Parenchymal Kidney Disease: Paraproteinemia and Deposition Diseases
- Enhanced understanding of ALECT2 amyloidosis
- Best practice for typing of amyloidosis
- Evidence for distinguising among diseases with organized deposits
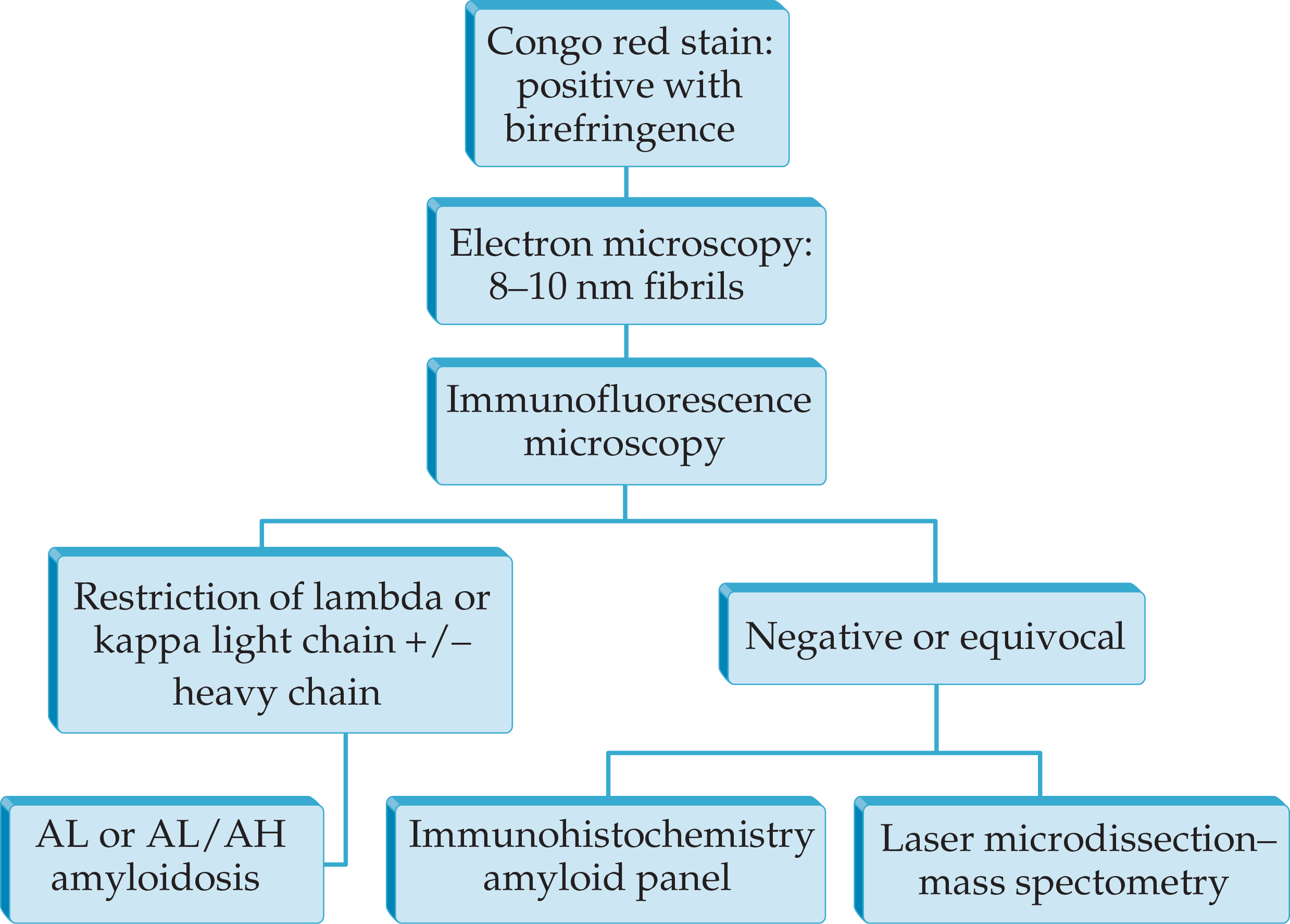
Parenchymal Kidney Disease: Paraproteinemia and Deposition Diseases
Pain Related Disease States: Lumbar Disk Herniation
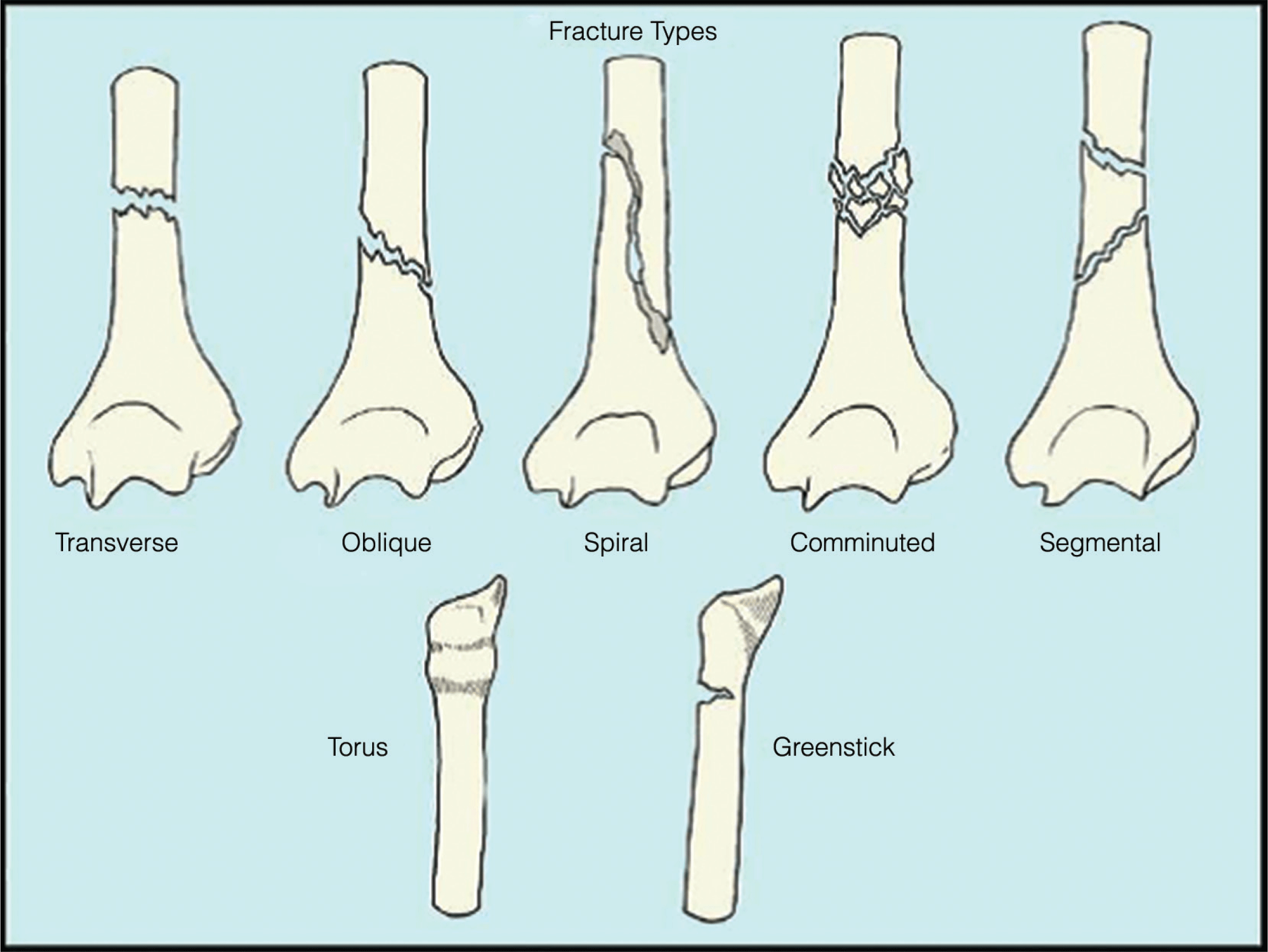
Trauma: Management of Extremity Fractures and Complications
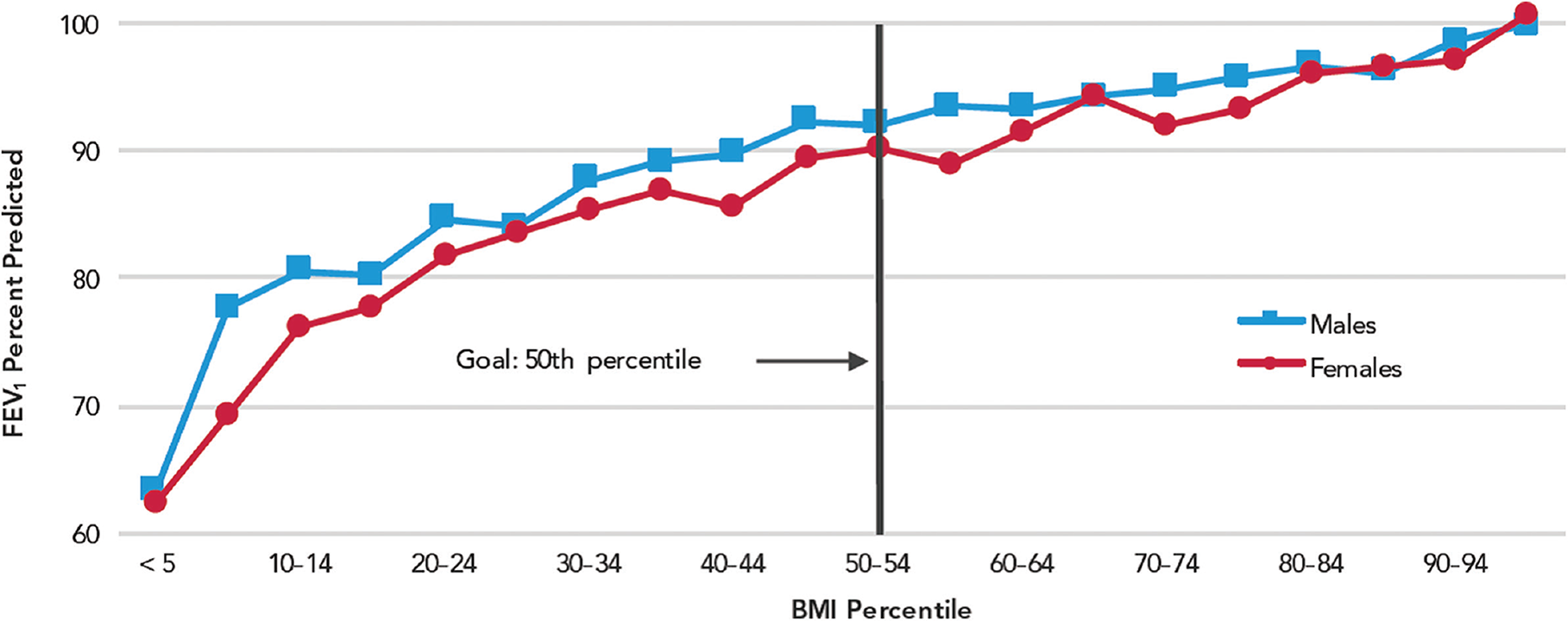
Pediatrics: Cystic Fibrosis in Childhood and Adolescence
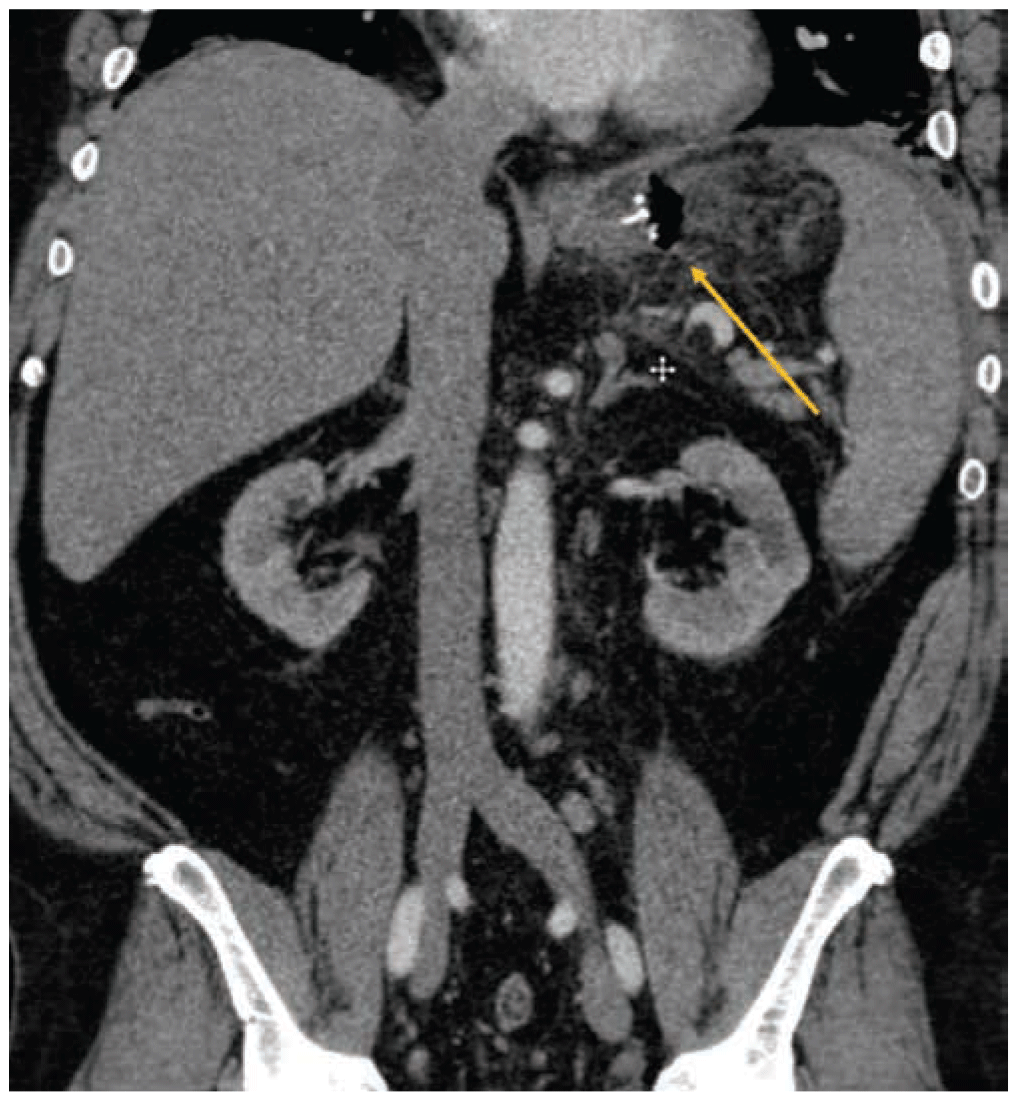
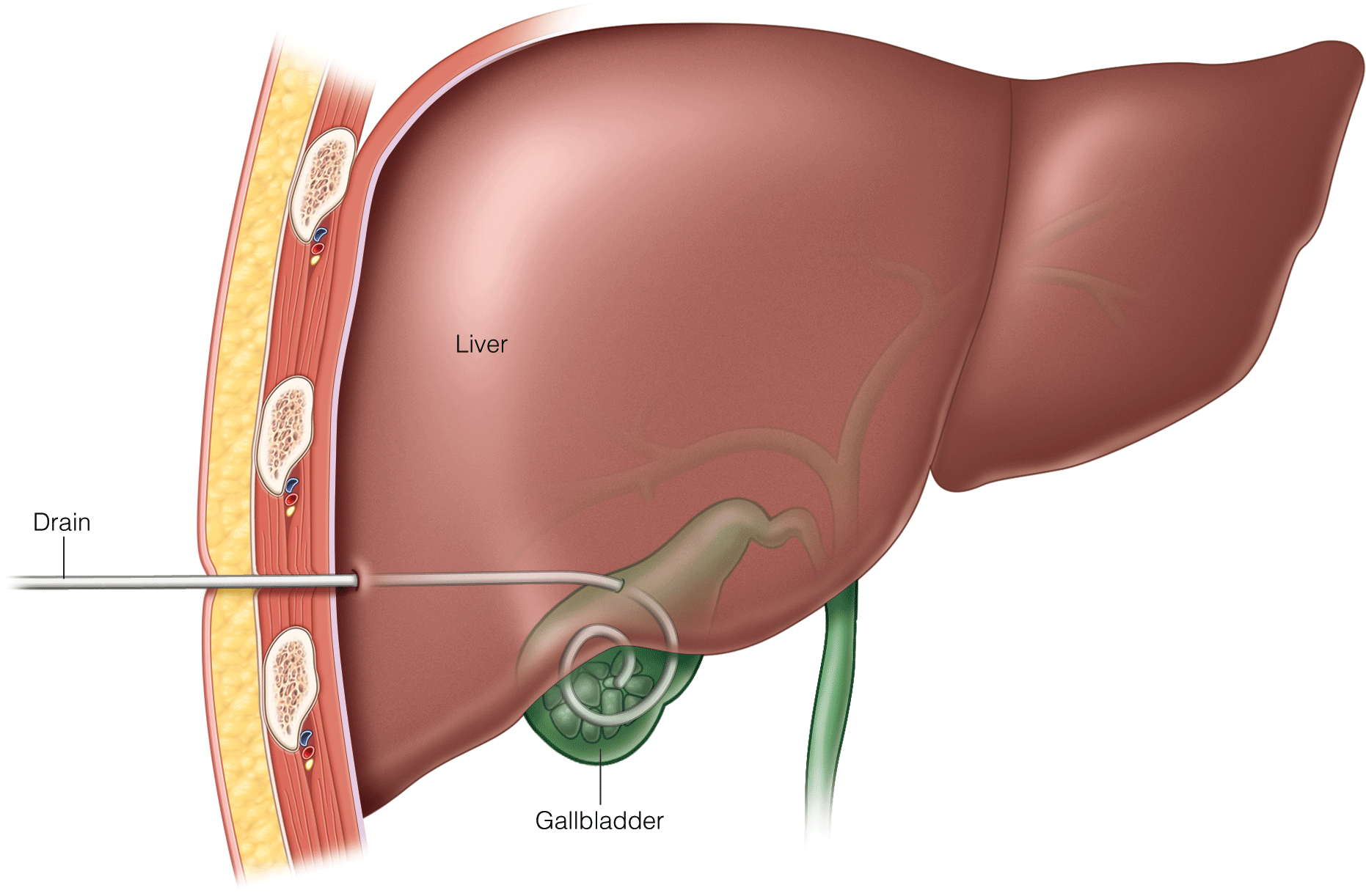
Complications Following Bariatric Surgery
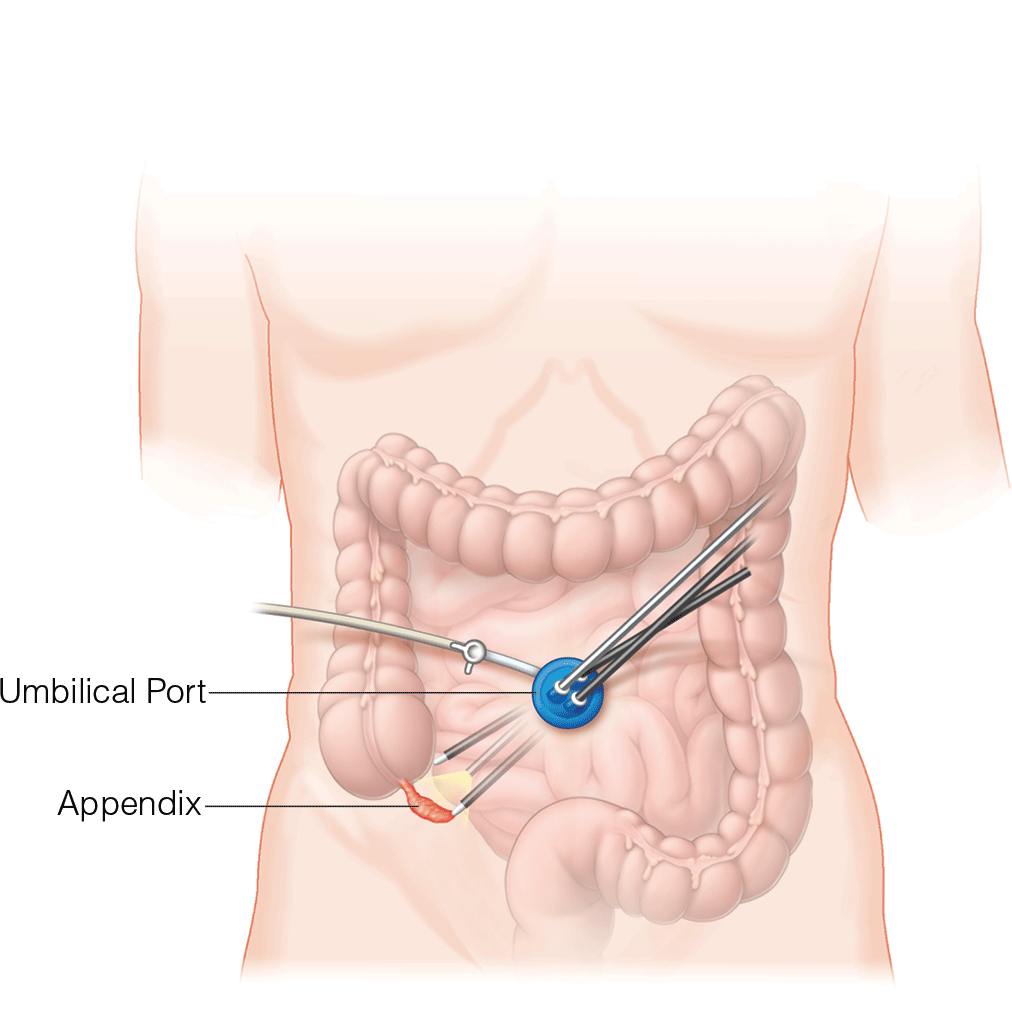
Gastroenterology \ Gastroenterology Miscellaneous: Appendectomy
Acute appendicitis remains a therapeutic challenge during active pregnancy. Both laparascopic and open approaches can be considered; the techniques remain largely the same, with a few caveats. Fetal monitoring may be performed using a transvaginal or left lateral abdominal wall approach. For open appendectomy, ultrasonography and magnetic resonance imaging may provide direction for the incision. Laparascopic appendectomies should be approached with a open trocar placement in the midline, with direct visualization. Late-term pregnancies may require alternative approaches in the subcostal region, and the patient may be rolled with their left side down to facilitate exposure of the appendix and relieve pressure on the inferior vena cava.
Infectious Diseases: Infections Due to Candida, Cryptococcus, Other Yeasts, and Pneumocystis