Ultrasound: Critical Care Ultrasonography
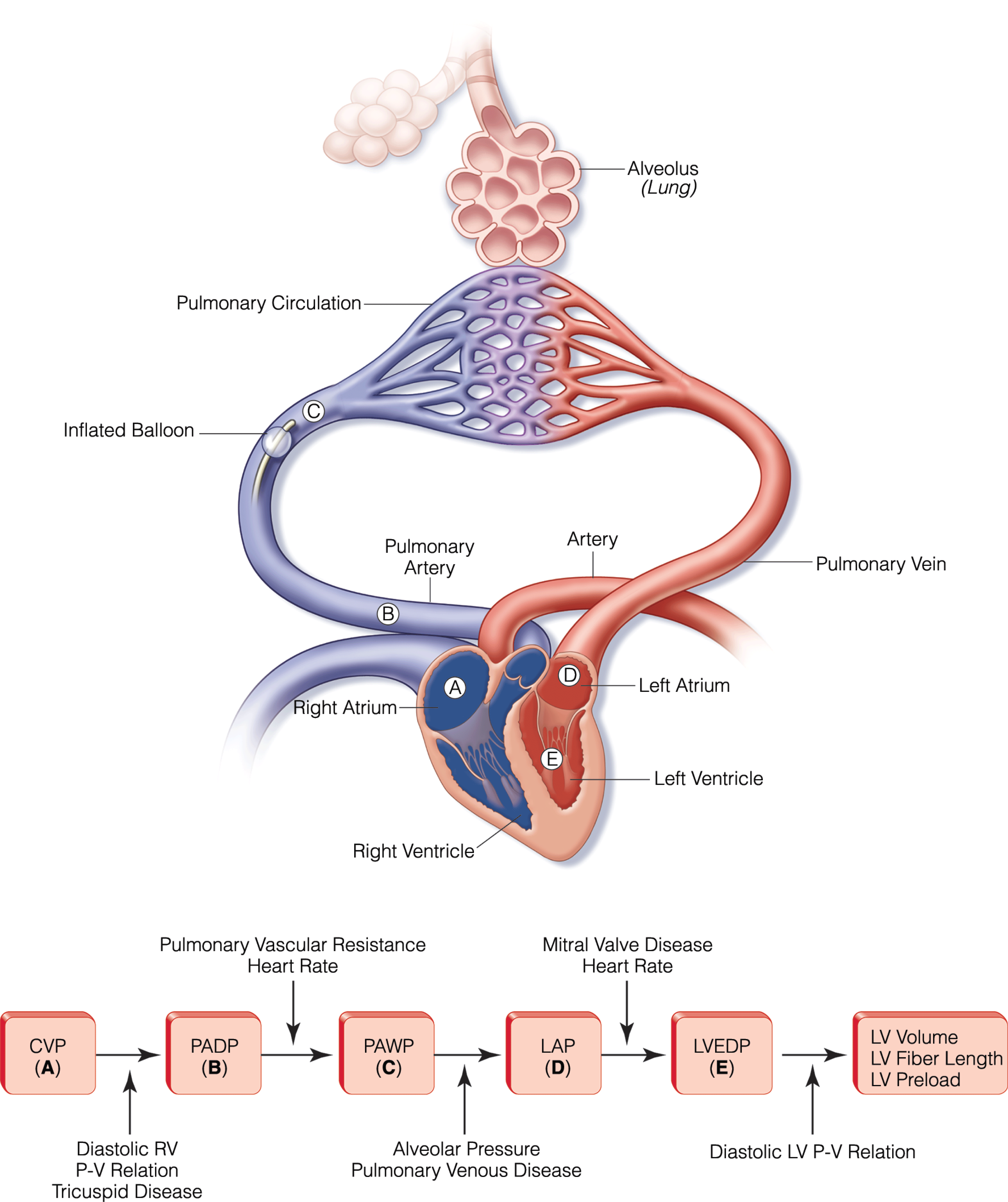
- Focused bedside echocardiographic examination, including assessment of ventricular function, volume status, and various cardiac pathologies
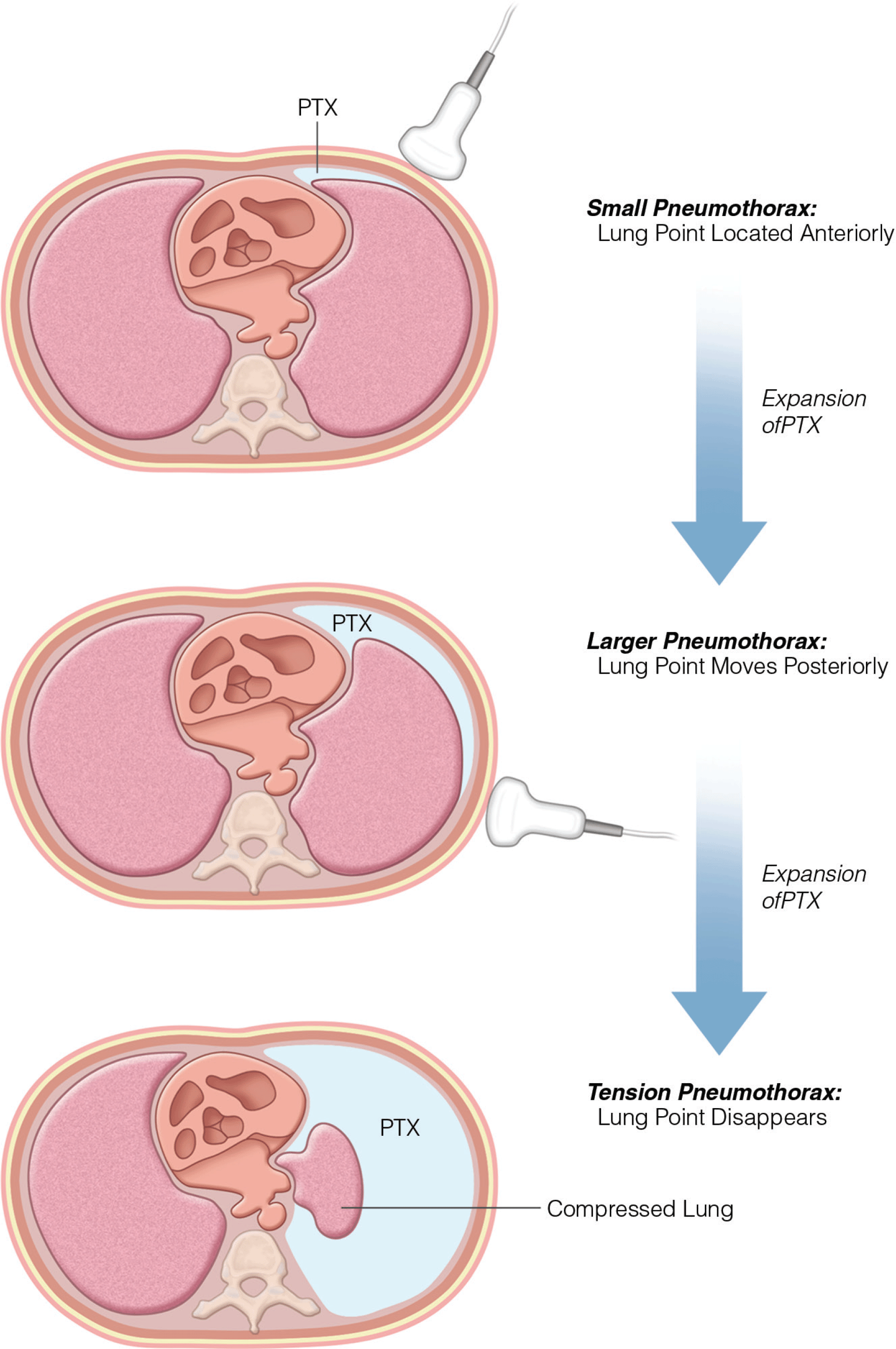
- Pulmonary ultrasonography, including pleural effusions and thoracentesis, assessment of lung parenchyma, and pneumothorax
- Abdominal ultrasonography, including focused assessment with sonography in trauma examination, paracentesis, and pneumoperitoneum
- Ultrasound-guided arterial and venous line placement