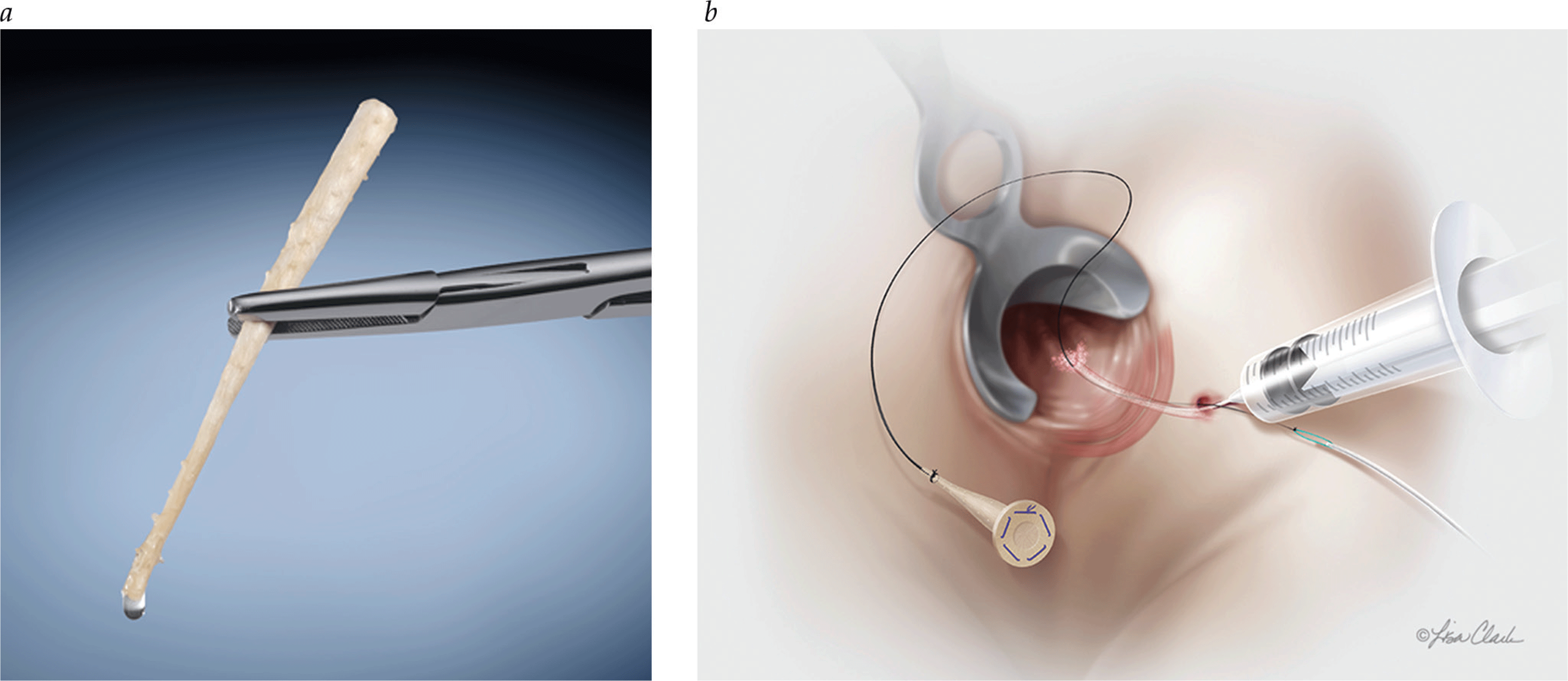
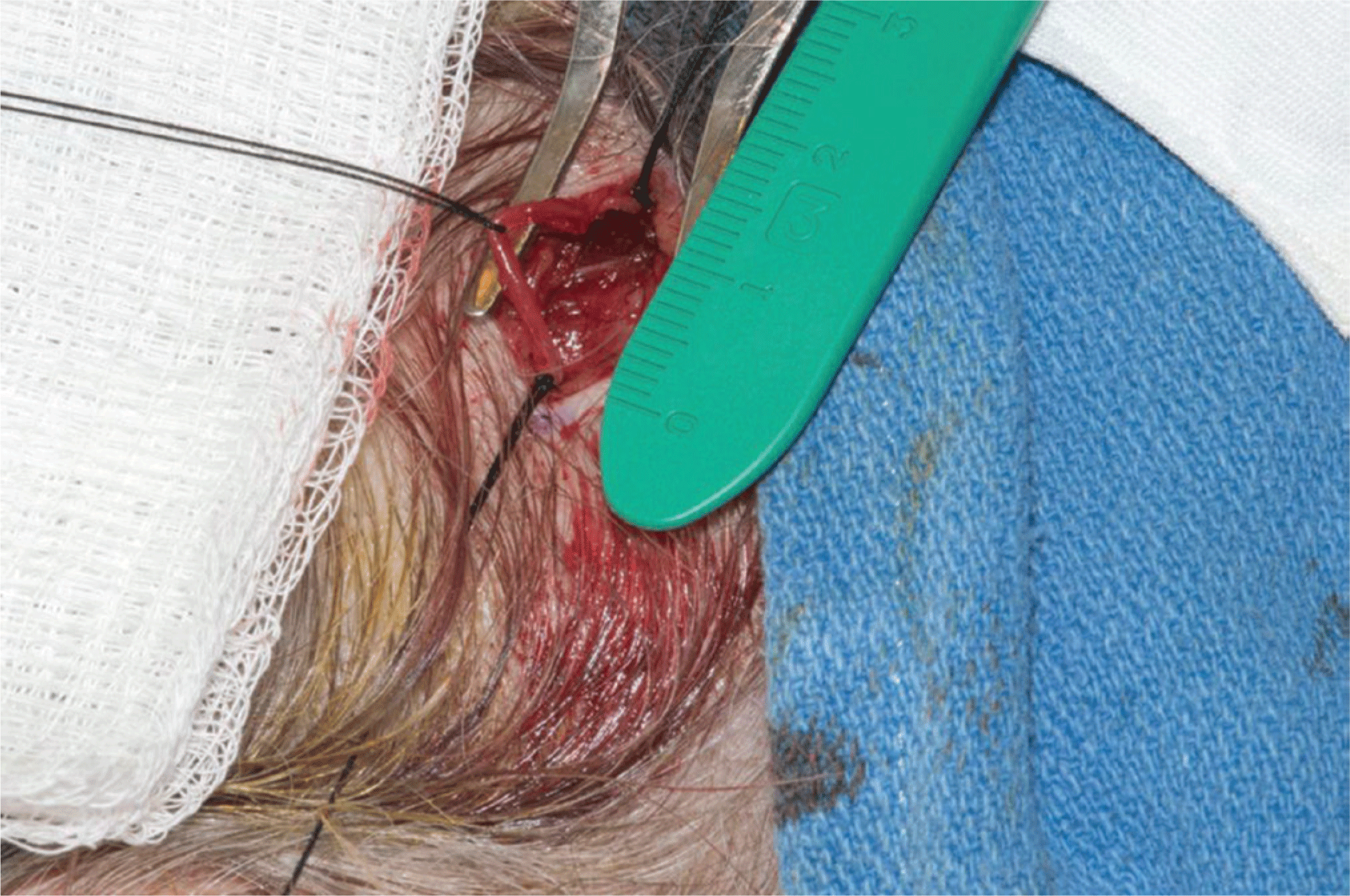
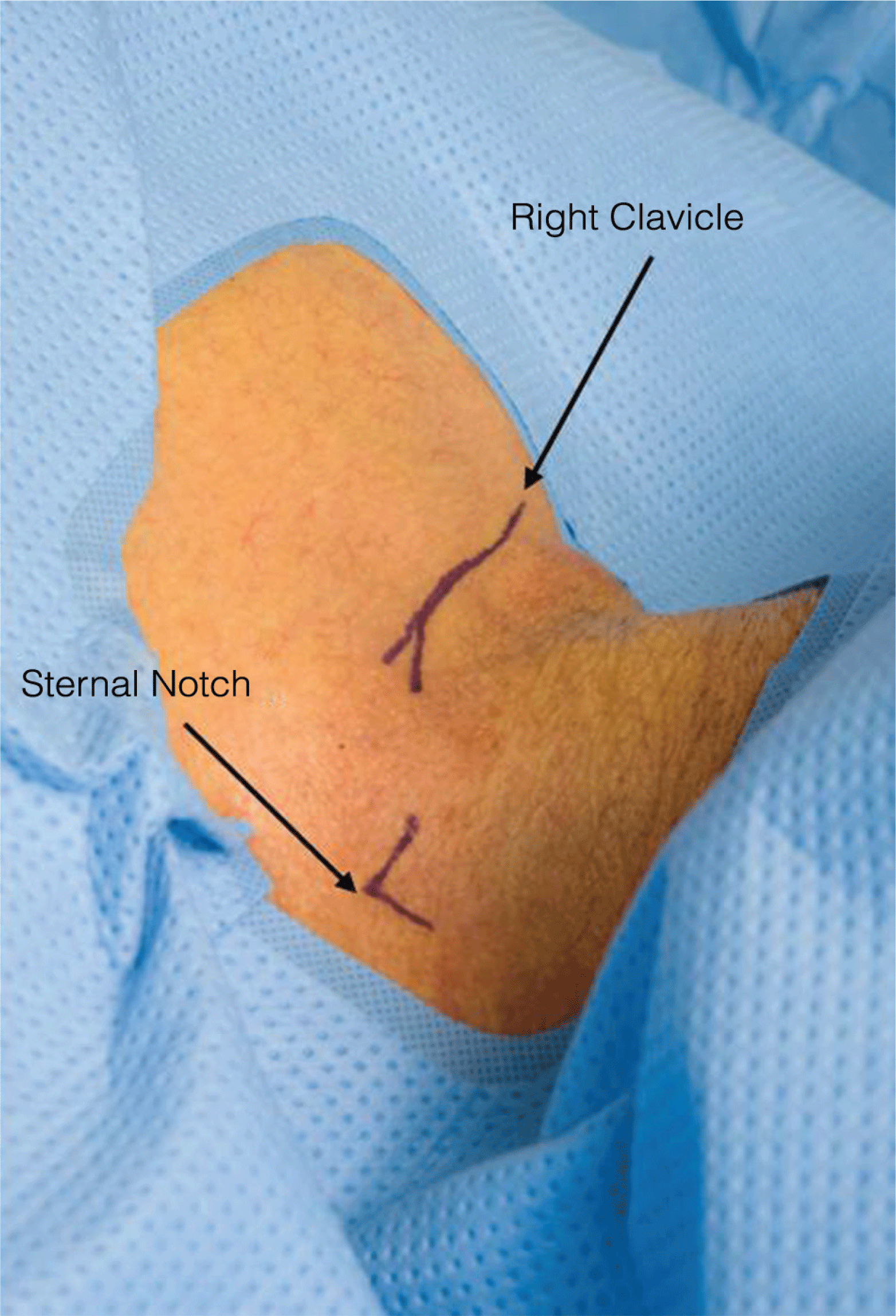
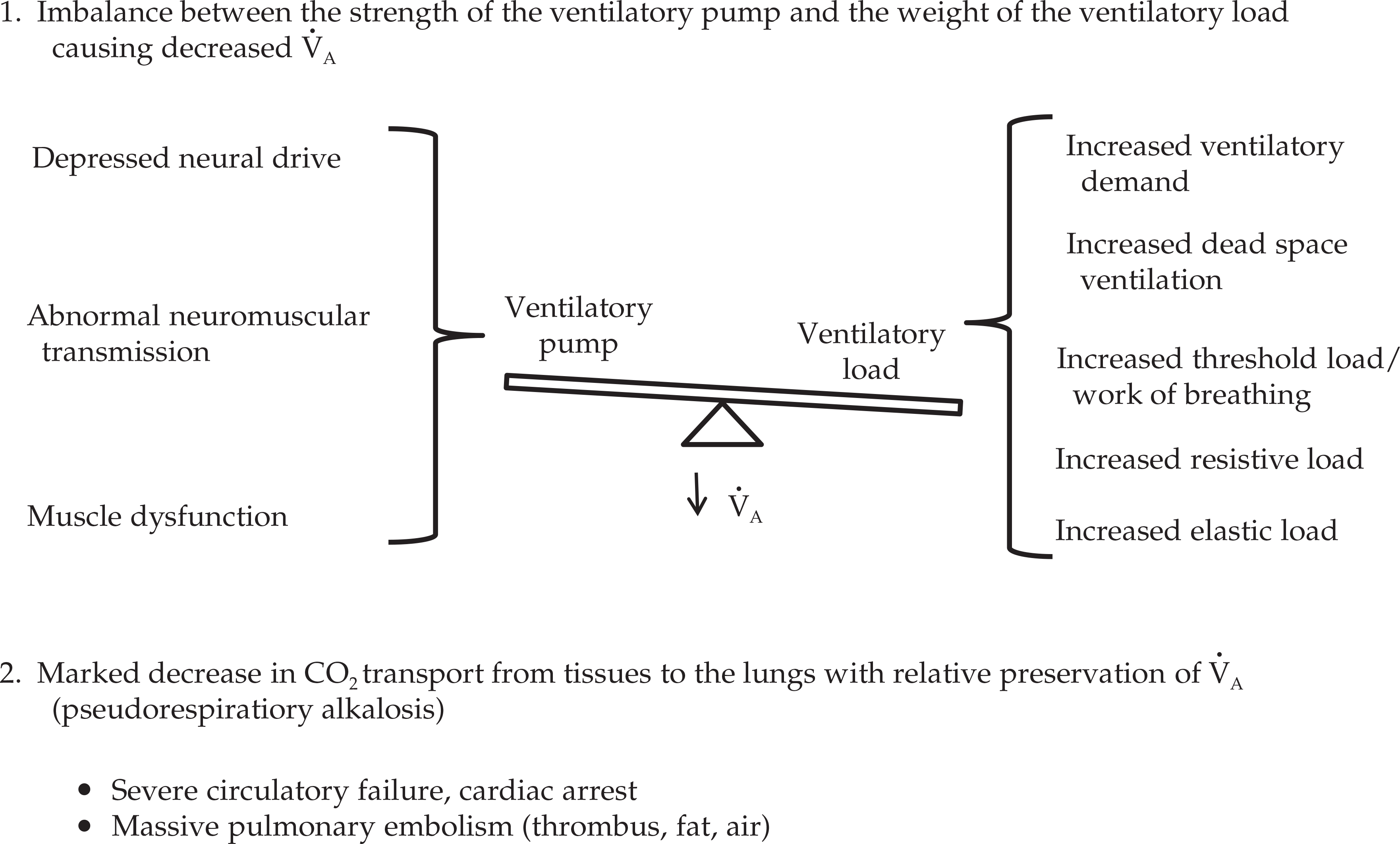
Gastroenterology \ Inflammatory Bowel Diseases: Complex Perianal Fistulas
- Updated illustrations reflect perianal anatomy in greater detail
- Detailed illustrations accompany descriptions of mucosal advancement flap, ligation of fistula tract, and episioproctotomy techniques
- Additional discussion focuses on management of anovaginal fistulas