- The incidence of Paget disease (PD) associated with an underlying invasive and/or noninvasive cancer is decreasing, whereas the incidence of PD identified without an associated underlying cancer has remained stable.
- Breast MRI is an effective method to screen the breast when PD is identified in the setting of an otherwise negative mammogram.
- Mastectomy has been the historical gold standard for treatment of PD; however, the use of breast-conserving surgery is on the rise and appropriate in many cases.
- Sentinel node biopsy is feasible in patients with PD and should be used in those presenting with PD and an underlying invasive carcinoma. Its use in patients with PD with ductal carcinoma in situ or PD alone is controversial.
Latest Updates
Skin Cancers: Basal Cell Carcinoma: Epidemiology, Risk Factors, and Treatment Options
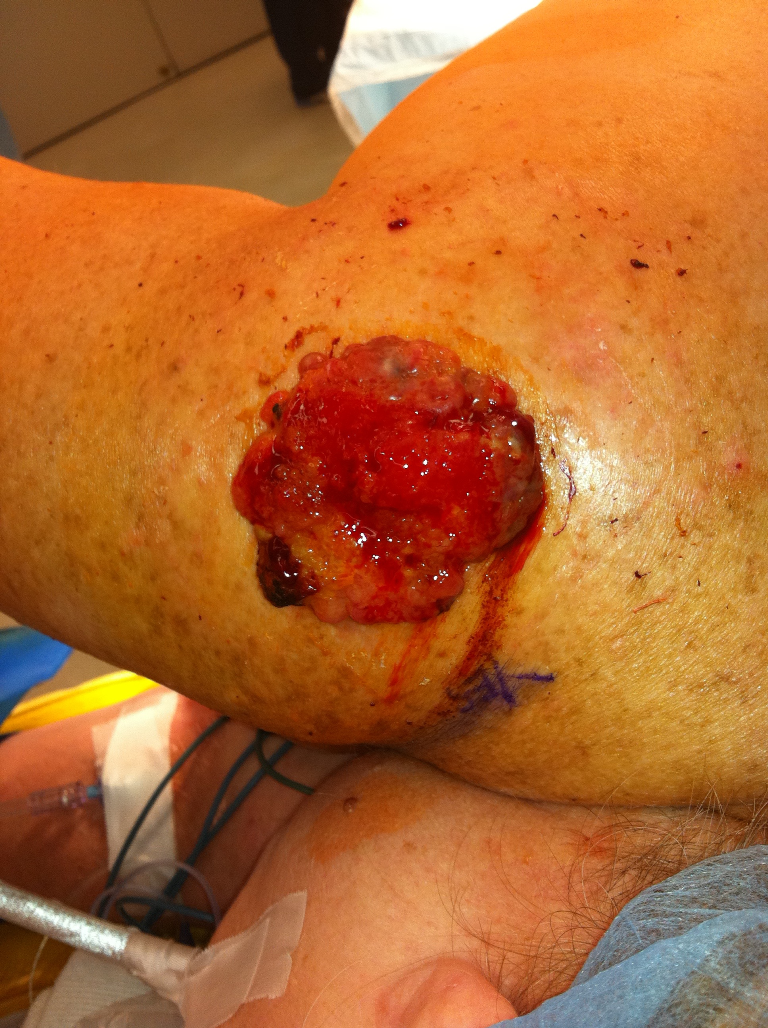
- Risk factors for patients at risk for developing basal cell skin cancers (BCCs) include exposure to UV solar radiation, long-term immunosuppression, exposure to ionizing radiation, and certain genetic disorders.
- Treatment modalities can be divided into surgical and nonsurgical therapies, although surgical therapy is generally the mainstay of treatment.
- Superficial therapies, such as topical imiquimod or 5-fluorouracil, photodynamic therapy, or cryotherapy, may be effective for anatomically challenging locations where surgery or radiation is contraindicated, but the cure rates of these approaches are lower compared with surgery.
- Recent FDA-approved hedgehog pathway inhibitors include vismodegib and sonidegib for patients who have exhausted surgical and radiation options for treating advanced BCC.
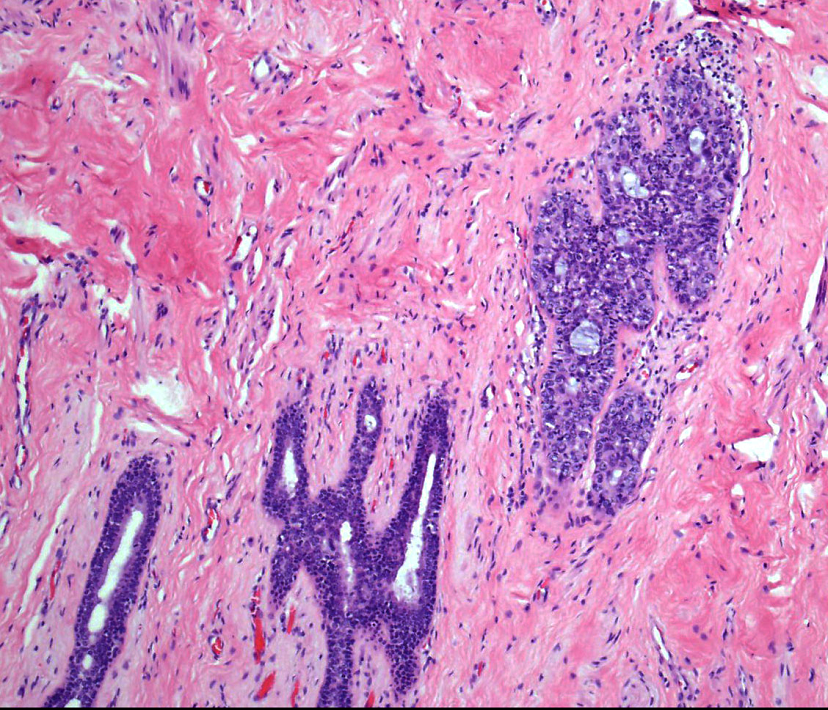
- Atypical ductal hyperplasia diagnosed on core biopsy requires excision because of the risk of cancer present at the site, but expert histologic review may be helpful because of the risk of misdiagnosis.
- Pleomorphic lobular carcinoma in situ should be treated as ductal carcinoma in situ based on its behavior and greater risk of associated invasive disease.
- Excision of pseudoangiomatous stromal hyperplasia has been questioned because of limited data suggesting that imaging discordance and the presence of suspicious clinical findings are the primary risk factors for associated cancer, and their absence may permit safe observation.

Breast Cancers: High-Risk Breast Lesions
- Atypical ductal hyperplasia diagnosed on core biopsy requires excision because of the risk of cancer present at the site, but expert histologic review may be helpful because of the risk of misdiagnosis.
- Pleomorphic lobular carcinoma in situ should be treated as ductal carcinoma in situ based on its behavior and greater risk of associated invasive disease.
- Excision of pseudoangiomatous stromal hyperplasia has been questioned because of limited data suggesting that imaging discordance and the presence of suspicious clinical findings are the primary risk factors for associated cancer, and their absence may permit safe observation.

Basal Cell Carcinoma: Epidemiology, Risk Factors, and Treatment Options
- Risk factors for patients at risk for developing basal cell skin cancers (BCCs) include exposure to UV solar radiation, long-term immunosuppression, exposure to ionizing radiation, and certain genetic disorders.
- Treatment modalities can be divided into surgical and nonsurgical therapies, although surgical therapy is generally the mainstay of treatment.
- Superficial therapies, such as topical imiquimod or 5-fluorouracil, photodynamic therapy, or cryotherapy, may be effective for anatomically challenging locations where surgery or radiation is contraindicated, but the cure rates of these approaches are lower compared with surgery.
- Recent FDA-approved hedgehog pathway inhibitors include vismodegib and sonidegib for patients who have exhausted surgical and radiation options for treating advanced BCC.
Gastrointestinal: Upper Gastrointestinal Bleeding
- Several clinical prediction scores have been developed to risk-stratify patients presenting with upper gastrointestinal bleeding (UGIB) and can help guide the sequence of diagnostic tests and subsequent management. The two most commonly used are the Glasgow-Blatchford score and Rockall score. These scoring systems are designed to aid in the identification of patients who will require acute interventions and determine the risk of rebleeding and mortality.
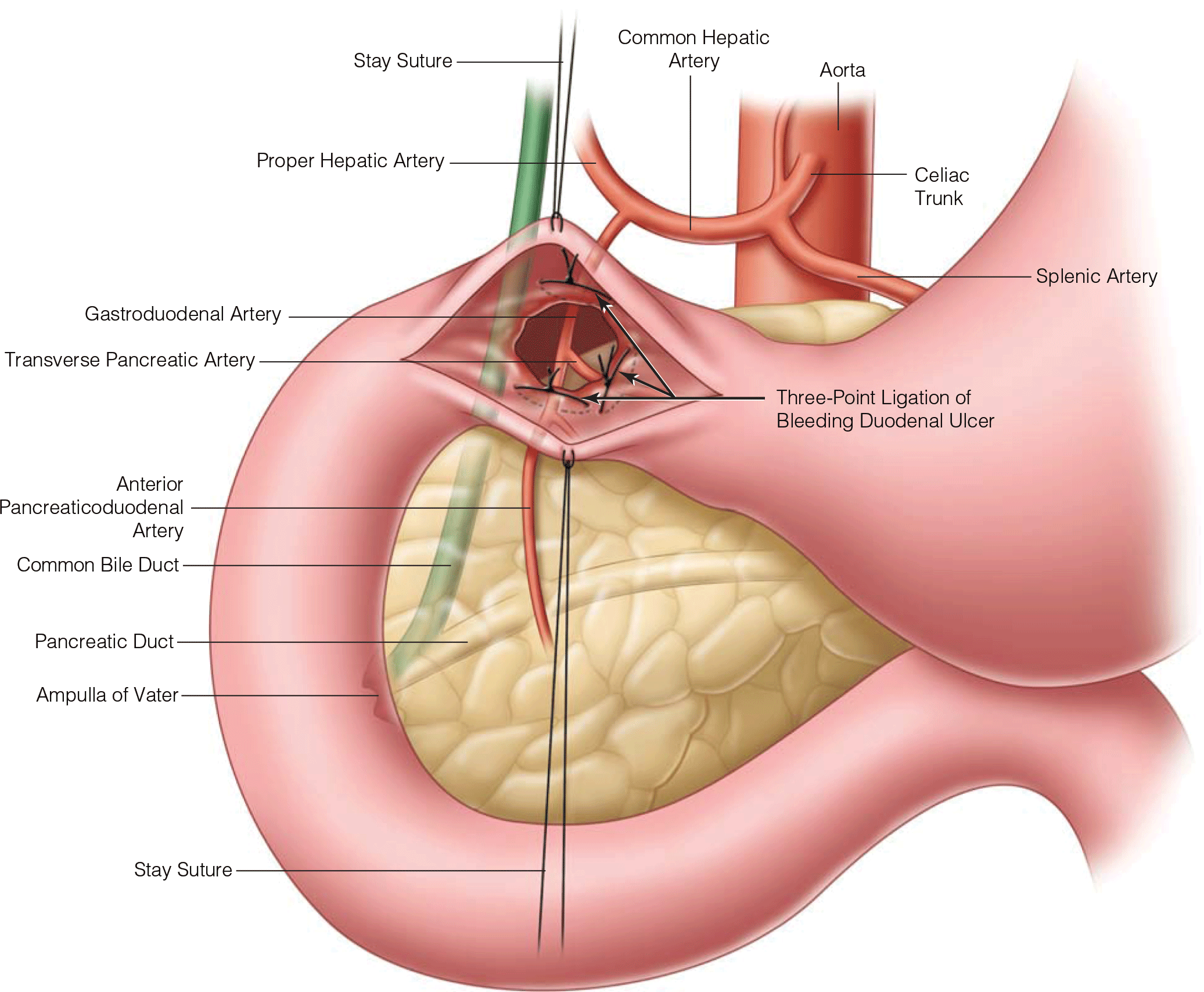
- Endoscopic intervention is beneficial in high-risk patients with UGIB, reducing the rate of rebleeding, the need for surgical intervention, and mortality. Recent advances in the use of combination therapies and newer mechanical means of hemostasis have increased the success of endoscopic management.
- Contrast-enhanced, multiphase computed tomography (CT) techniques have improved dramatically over the last decade. CT serves as an excellent complementary test to endoscopic techniques in the management of the hemodynamically stable patient.
- Transcatheter angiographic embolization is an attractive alternative to surgical intervention in select patients. Advances in catheter-based delivery systems have increased the success rate of angiographic embolization, particularly in patients who have a failed second attempt at endoscopic hemostasis.
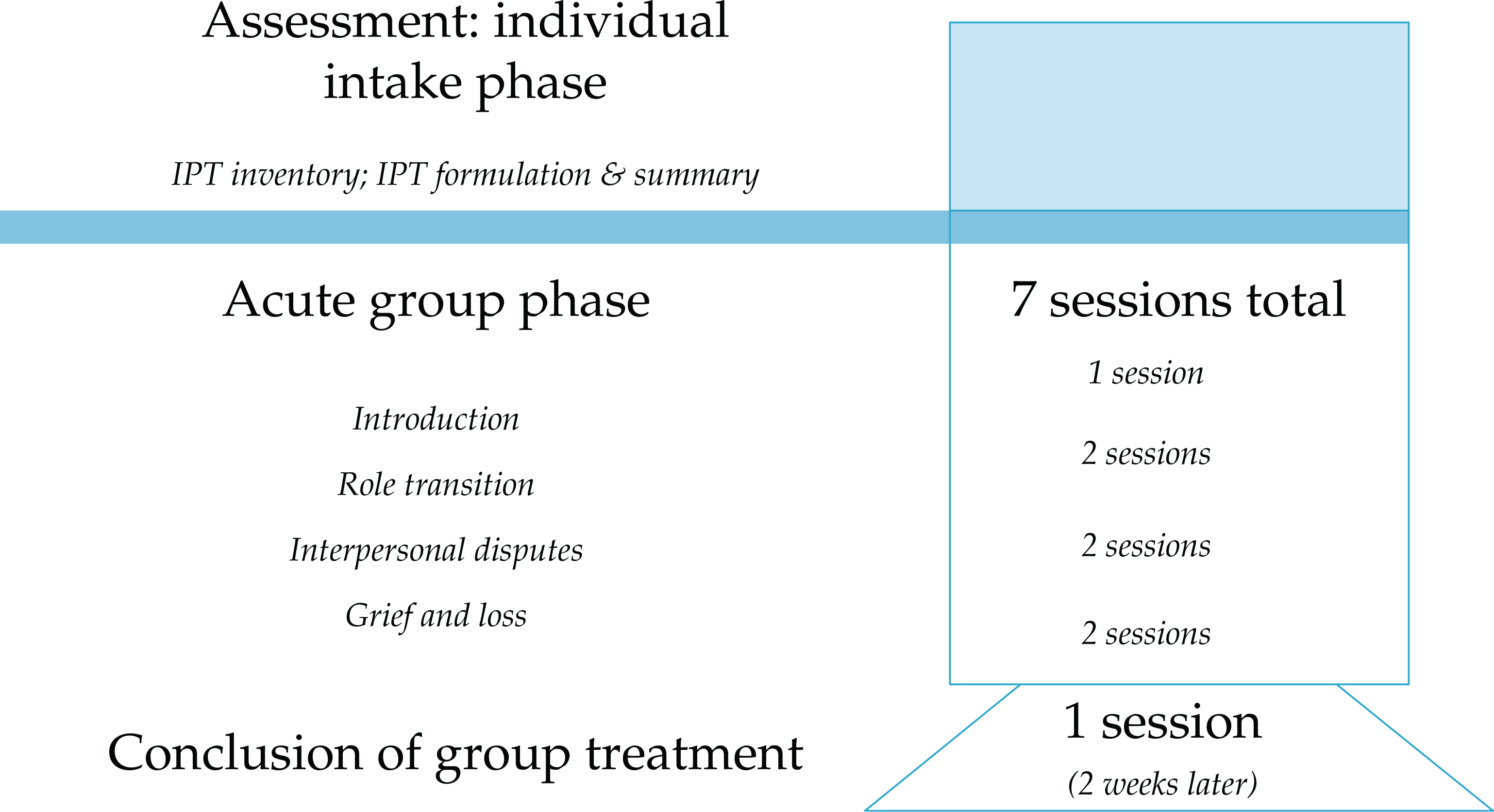
Psychotherapy: Interpersonal Psychotherapy
- New clinical tools have increased fidelity to IPT and enhanced its clinical application
- IPT has been shown to be effective with PTSD
- Dissemination of IPT is greatly increasing
- Training protocols and guidelines for IPT have been established
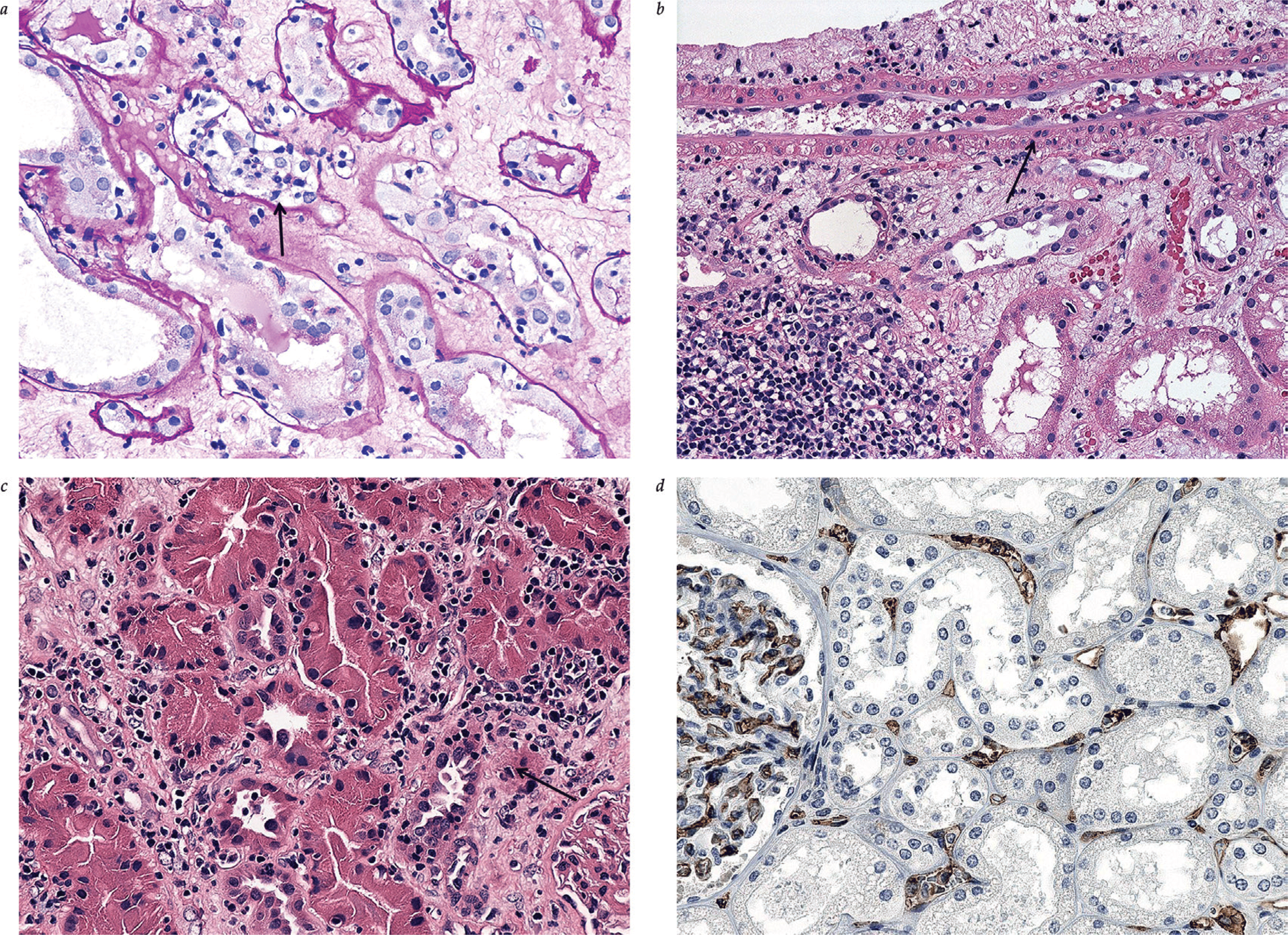
Nephrology: Acute Graft Dysfunction
- Differential diagnosis of acute allograft dysfunction
- Biomarker use in the evaluation of acute graft dysfunction
- Treatment options for acute allograft rejection


