Medical Management of Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension
- Over the past two decades, considerable progress has been made in the medical management of pulmonary arterial hypertension and chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension.
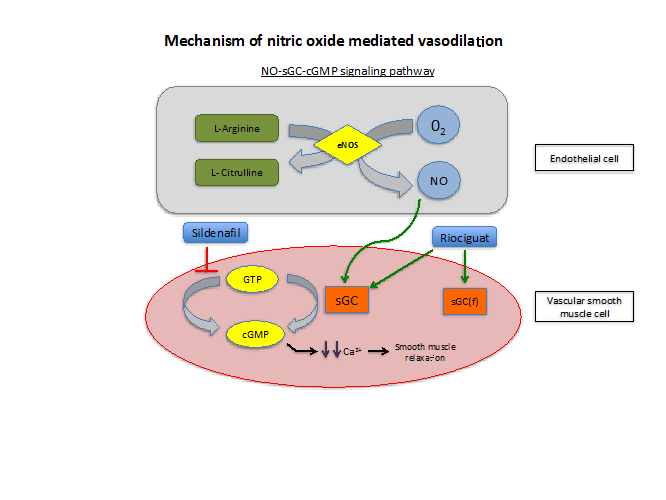
- Recently the field has seen the addition of several new pulmonary vasodilator agents: a soluble guanylate cyclase stimulator (riociguat), a new endothelin receptor antagonist (macitentan) and two new oral prostanoid agents (treprostinil and selexipag).
- Initial combination therapy for the treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension has heralded a new era in the treatment of PAH. Patients receiving initial combination therapy with a phosphodiesterase inhibitor, tadalafil and an endothelin receptor antagonist, ambrisentan demonstrated improved progression-free survival compared with monotherapy with either tadalafil or ambrisentan.
- For patients with inoperable or persistent chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension, riociguat has emerged as an attractive alternative.