Imaging Of Lung Disease, Part II: Cavities, Cysts, Nodules, And Masses
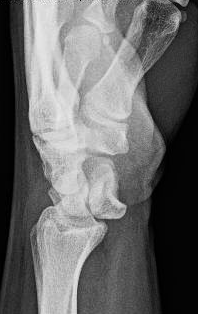
- Granulomatosis with polyangiitis, formerly called Wegener’s granulomatosis, is the most common pulmonary vasculitis and can present with (often cavitary) pulmonary nodules and/or consolidation
- Tracheobronchial papillomatosis is now known to be caused by human papillomavirus (HPV) and has an association with squamous cell carcinoma
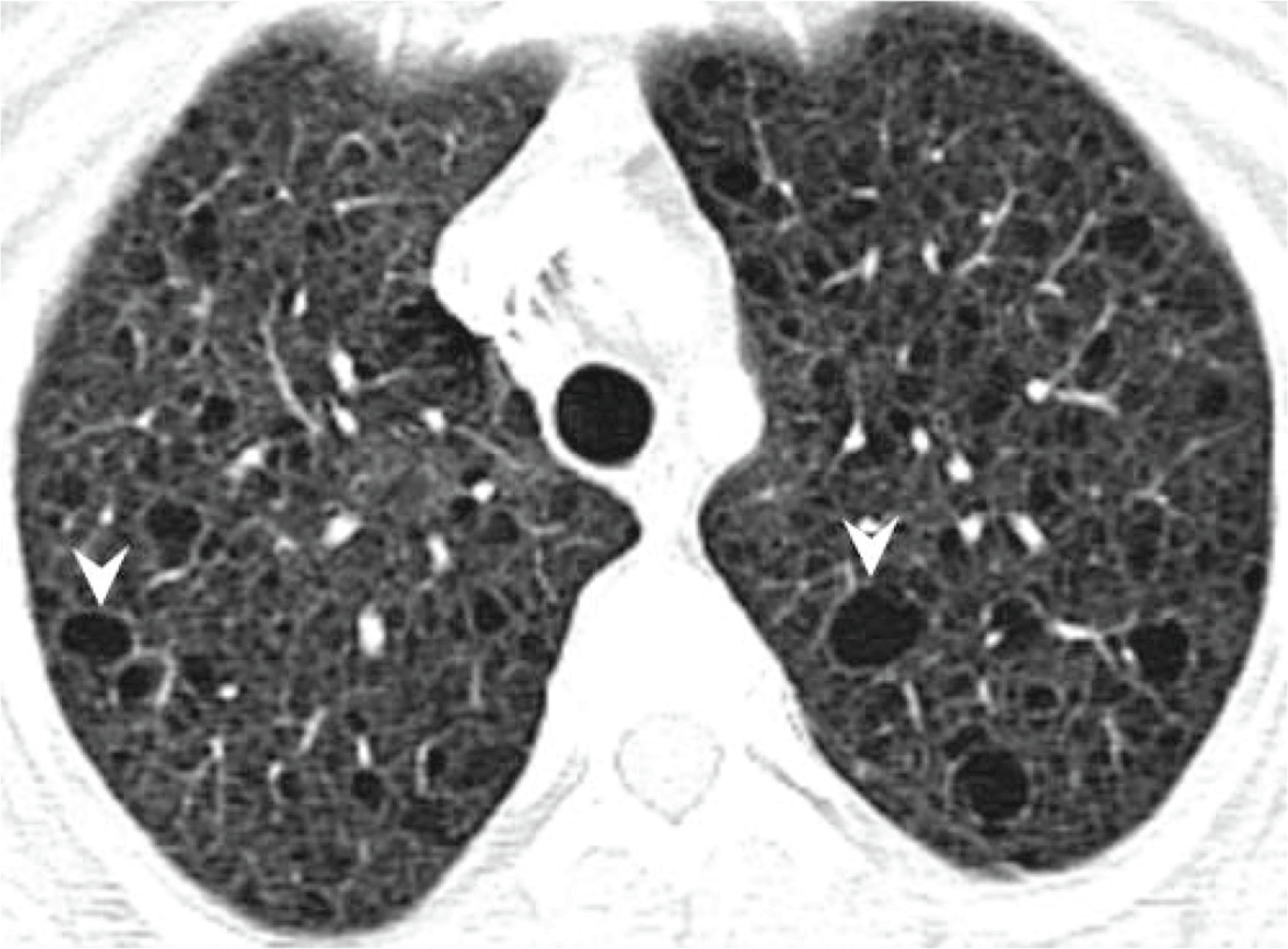
- Algorithms for management of incidental solid and sub-solid pulmonary nodules are available to provide recommendations for optimal follow-up decisions
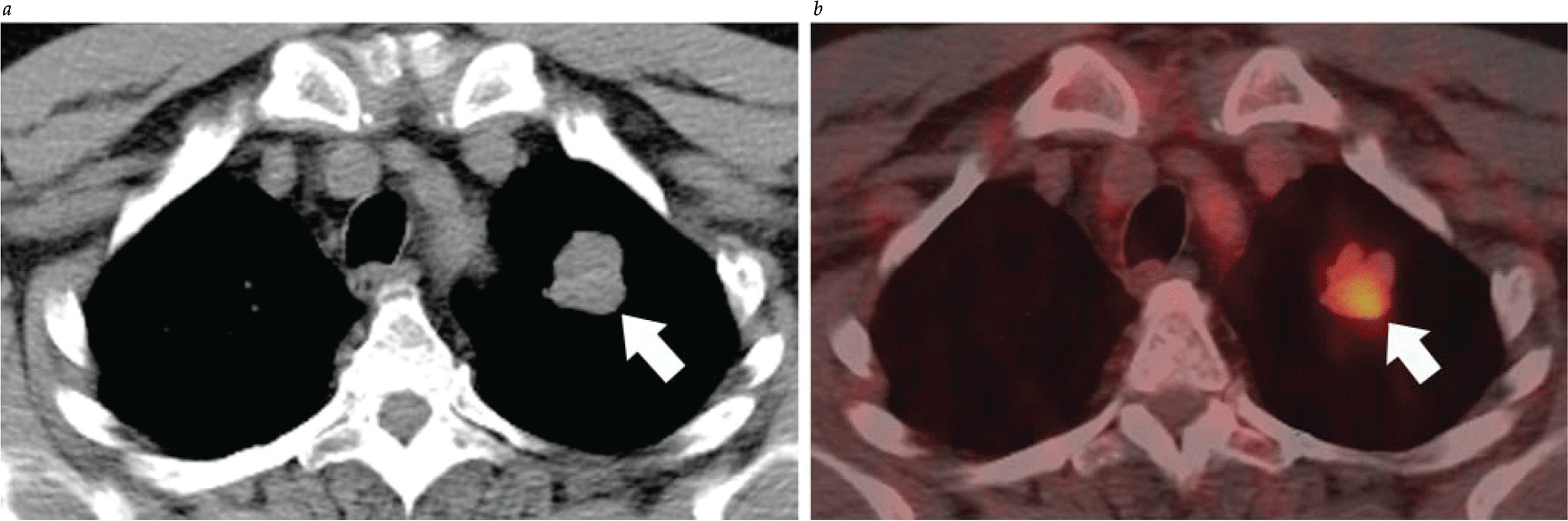
- Data from the National Lung Screening Trial (NLST) demonstrated a 20% reduction in mortality with lung cancer screening CT and forms the rationale for lung cancer screening in high-risk patients
- Lung cancer screening should utilize the American College of Radiology (ACR) Lung Imaging Reporting and Data System (Lung-RADS)