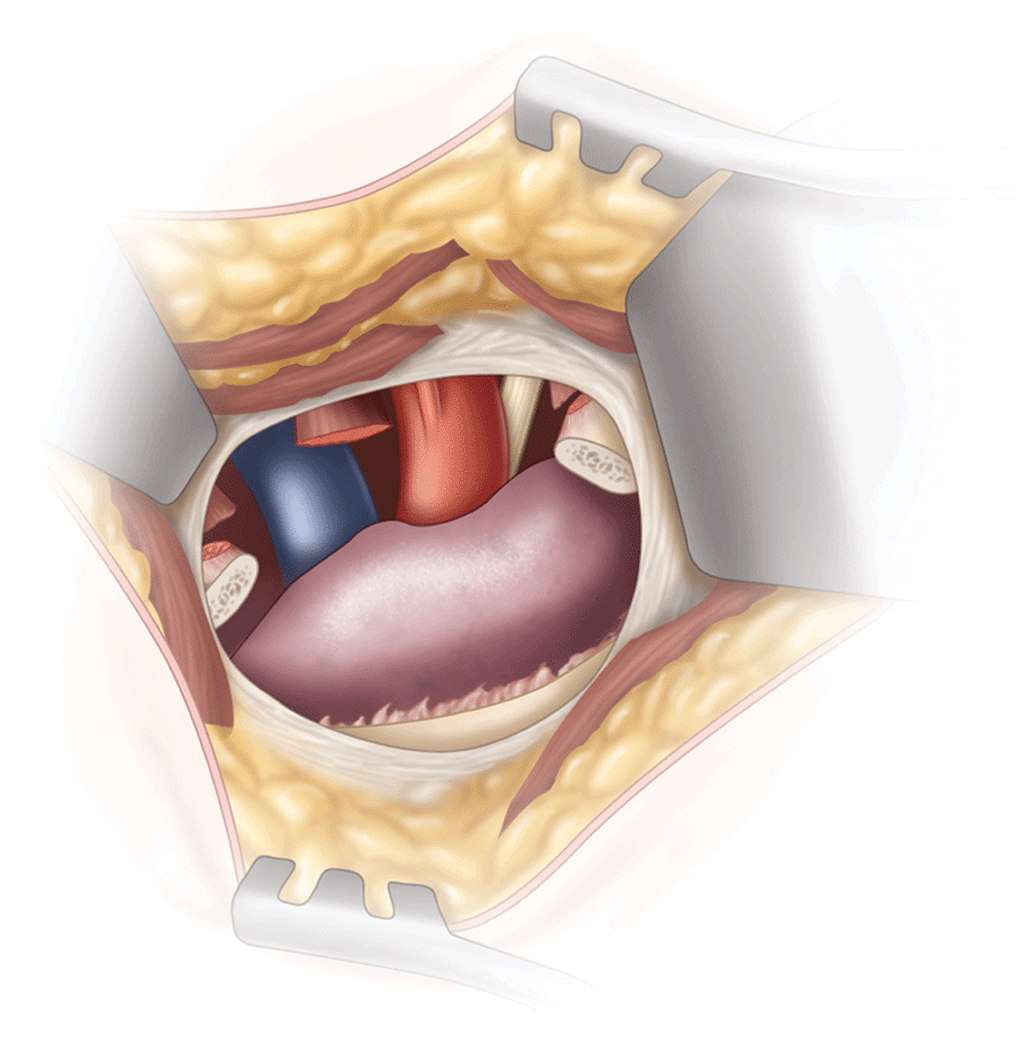
- TOS is divided into three distinct subtypes: neurogenic, venous, and arterial. Symptoms are produced relative to which of the neurovascular structures is compressed in the thoracic outlet.
- Recent data on long-term results after thoracic outlet decompression for neurogenic thoracic outlet syndrome
- New video of transaxillary first rib resection and anterior scalenectomy from the surgeon’s perspective


