- Robotic retromuscular incisional hernia repair has demonstrated a shorter length of stay compared to open retromuscular repair
- Robotic intraperitoneal mesh placement is associated with a shorter length of stay compared to standard laparoscopic intraperitoneal mesh placement
- Robotic-assisted pancreatectomy demonstrates superior results to open midline pancreatectomy
- Robotic single-site cholecystectomy is associated with improved cosmesis compared to standard port laparoscopic cholecystectomy
Latest Updates

- Robotic retromuscular incisional hernia repair has demonstrated a shorter length of stay compared to open retromuscular repair
- Robotic intraperitoneal mesh placement is associated with a shorter length of stay compared to standard laparoscopic intraperitoneal mesh placement
- Robotic-assisted pancreatectomy demonstrates superior results to open midline pancreatectomy
- Robotic single-site cholecystectomy is associated with improved cosmesis compared to standard port laparoscopic cholecystectomy
Prevention and Management of Obstetric Perineal Lacerations
- Practice Bulletin 165: August, 2016 – prevention and management of obstetric lacerations at vaginal delivery. This bulletin provides evidence-based guidelines for prevention, identification, and management of obstetric lacerations.
- The rise and fall of episiotomy: The routine practice of episiotomy is an independent risk factor for third- and fourth-degree lacerations.
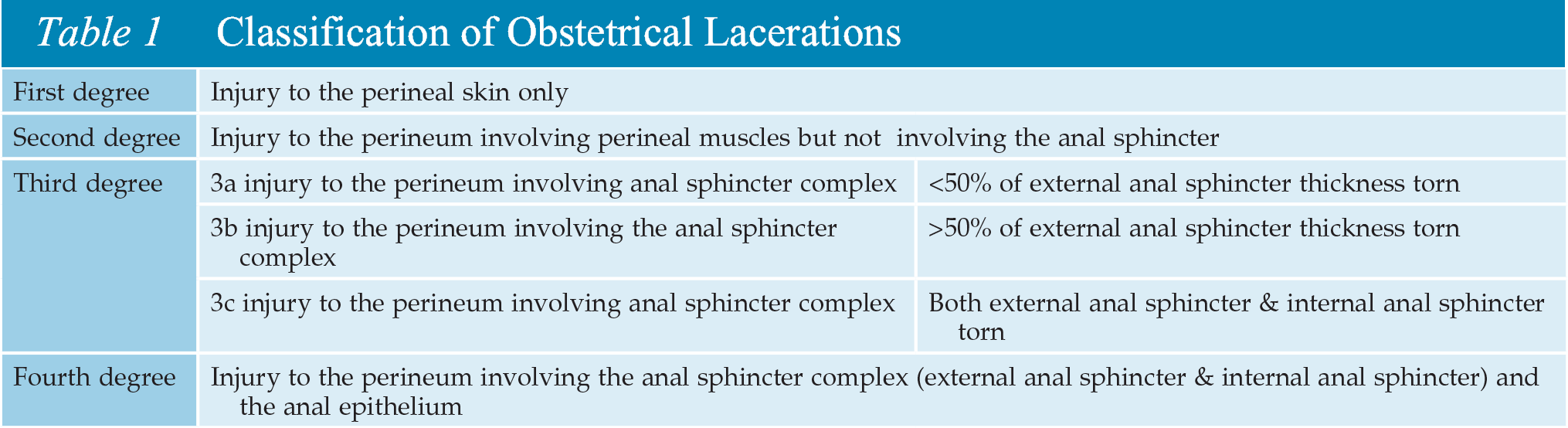
- ReVITALize: changing the classification of lacerations. Third-degree lacerations are divided into three categories to characterize degree of insult
Pain Syndromes Other Than Headache
- Treatment of complex regional pain syndrome begins with the principle that the patient must use the involved extremity no matter how much it hurts. Psychological support is often very important to encourage participation, motivate, and maintain compliance in these difficult treatment regimens. Pain is treated with neuropathic medications, nerve blocks, and other interventional therapies. Controlling the pain is vital for participation in rehabilitative therapies because if an extremity is not used, function will decrease, potentially leading to joint ankylosis and even irreversible atrophy. Using the extremity is important for desensitization and reeducating centrally mediated pain.
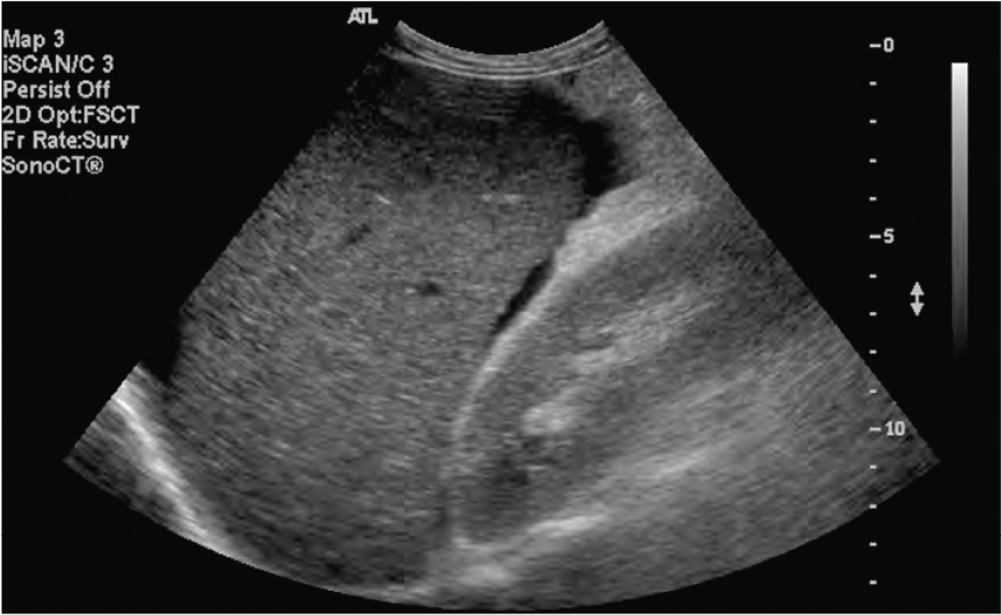
Trauma to the Abdomen and Pelvis
- Recent data on selective non-operative management of stable patients with penetrating abdominal trauma has shown promising outcomes.
- Resuscitative Endovascular Balloon Occlusion of the Aorta (REBOA) is being used in select trauma centers as an alternative to thoracotomy (with aortic cross clamp) for proximal aortic control in patients with hemorrhagic intraabdominal injuries.
- Hemodynamically tenuous patients with blunt abdominal trauma are resuscitated aggressively while being worked up by a Focused Assessment with Sonography for Trauma (FAST) exam.
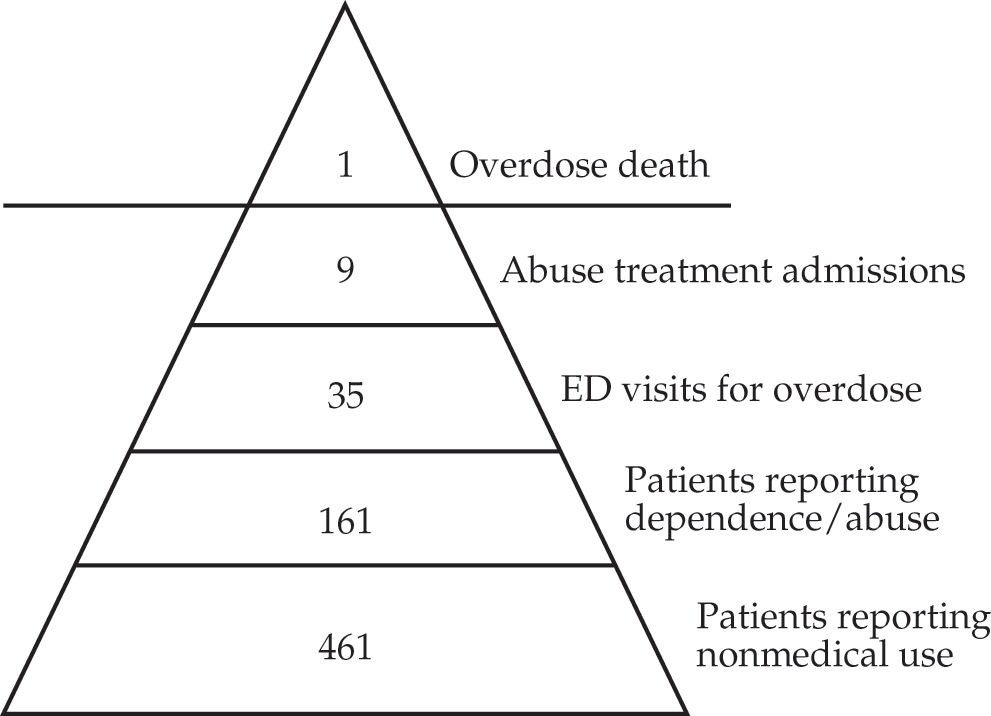
Physicians' Role in Curbing the Worst Drug Crisis in America: Prescription Opioid Abuse
- Use of screening tools to stratify patients into different risk categories of opioid misuse to accomplish appropriate opioid prescribing
- Emphasis on monitoring techniques to assess compliance of patients on opioids
- Importance of opioid dose limitations in curbing opioid abuse

Bipolar Disorder: An Update on Diagnosis, Etiology, and Treatment
- In the DSM-5, the diagnosis of mania or hypomania requires the presence of increase in energy or goal-directed activities compared with the habitual in the subject along with mood elevation. This change will contribute to increasing diagnostic reliability.
- In the DSM-5, the term mixed feature is a course specifier and can be applied to depressive, manic, and hypomanic episodes. Seasonal patterns can now be used for all types of mood episodes. These changes will lead to alterations in study designs and data analysis and potentially advance mental health research.
- There is increasing evidence of the thinning of cortical gray matter in the brains of patients with bipolar disorder when compared with healthy controls. The greatest deficits were found in parts of the brain that control inhibition and emotion, such as the frontal and temporal regions. This finding clarifies aspects of the mechanisms underlying the developments and maintenance of bipolar symptoms.
- Neuroimaging studies showed that lithium treatment was associated with reduced thinning of gray matter, which suggests a protective effect of this medication on the brain.
- Combining pharmacotherapy and psychotherapy can reduce the rate of recurrence mood episodes and medication adherence in bipolar patients. Electroconvulsive therapy is highly effective and can be beneficial in treatment-resistant patients.