Reconstruction of the Thumb after Traumatic Tissue Loss
- Microsurgical toe transfer in children after traumatic amputation
- Single stage thumb reconstruction
- Cultural considerations in thumb reconstruction
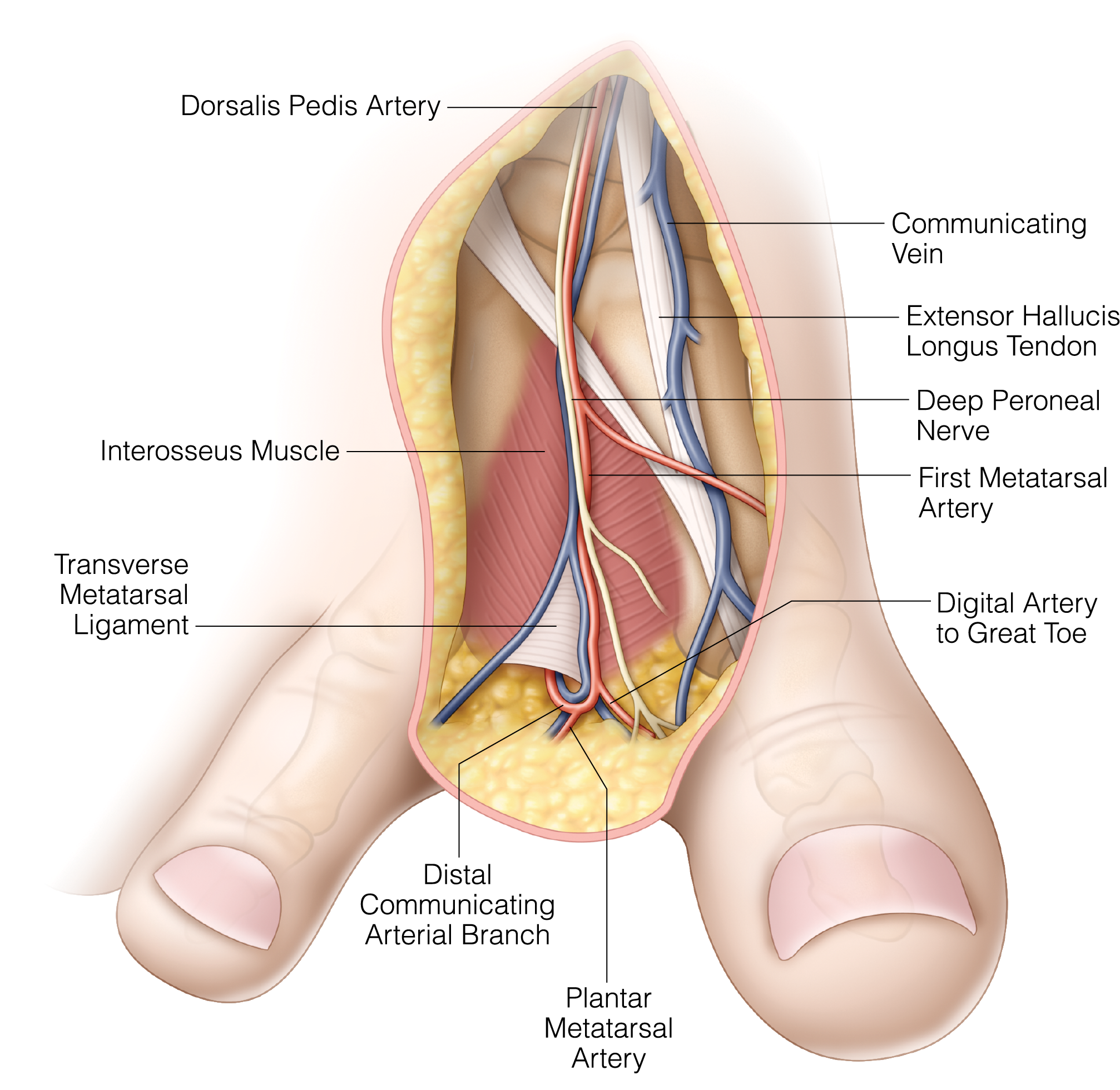
Reconstruction of the Thumb after Traumatic Tissue Loss
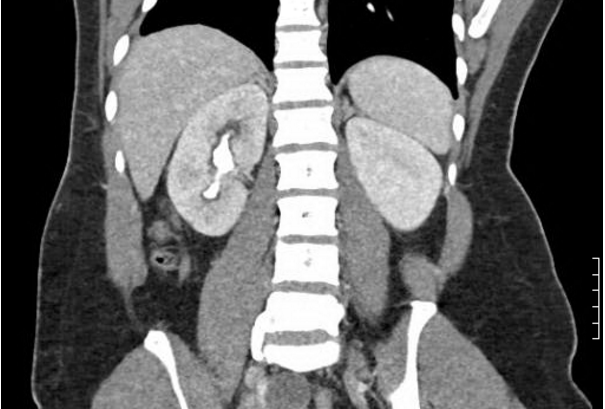
Pathophysiology and Treatment of Infection Stones
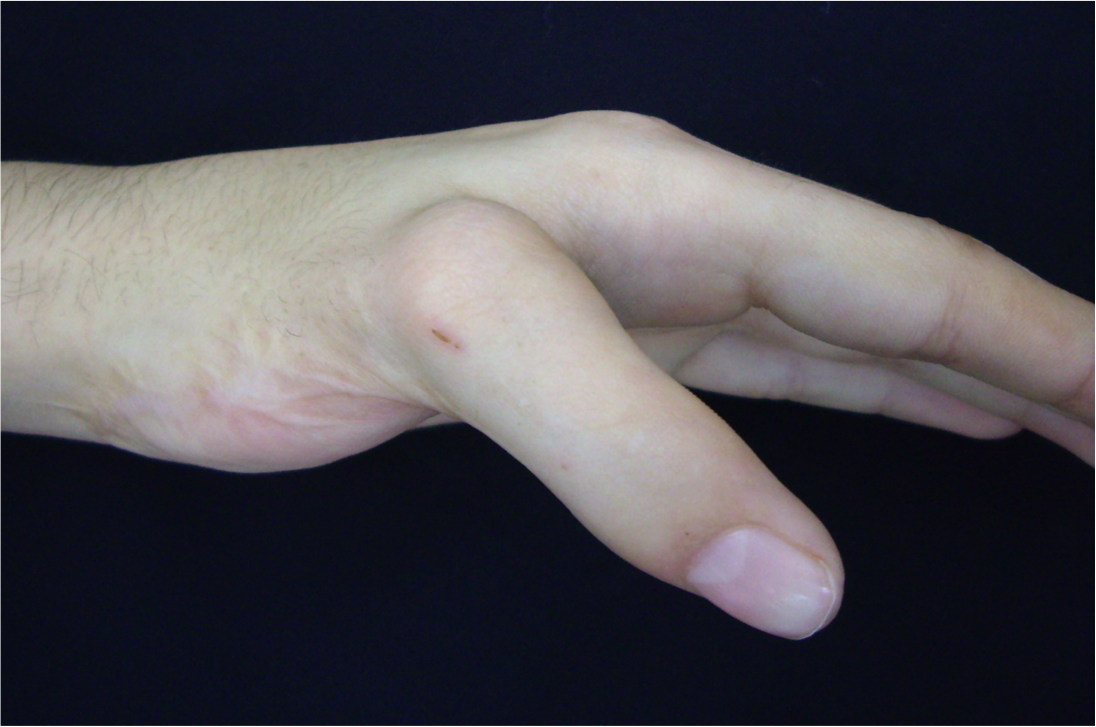
Common Congenital Hand Differences
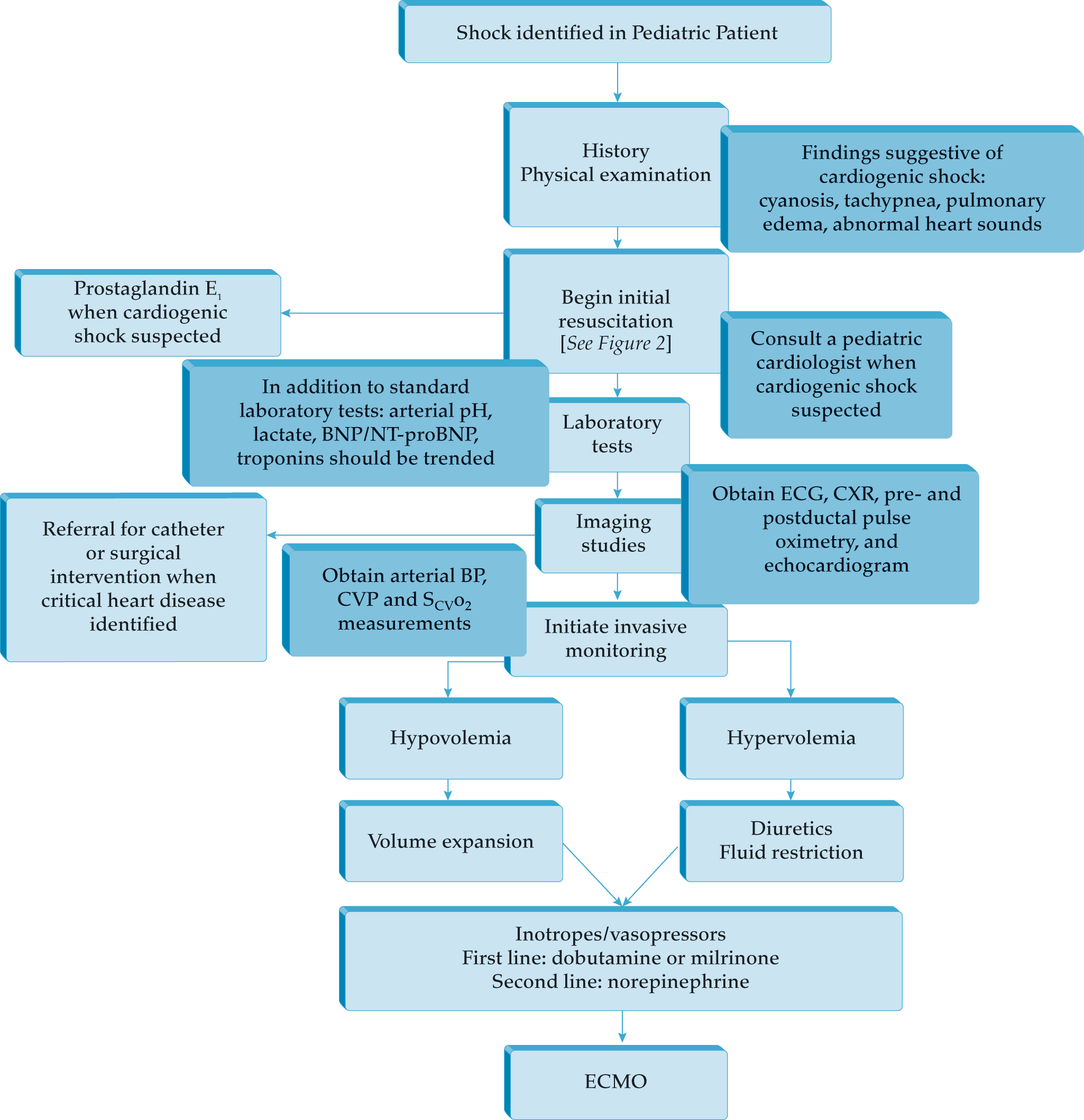
Management of Shock in Infants and Children
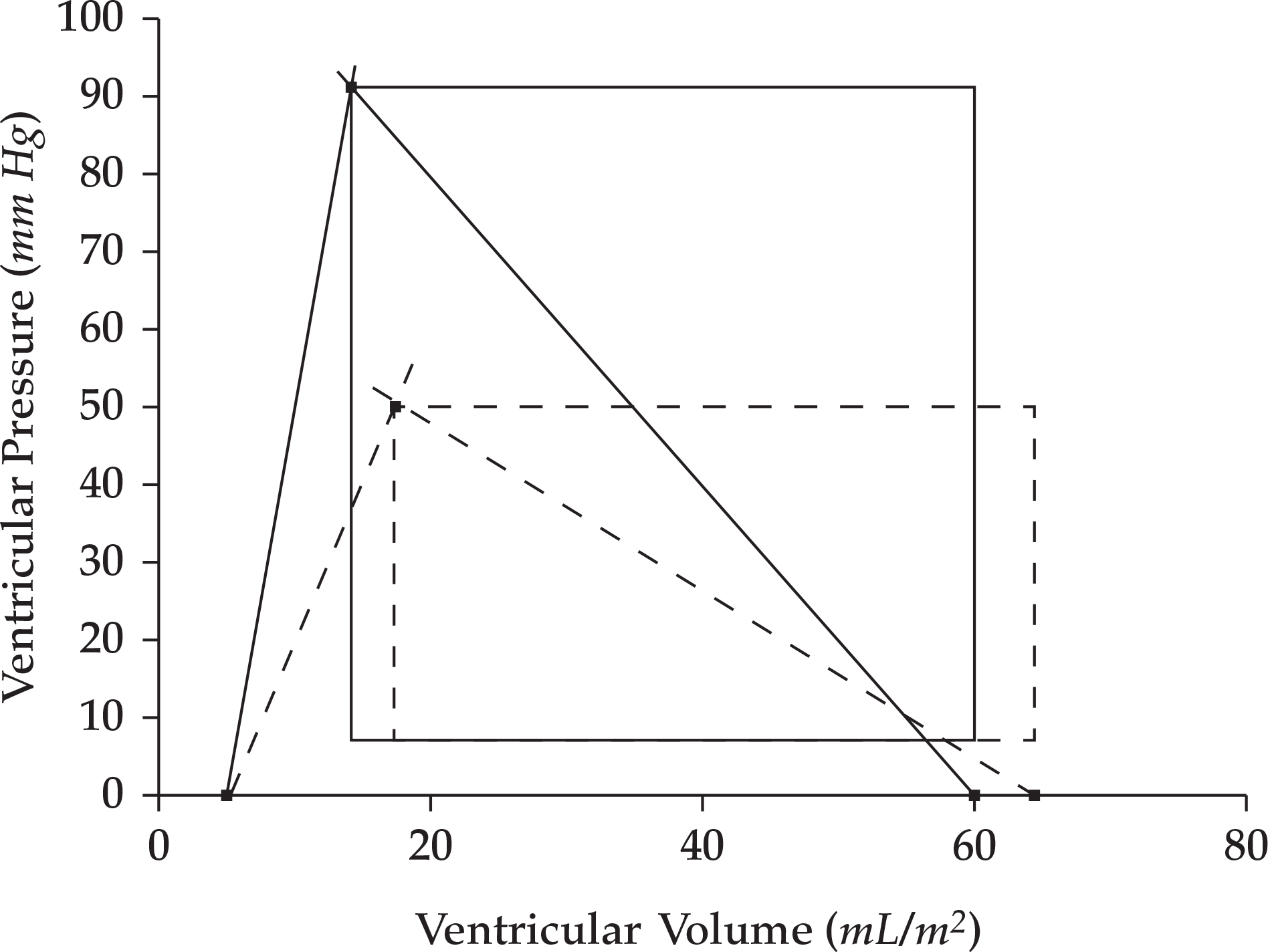
Invasive Hemodynamic Monitoring in the Intensive Care Unit
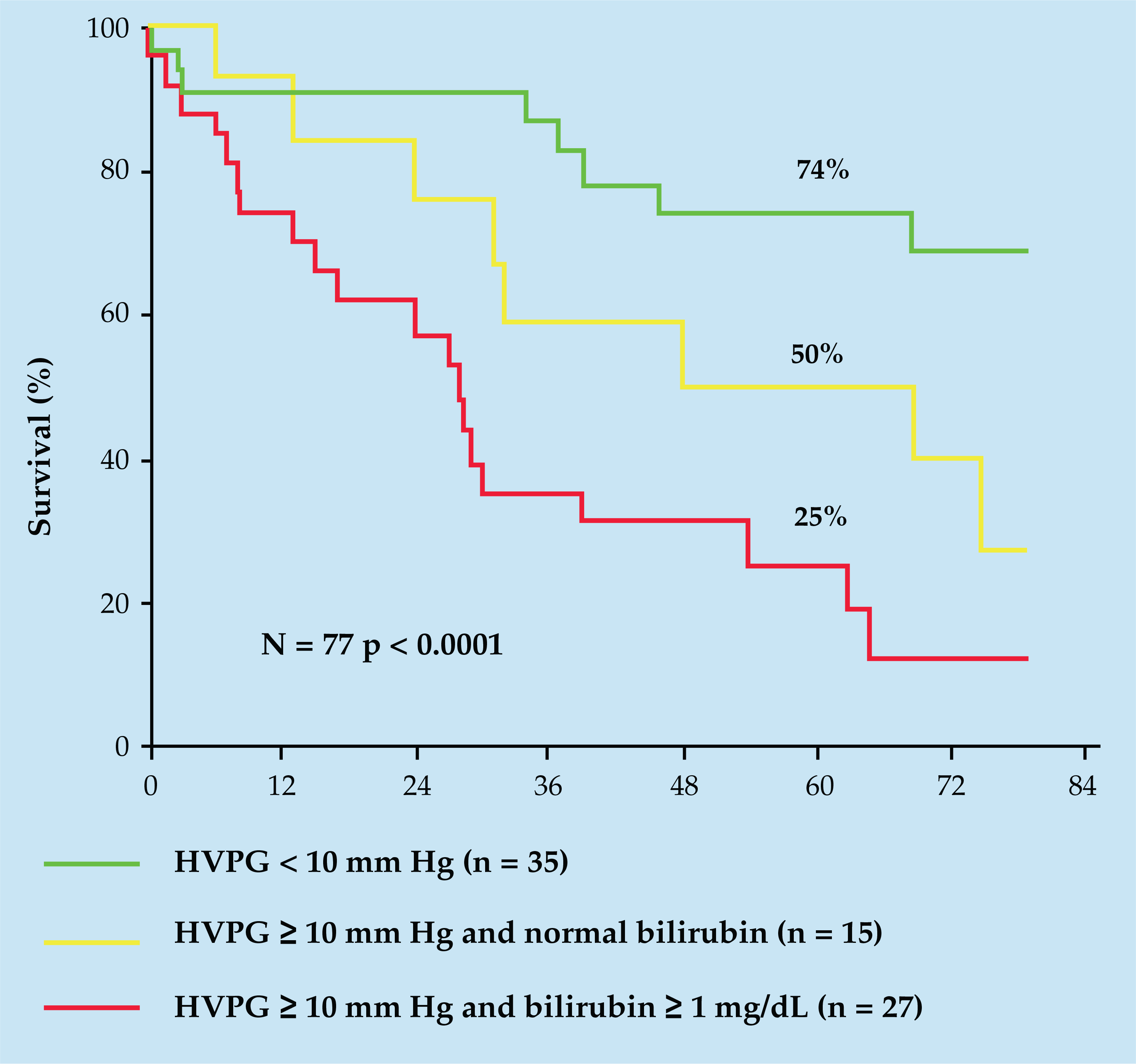
The Risk Of Surgery In Patients With Liver Disease 2
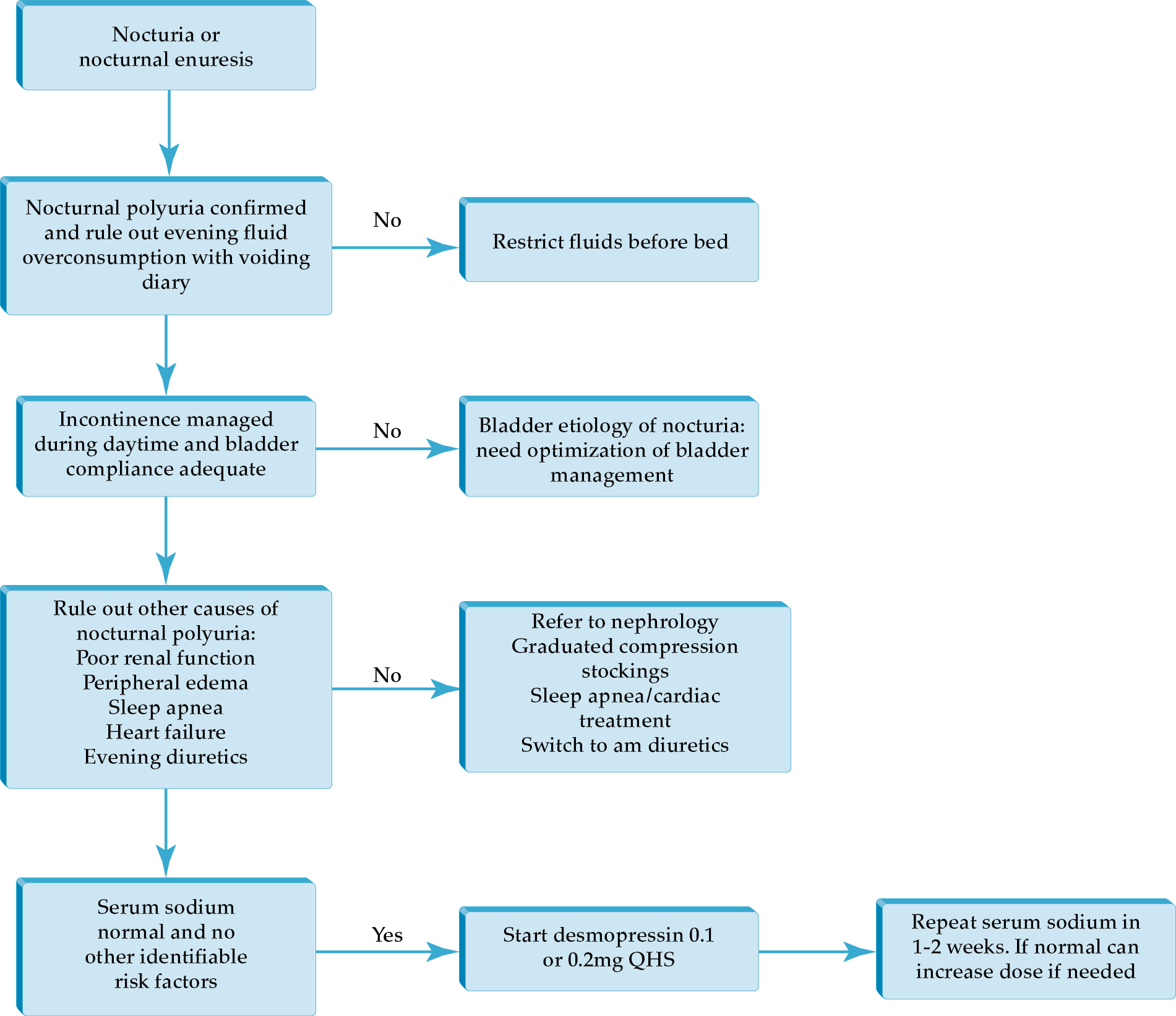
Medical Management of Neurogenic Bladder
• First -line therapy for neurogenic bladder with detrusor overactivity, poor compliance, or related incontinence areis antimuscarinic agents,; however, treatment failures need to be addressed quickly, with dose optimization and progression to botulinum toxin.
• Endless cycling of different oral medications that are ineffective is of little value to the patient because most are pharmacologically quite similar. The provider must move to a more effective therapy, such as botulinum toxin, in a timely fashion.
• Desmopressin is an often overlooked therapy for nocturnal polyuria, and if other reversible causes are treated and the patient is properly screened, this can be a very therapeutic intervention.