- 2017 ACC/AATS/AHA/ASE/ASNC/SCAI/SCCT/STS appropriate use criteria for coronary revascularization in stable ischemic heart disease
- Latest ACCF/AHA focused update of the guideline for unstable angina/non–ST elevation myocardial infarction
- Published Guidelines as at May 2017
Latest Updates

- Increasing recognition of the importance of home-based and ambulatory blood pressure monitoring reflected in expanded indications for use
- Specific guidance from professional societies with regard to patients with chronic kidney disease
- Recent clinical outcomes trials adding important data about optimal treatment targets
- Recent clinical outcomes trials adding important data regarding treatment in the elderly

- 2017 ACC/AATS/AHA/ASE/ASNC/SCAI/SCCT/STS appropriate use criteria for coronary revascularization in stable ischemic heart disease
- Latest ACCF/AHA focused update of the guideline for unstable angina/non–ST elevation myocardial infarction
- Published Guidelines as at May 2017
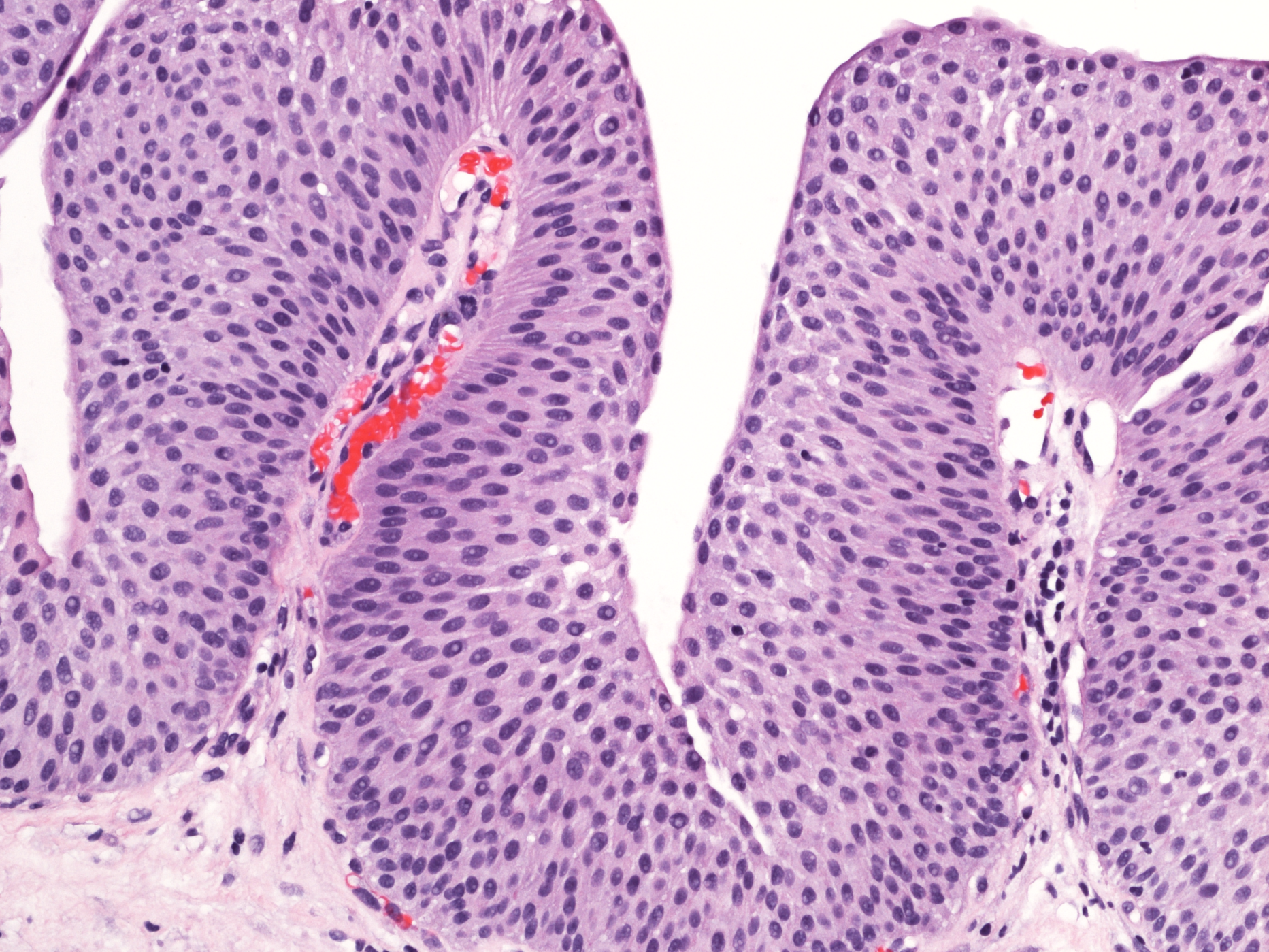
Approach to the Patient with Cough
- A number of subjective and objective tools have been developed recently to assess cough severity. An encouraging development to aid in the assessment of new antitussives is the automated cough counter. Researchers will now be able to make objective measurements of cough frequency rather than relying exclusively on reported cough symptoms such as recorded in cough diaries and visual analogue scales describing cough severity.
- Approved devices are available that appear to accurately distinguish cough from throat clearing, snoring, and ambient background noises. They are compact and noninvasive, with a long battery life for extended recording times. Their role is currently limited to cough research rather than clinical practice.

Bipolar Disorder: An Update on Diagnosis, Etiology, and Treatment
- In the DSM-5, the diagnosis of mania or hypomania requires the presence of increase in energy or goal-directed activities compared with the habitual in the subject along with mood elevation. This change will contribute to increasing diagnostic reliability.
- In the DSM-5, the term mixed feature is a course specifier and can be applied to depressive, manic, and hypomanic episodes. Seasonal patterns can now be used for all types of mood episodes. These changes will lead to alterations in study designs and data analysis and potentially advance mental health research.
- There is increasing evidence of the thinning of cortical gray matter in the brains of patients with bipolar disorder when compared with healthy controls. The greatest deficits were found in parts of the brain that control inhibition and emotion, such as the frontal and temporal regions. This finding clarifies aspects of the mechanisms underlying the developments and maintenance of bipolar symptoms.
- Neuroimaging studies showed that lithium treatment was associated with reduced thinning of gray matter, which suggests a protective effect of this medication on the brain.
- Combining pharmacotherapy and psychotherapy can reduce the rate of recurrence mood episodes and medication adherence in bipolar patients. Electroconvulsive therapy is highly effective and can be beneficial in treatment-resistant patients.
Assessment and Management of the Geriatric Patient
When investigating malnutrition and weight loss in older patients, clinicians should screen for physiologic, psychological, and social risk factors. Malnutrition may be caused by social isolation and lack of awareness regarding healthy eating and may be associated with depression, bereavement, dementia, or alcohol use. Patients with malignancy, nonmalignant gastrointestinal diseases, psychiatric conditions, and diseases that become more common with aging (such as diabetes mellitus and cancer) should be considered high risk for unintentional weight loss.

Approach to the Patient with Cough
- A number of subjective and objective tools have been developed recently to assess cough severity. An encouraging development to aid in the assessment of new antitussives is the automated cough counter.
- Researchers will now be able to make objective measurements of cough frequency rather than relying exclusively on reported cough symptoms such as recorded in cough diaries and visual analogue scales describing cough severity.
- Approved devices are available that appear to accurately distinguish cough from throat clearing, snoring, and ambient background noises. They are compact and noninvasive, with a long battery life for extended recording times. Their role is currently limited to cough research rather than clinical practice.