- Recent advances in treatment of chronic HCV to include interferon-free direct-acting antiviral agent regimens
- Latest treatment recommendations, including special populations
- Issues surrounding treatment-emergent resistance-associated variants
Latest Updates
Minimally Invasive Approaches to Forehead Rejuvenation
- Evolution in fixation techniques
- Endoscopic dissection
- Temporal changes in the Aesthetic Brow
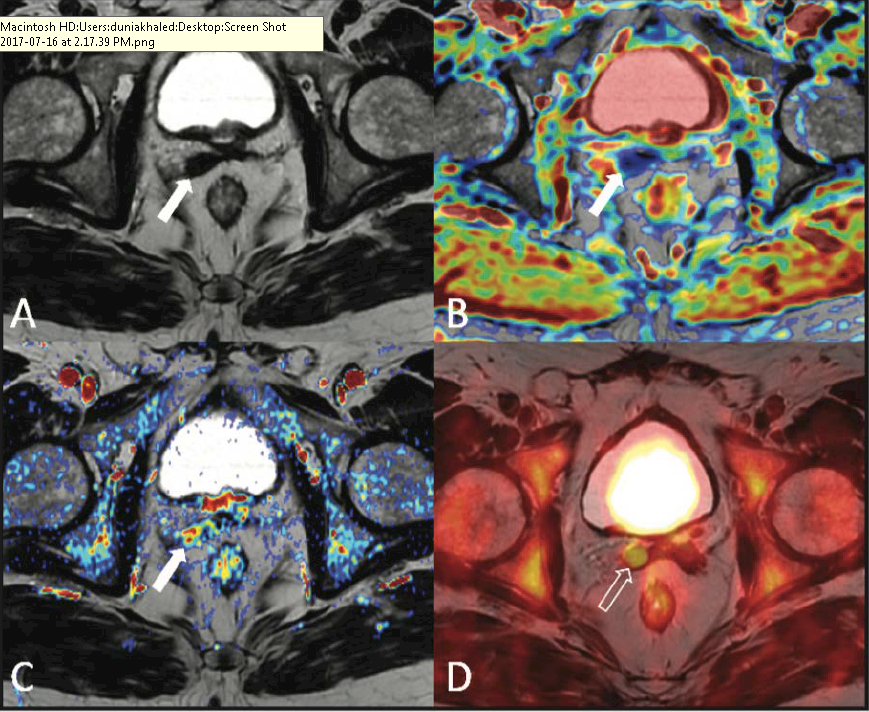
Biochemical Recurrence after Radical Prostatectomy
- Historical versus novel predictors of biochemical recurrence (BCR), metastasis, and cancer-specific mortality
- Historical versus novel imaging modalities in staging of BCR
- Emerging salvage therapies for BCR
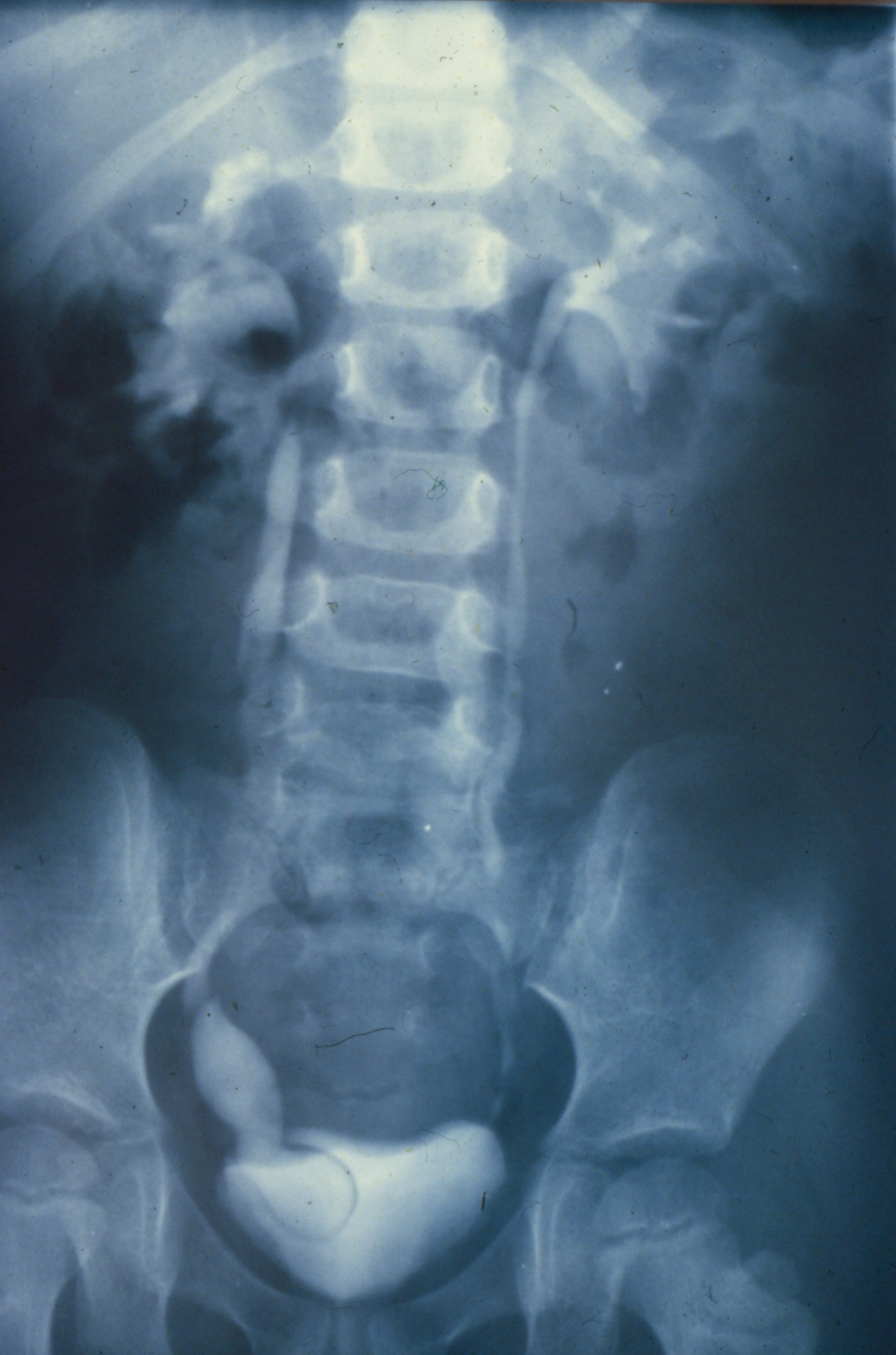
Introduction to Ureteroceles: Presentation, Diagnosis, and Initial Management
- Goals of ureterocele management include: prevention of renal damage, prevention of infection, and preservation of continence.
- Prenatal diagnosis of ureteroceles results in decreased morbidity both before and after surgical intervention.
- Patients presenting with obstruction and sepsis benefit from prompt, transurethral decompression.
- Any endoscopic technique chosen should aim to relieve obstruction while minimizing surgical morbidity and de novo reflux.
Cardiac Arrest And Resuscitation
- Despite continued research, the principal evidence-based interventions are high-quality chest compressions and early defibrillation when indicated.
- Advanced airway management is not shown to improve neurologically intact survival.
- Minimizing interruptions in chest compressions improves survival.
- Vasopressin has been removed from ACLS guidelines.
- Amiodarone is only recommended in ventricular fibrillation or ventricular tachycardia that is refractory to chest compressions, vasopressors, and defibrillation.
- Capnography provides useful information with regard to the effectiveness of chest compressions, confirmation of endotracheal tube placement, and prognostic information.
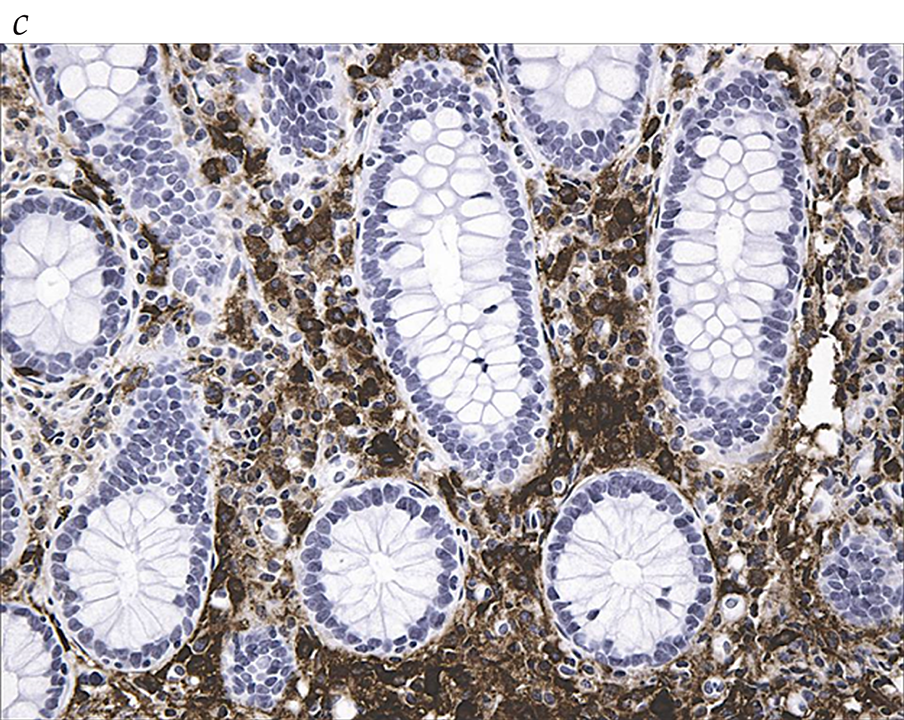
- The most prominent symptoms of SM are those caused by mast cell activation and include flushing, abdominal pain, and cramping.
- SM is diagnosed by defined criteria including appearance and number of the clonal mast cells on bone marrow or intestinal biopsy.
- Treatment for the most common form of SM is directed at mast cell activation and symptom control.