- When massive bleeding exists and direct control of the site of bleeding is under way, the decision to transfuse should be based primarily on hemodynamic status rather than on the hemoglobin or hematocrit level. These laboratory values do not reflect acute hemorrhage because there is a time lag before these levels equilibrate from fluid shift between the extravascular and vascular compartments and from administration of IV fluids.
- The concept of liberal, early use of plasma and platelets developed in large part from the recent US-led military campaigns in Iraq and Afghanistan. Initially in those conflicts, the lack of a reliable supply of blood products near the scene of injury—and platelets especially—led to the use of fresh whole blood transfusion. Although fresh whole blood would be impractical in the civilian setting because of logistical issues and the risk of transmitting transfusion-related infections, the perception of improved outcomes associated with its use prompted military surgeons to advocate 1:1:1 transfusion.
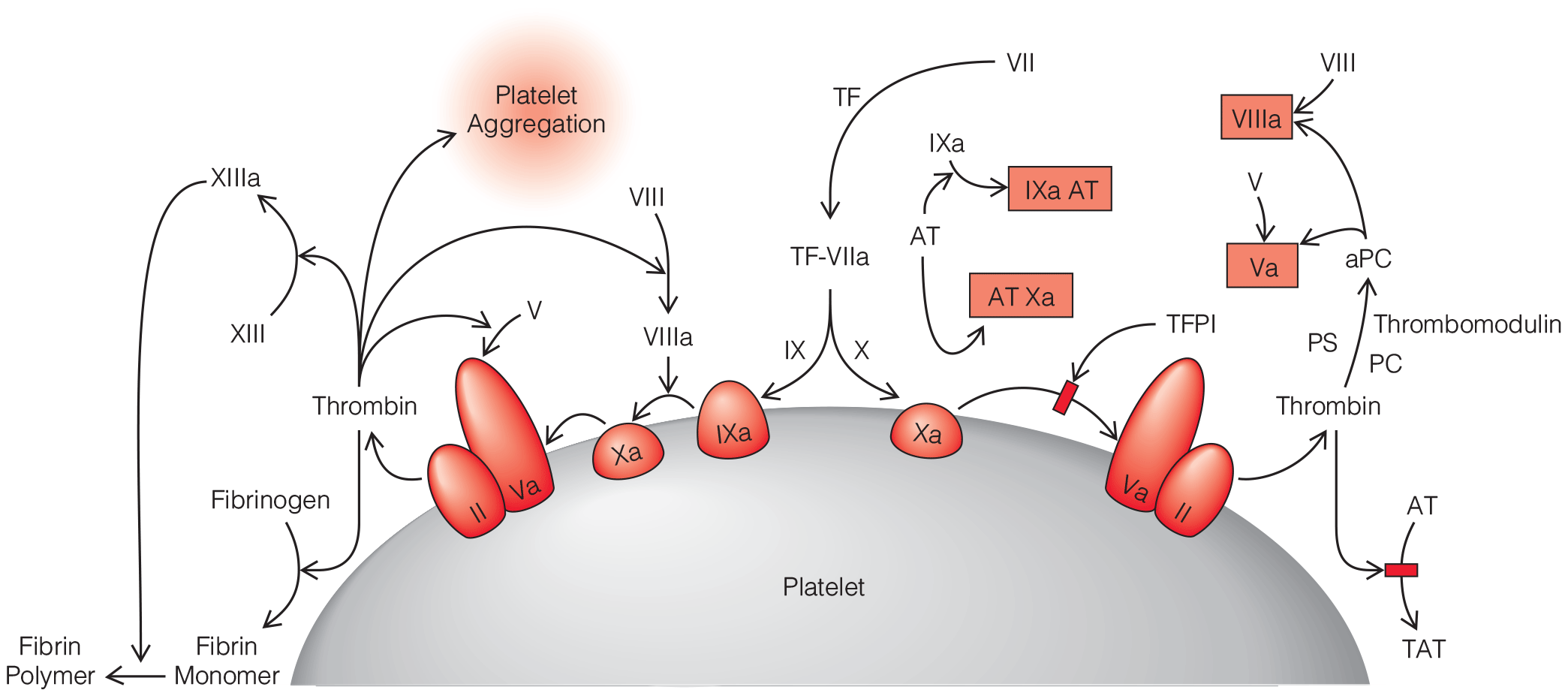
- Beyond recognition and correction of the underlying problem causing DIC and the associated coagulopathy, the diagnosis of DIC represents something of an academic exercise because there is no specific treatment for the condition. Scoring systems that assess the severity of DIC are most useful for distinguishing DIC from other causes of coagulopathy (e.g., hypothermia, dilution, and drug effects).
Latest Updates
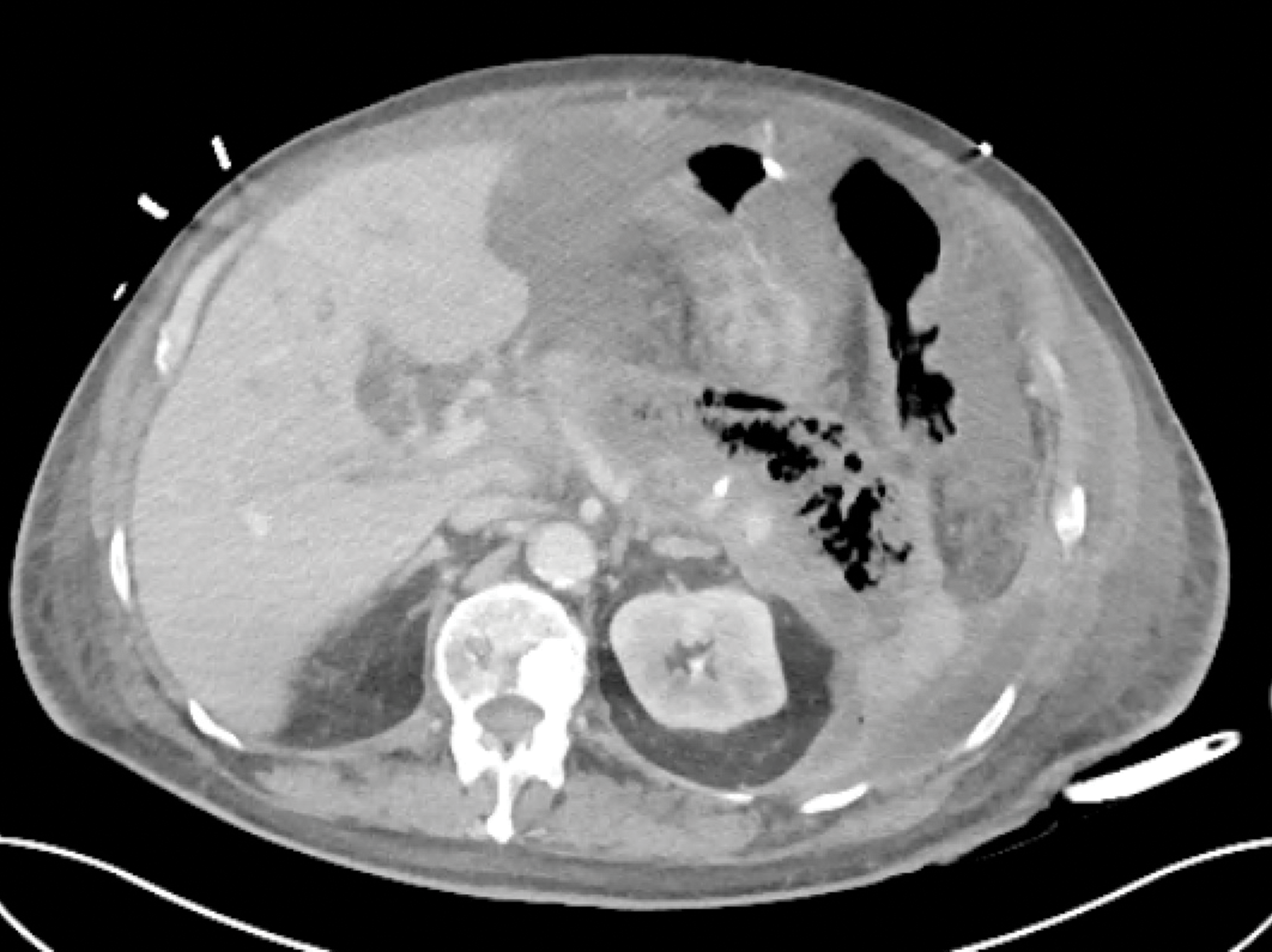
- The mortality for severe acute pancreatitis is 15 to 30%; however, the overall mortality for all patients with acute pancreatitis is less than 5%. Over the last several decades, mortality related to acute pancreatitis has decreased substantially, which likely reflects improved critical care and better strategies for operative management.
- Recent guidelines identify the SIRS criteria as the best and most pragmatic predictor of severe acute pancreatitis at admission and at 48 hours. A 1991 consensus committee first coined the term SIRS as the clinical manifestation of the hypermetabolic response to infection or a noninfectious insult. SIRS criteria include (1) temperature greater than 38°C (100.4°F) or less than 36°C (96.8°F); (2) heart rate greater than 90 beats/min; (3) tachypnea with a respiratory rate greater than 20 breaths/min or hyperventilation with arterial carbon dioxide tension (PaCO2) less than 32 mm Hg; and (4) a white blood cell count greater than 12,000/µL or less than 4,000/µL or greater than 10% immature neutrophils (“bands”).
- The optimal strategy for intervention in patients with confirmed infected necrotizing pancreatitis is initial image-guided percutaneous retroperitoneal catheter drainage or endoscopic transluminal drainage, followed, when necessary, by minimally invasive endoscopic or surgical necrosectomy.
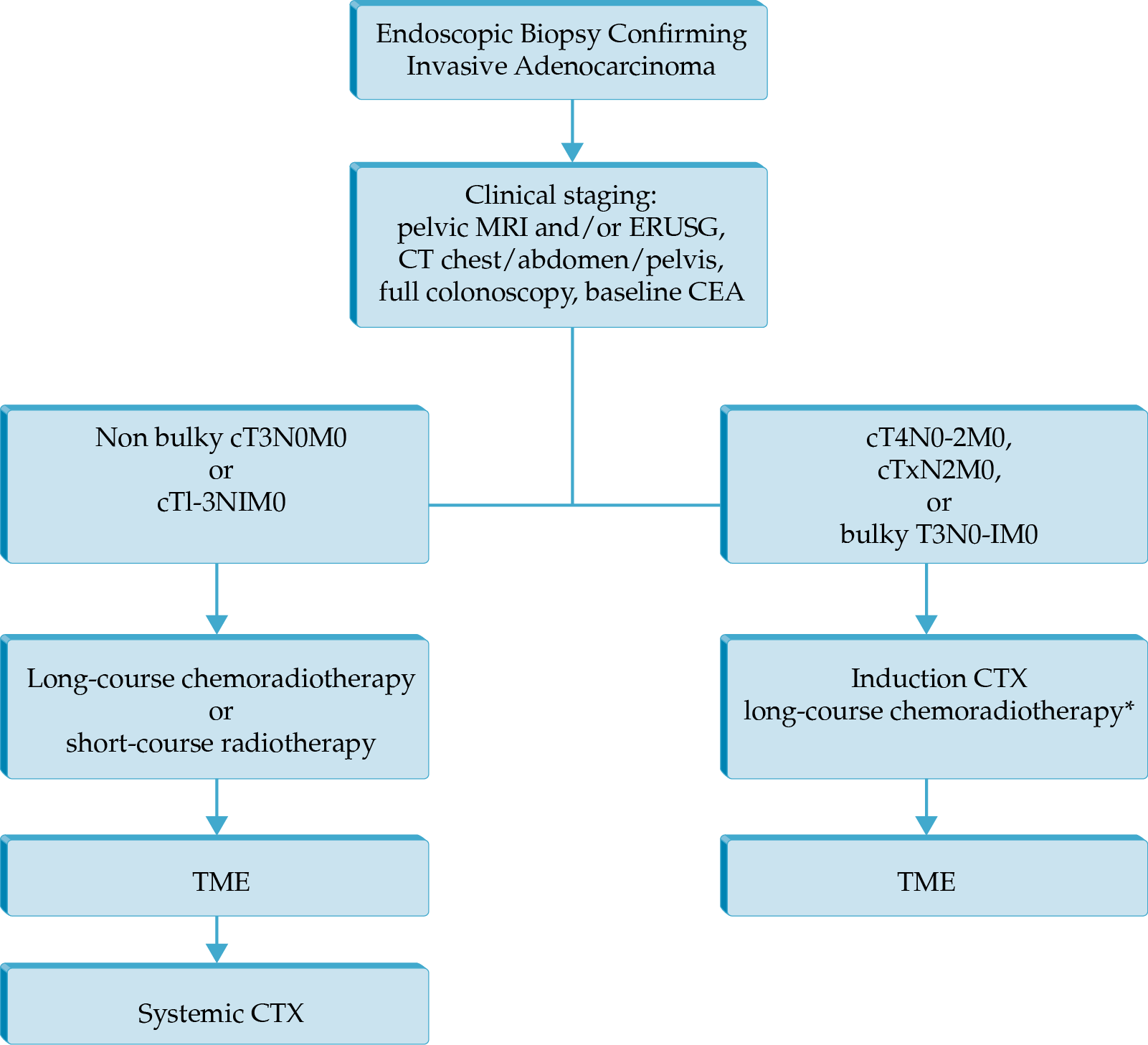
Locally Advanced Rectal Cancer
- Total neoadjuvant therapy (neoadjuvant chemotherapy and chemoradiation prior to total mesorectal excision)
- Minimally invasive techniques for surgery of rectal cancer (laparoscopy, robotic surgery, and transanal total mesorectal excision)
- A novel PD-1 blocker, dostarlimab, has shown very promising results in a phase 2 trial, current demonstrating a 100% clinical remission rate; further study is required to ascertain if this result lasts

Locally Advanced Rectal Cancer
- Total neoadjuvant therapy (neoadjuvant chemotherapy and chemoradiation prior to total mesorectal excision)
- Minimally invasive techniques for surgery of rectal cancer (laparoscopy, robotic surgery, and transanal total mesorectal excision)
- A novel PD-1 blocker, dostarlimab, has shown very promising results in a phase 2 trial, current demonstrating a 100% clinical remission rate; further study is required to ascertain if this result lasts

- Currently, there is a belief that the incidence of SS is congruent with the increasing number of serotoninergic agents prescribed and nutraceutical agents, such as St. John’s wort. In 2002, the Toxic Exposure Surveillance System reported 26,633 incidences of exposure to selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) that caused significant adverse events in 7,349 patients, with a total of 93 deaths within the year.
- The Hunter Serotonin Toxicity Criteria are simpler, more sensitive, and more specific compared with Sternbach’s criteria. The Hunter criteria require a patient to have taken a serotoninergic agent and to meet one of the following conditions: spontaneous clonus; inducible clonus with agitation or diaphoresis; ocular clonus with agitation or diaphoresis; tremor with hyperreflexia; hypertonia with temperature above 38ºC (100.4°F) with ocular clonus or inducible clonus.
- In the setting of severe hyperthermia (temperature greater than 41°C [105.8°F]), immediate sedation with neuromuscular paralysis and intubation should occur to eliminate excessive muscle activity and thus prevent further complications. Nondepolarizing agents (e.g., vecuronium or atracurium) should be used for paralysis prior to intubation.

Equity, Inclusion, and Diversity in Healthcare
- Equity, Inclusion, and Diversity education has increasingly been integrated into medical training

Nonobstetric Surgery during Pregnancy: An Overview for Anesthesia Providers
- We provide a review of the physiologic changes during pregnancy and how they might affect non-obstetric surgery in parturients.
- We discuss pharmacology as is pertinent in parturients undergoing non-obstetric surgery.
- Specific considerations for parturients undergoing laparoscopy, trauma or non-obstetric gynecologic surgery are made.



