Health Economics: National Health Expenditures
- 2015 US National Health Expenditures are reviewed.
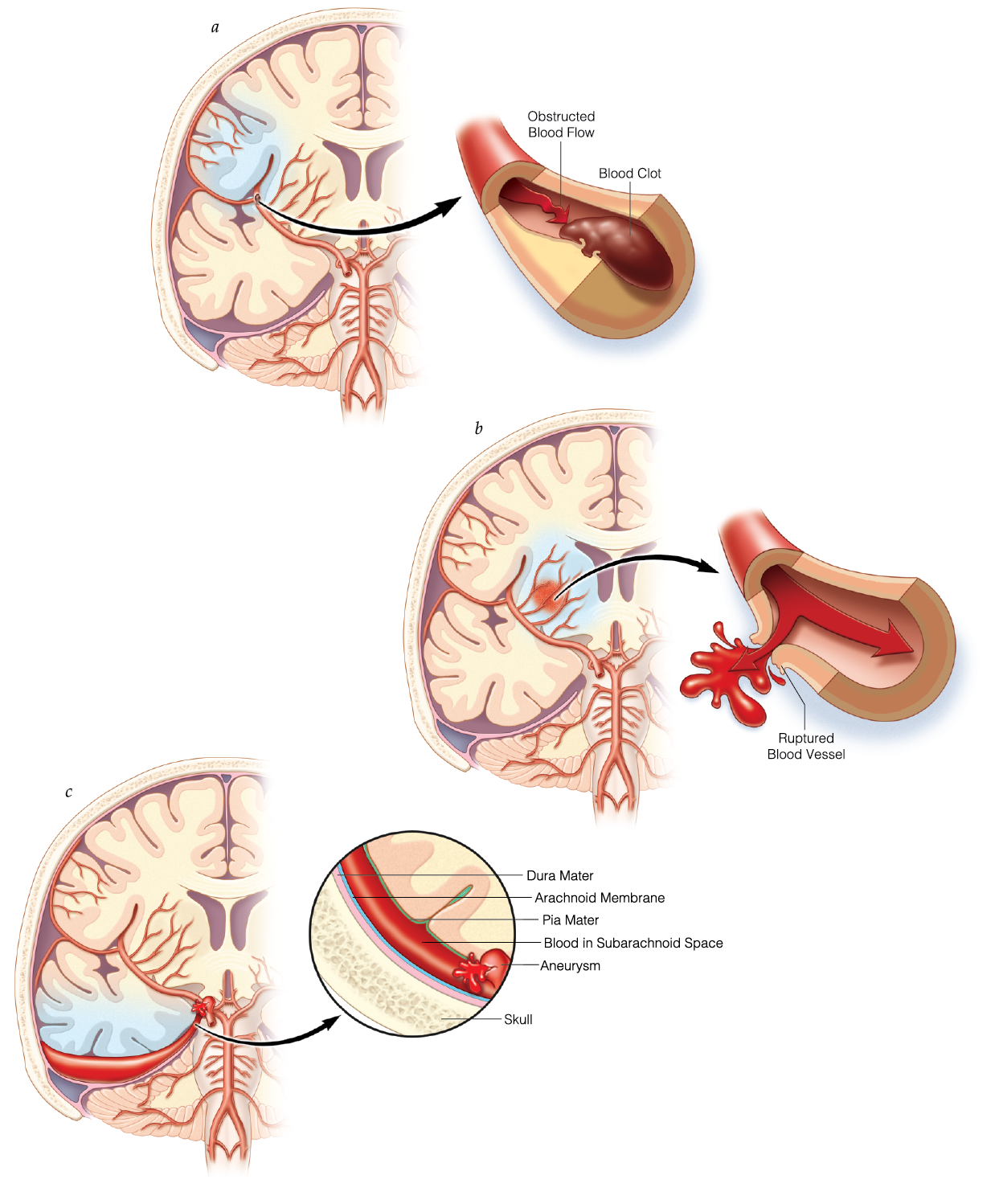
Acute Neurologic Events (Cerebrovascular Accidents, Subarachnoid Hemorrhage) and Complications
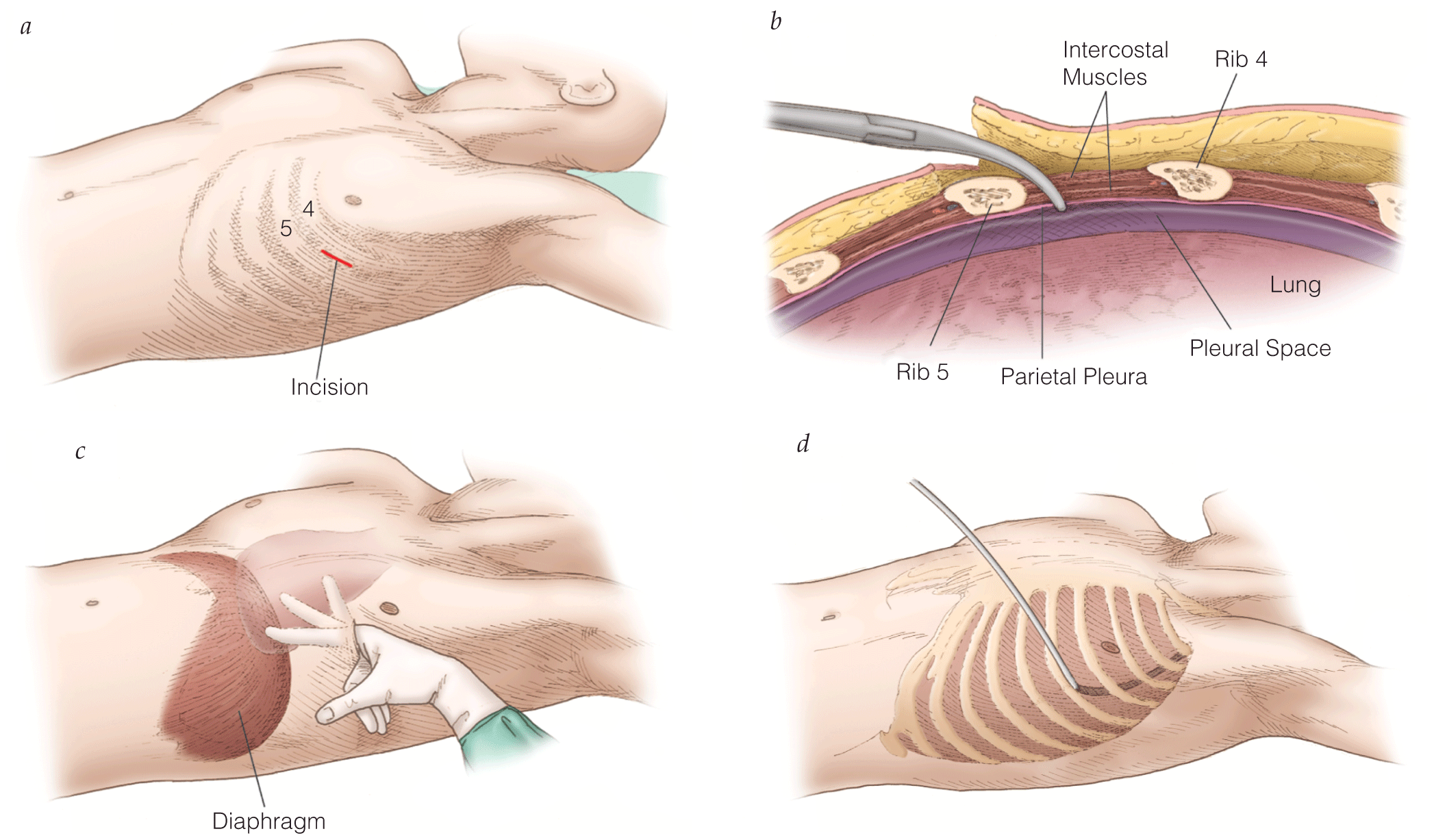
Initial Management of Life-Threatening Trauma

Initial Management of Life-Threatening Trauma

Initial Management of Life-Threatening Trauma

Initial Management of Life-Threatening Trauma
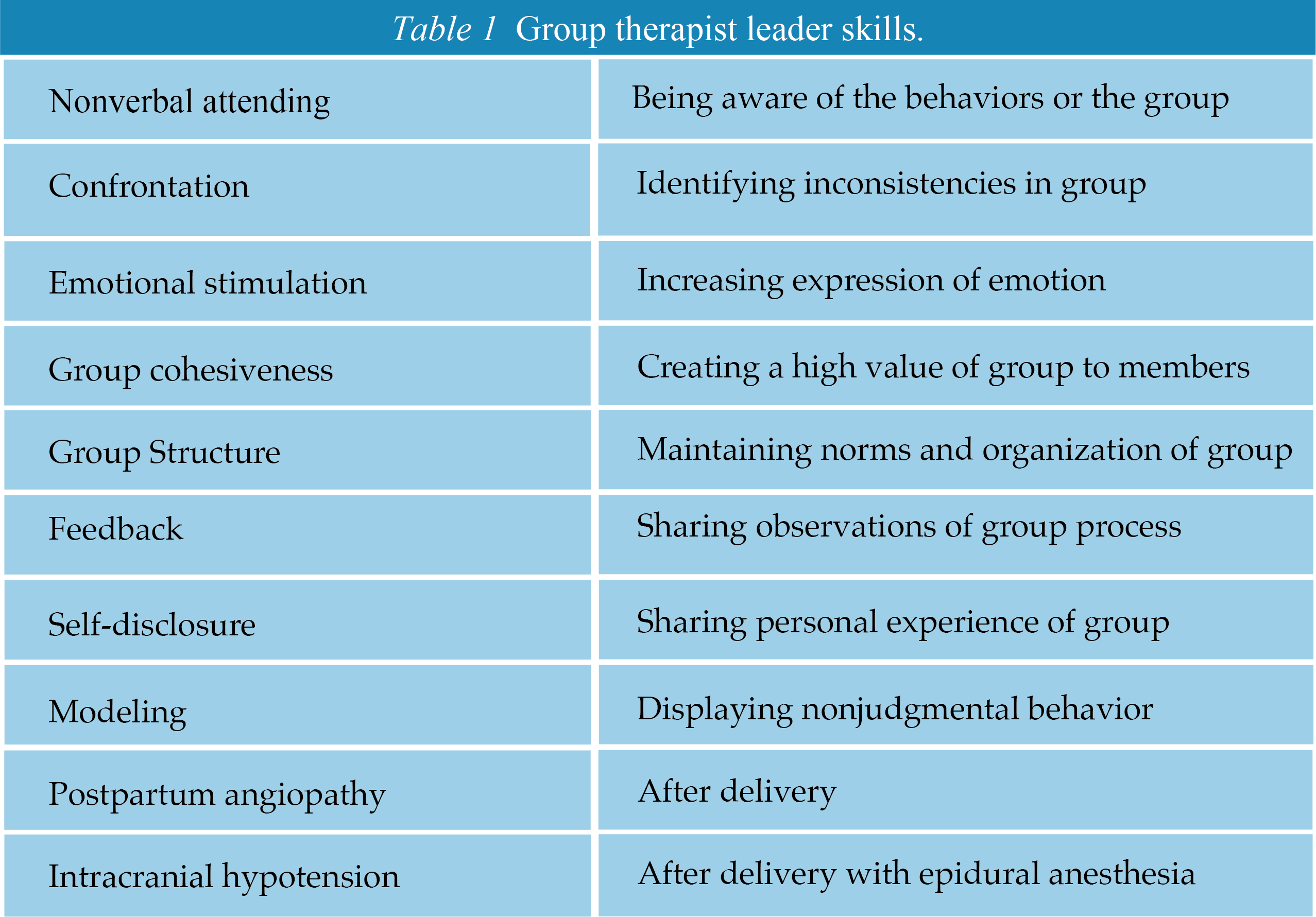
Group Psychotherapy: Group Therapist Leadership Skills